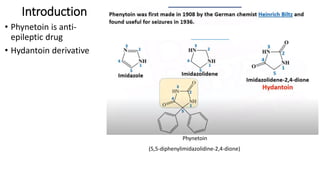
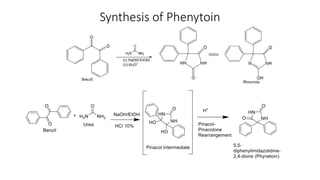
The document summarizes the synthesis of the anti-epileptic drug phenytoin. It involves a two-step process: (1) benzoin condensation to form benzil from benzaldehyde, followed by oxidation; (2) reaction of benzil with urea in ethanol and sodium hydroxide to form an intermediate that undergoes rearrangement in acid to yield phenytoin. The required chemicals, equipment, procedure, calculations for theoretical and percent yield are provided. Phenytoin works by binding to voltage-gated sodium channels in neurons to reduce repetitive firing and prevent seizure discharge.