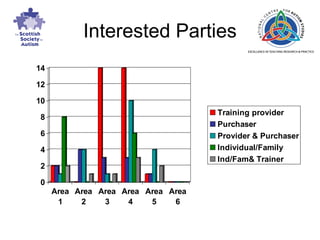
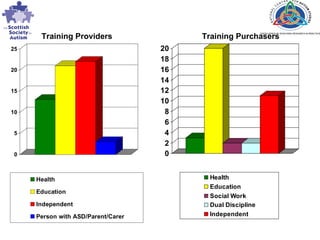
The document discusses the development of an accreditation system for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) training and trainers in Scotland. It describes a multi-phase consultation process to develop national training standards and an accreditation framework. Key areas investigated through consultation included the need for accreditation, the accreditation process and components, and how training should be evaluated. Feedback from consultation events helped identify themes and issues to inform the final accreditation system design.
![Accreditation System for Training & Trainers in ASD: a work in progress Anna Robinson [email_address] Charlene Tait [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/111-1202308530127520-2/75/pepe111-1-2048.jpg)