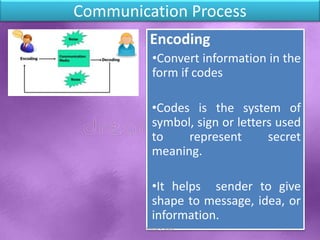
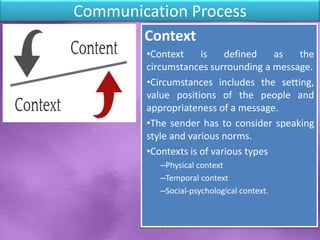
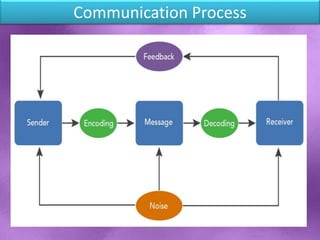
The document discusses the importance and process of communication, emphasizing that it involves the exchange of information through symbols and messages. It outlines key components such as the sender, message, encoding, channel, decoding, receiver, and feedback, while also identifying barriers to effective communication. Good communication fosters teamwork, builds strong relationships, and enhances productivity within organizations.