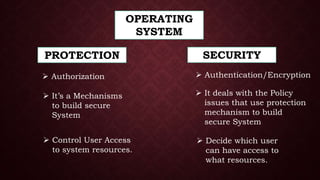
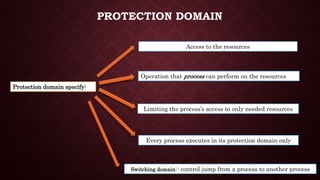
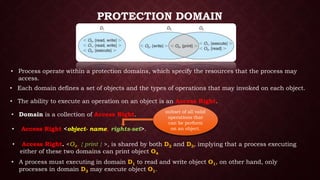
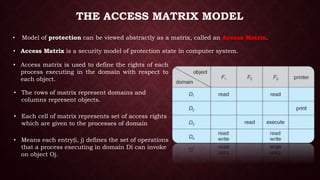
This document discusses protection and security in operating systems. It covers authorization, authentication, encryption, and how operating systems control user access to system resources by deciding which users can access which resources. Protection deals with access to system resources and determines which files can be accessed by special users. Protection domains specify the resources a process can access and the operations it can perform on those resources. The access matrix model represents the protection state of a system using a matrix with rows for domains and columns for objects to define the access rights for each domain-object pair.








![THE PROTECTION STATE OF SYSTEM
• It represented by Triplet( S,O,P )
O
P [s , o]
S
Subjects
Objects
Schematic Diagram of Access Matrix](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/protectiondomainunit5-200619204512/85/Protection-Domain-and-Access-Matrix-Model-Operating-System-13-320.jpg)
