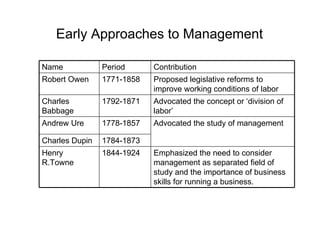
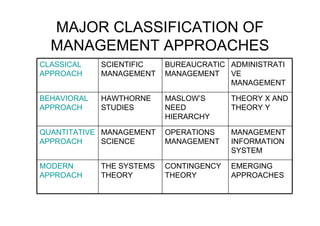
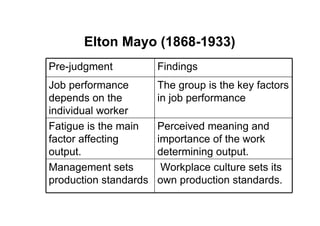
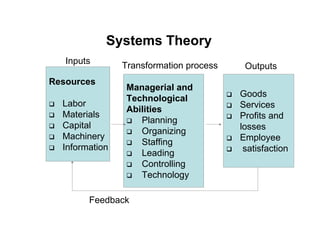
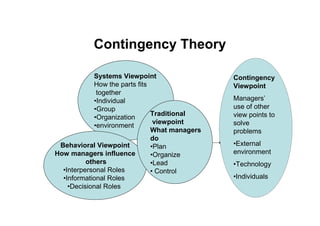
The document provides an overview of the history and evolution of management thought. It discusses early approaches, the classical approach including scientific management, administrative theory and bureaucratic management. It then covers the behavioral approach including Hawthorne studies and Maslow's hierarchy of needs. The quantitative approach involving management science, operations management and management information systems is examined. Modern approaches such as systems theory and contingency theory are outlined. Emerging approaches like Theory Z and quality management are also mentioned.