This document discusses railway track gauge and related concepts in India. It covers the following key points:
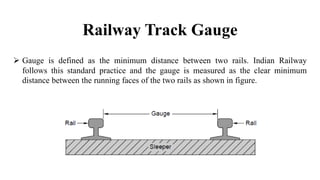
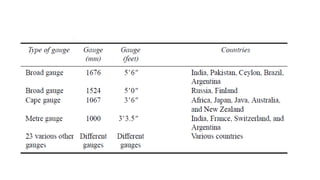
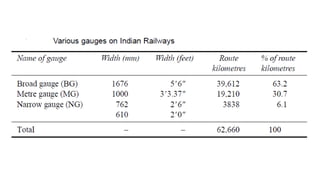
1) Railway track gauge is defined as the minimum distance between two rails, with Indian railways using broad (1676 mm), meter (1000 mm), and narrow (762 mm) gauges.
2) The use of multiple gauges in India has caused problems like inconvenience to passengers during gauge changes, difficulty trans-shipping goods, and inefficient use of rolling stock.
3) Full gauge conversion is difficult and requires widening tracks, bridges, tunnels, and procuring new rolling stock during the conversion period.