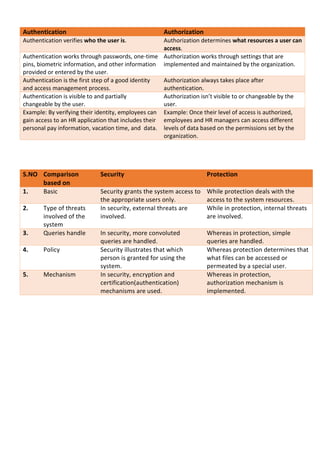
The document discusses security and protection in operating systems. It defines security as a mechanism that analyzes users and permits authorized access to system resources through authentication and encryption. Protection deals with controlling access to system resources and determining which files a user can access. The document provides examples of how organizations implement security and protection measures to restrict access to information.