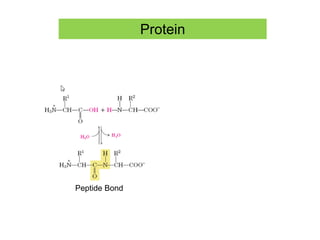
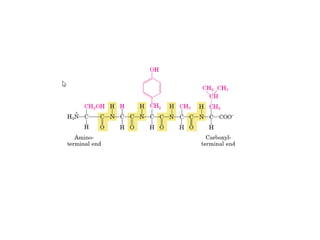
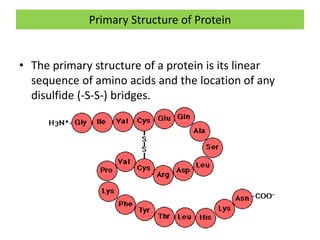
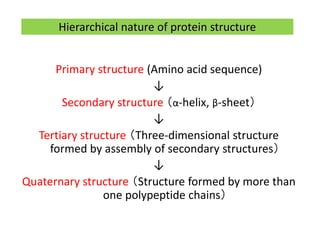
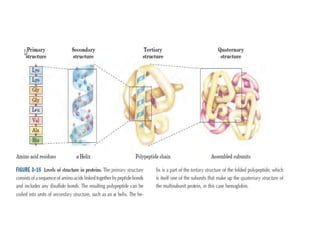
1) A protein's structure is determined by its amino acid sequence and consists of four levels: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary.
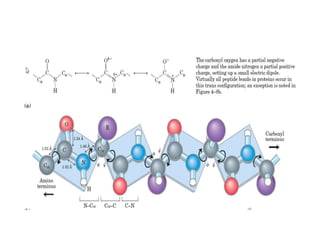
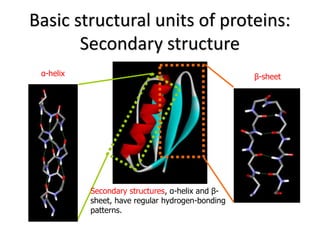
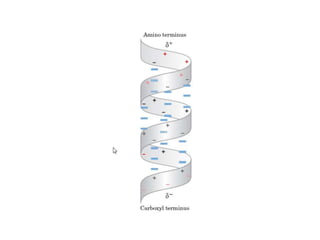
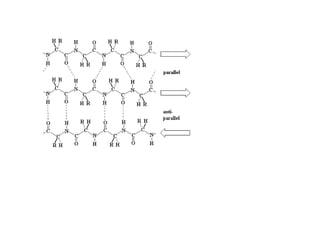
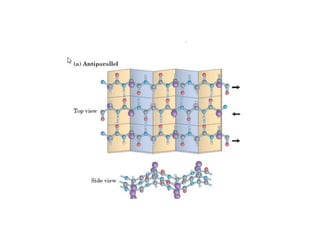
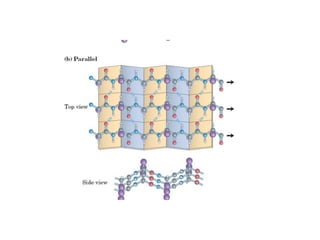
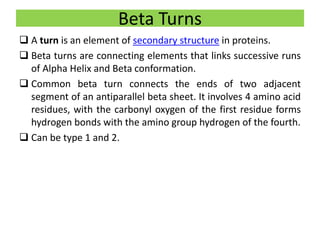
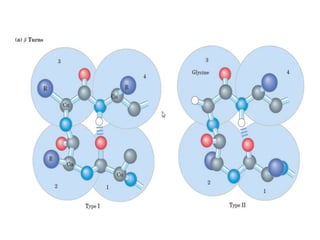
2) The two most common secondary structures are alpha helices and beta sheets, which are stabilized by hydrogen bonds between amino acids.
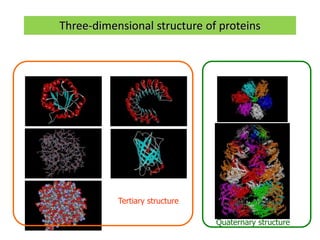
3) Tertiary structure describes the overall 3D shape of a protein formed by interactions between regions of the polypeptide chain distant in primary sequence. Quaternary structure involves interactions between multiple protein subunits.