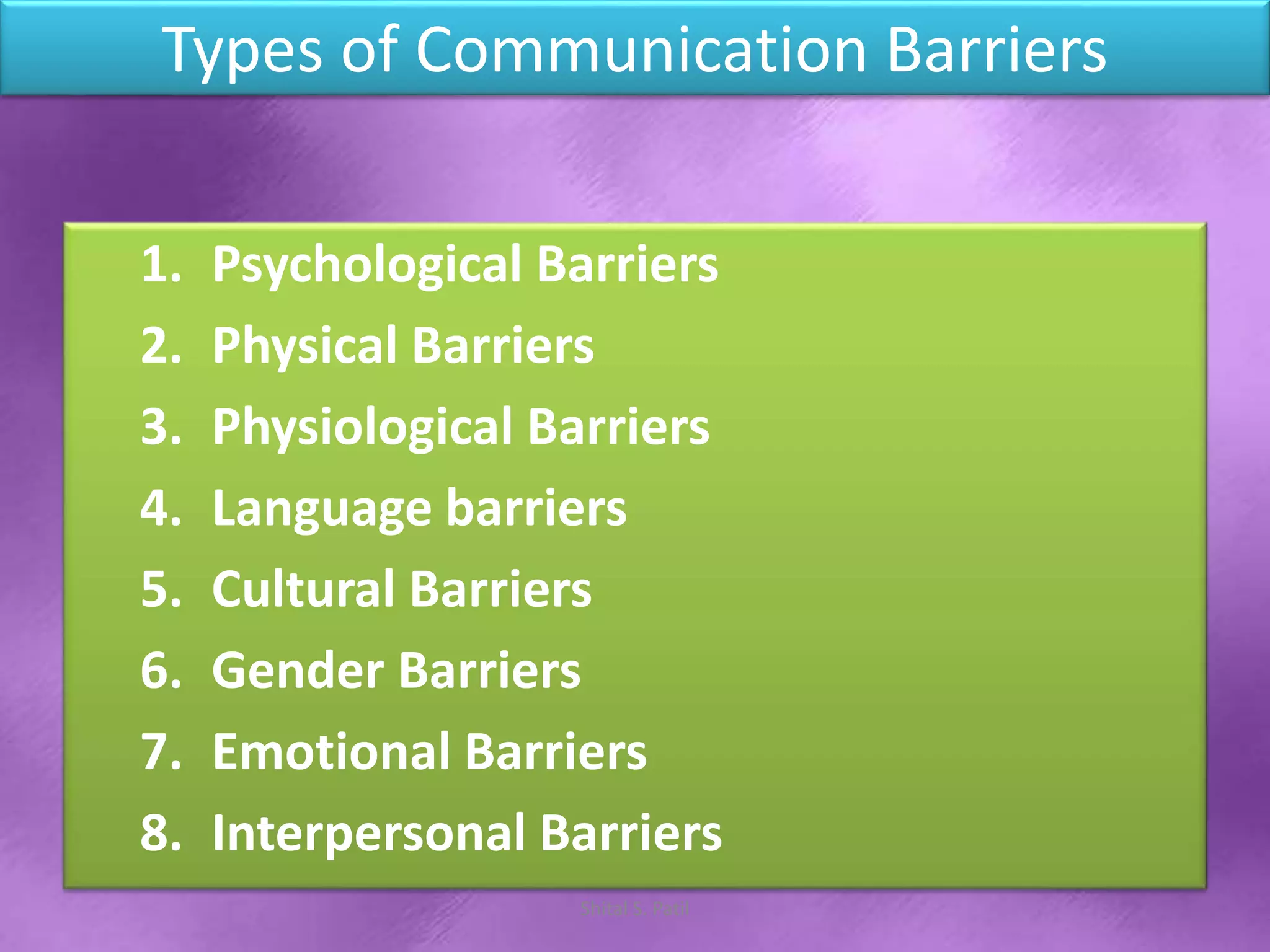
The document discusses various barriers to effective communication, including psychological, physical, physiological, language, cultural, gender, emotional, and interpersonal barriers. Each type of barrier is described in terms of its causes and impacts on communication, with examples such as noise and environmental distractions for physical barriers, and conditions like hearing impairment for physiological barriers. The document also offers suggestions to overcome these barriers, highlighting the importance of attention, environment, and technological updates.