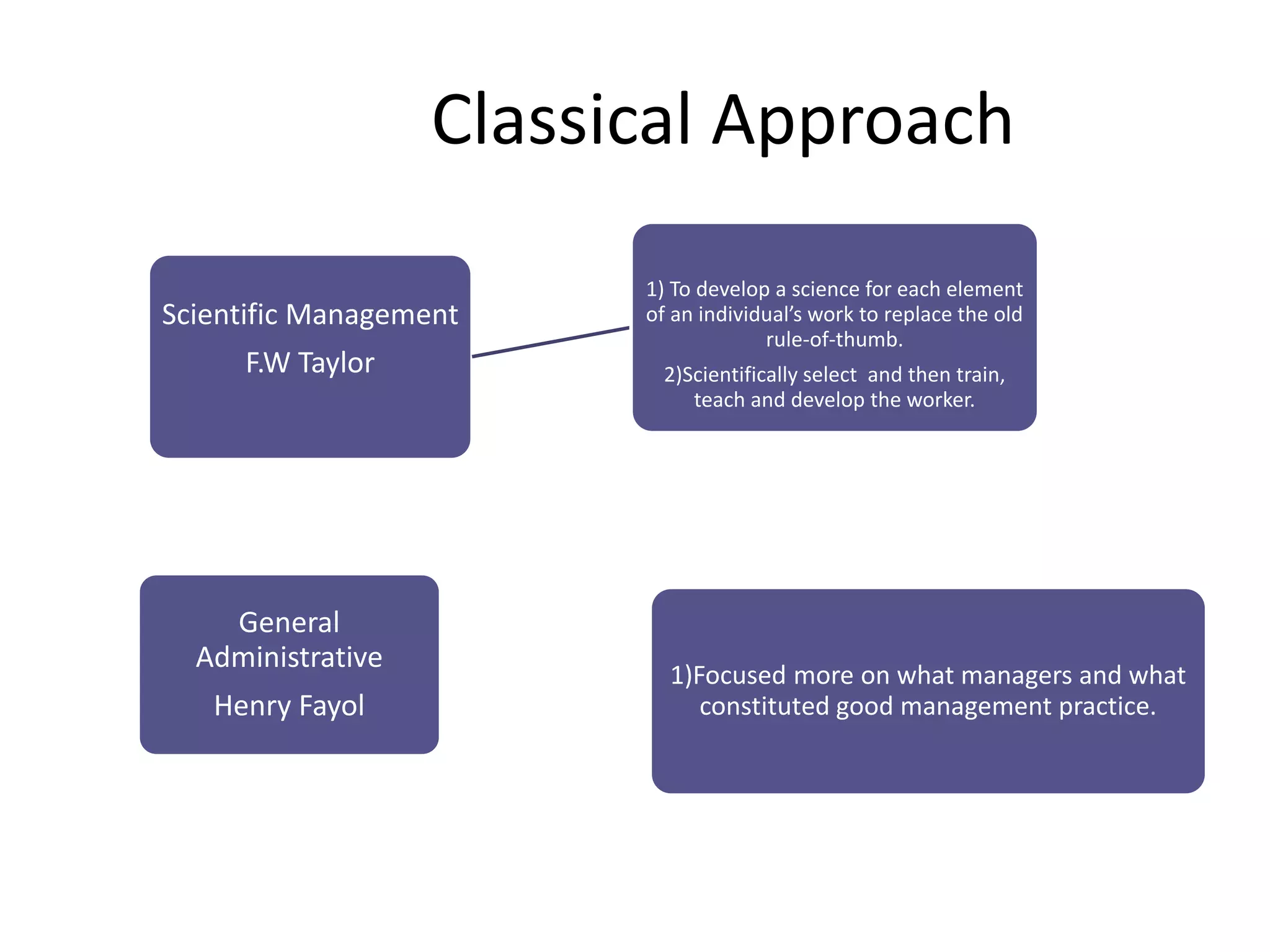
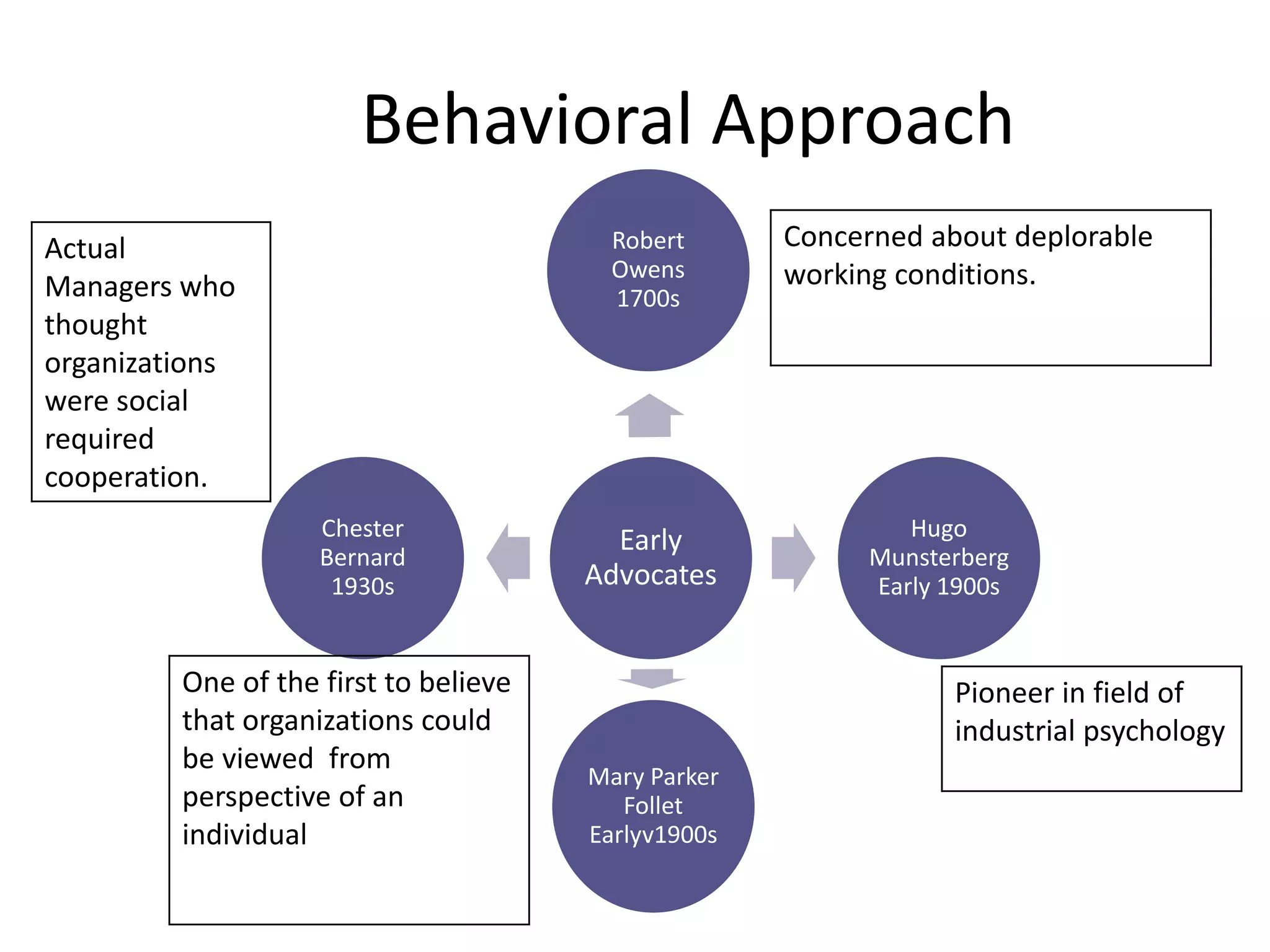
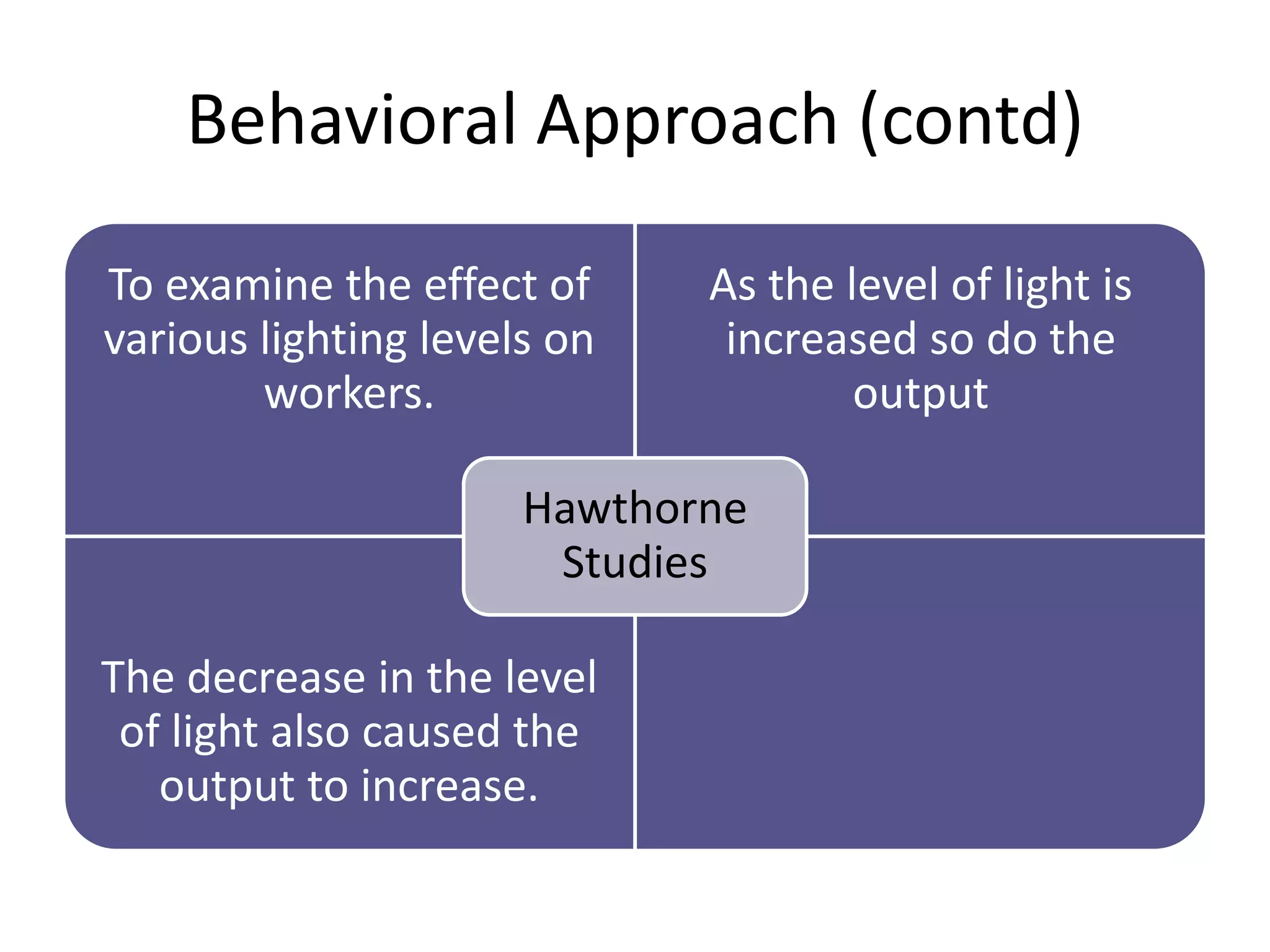
This document summarizes major management approaches including historical, classical, behavioral, quantitative, and contemporary approaches. The historical approach discusses organized endeavors dating back thousands of years. The classical approach covers scientific management by Taylor and general administrative theory by Fayol. The behavioral approach was pioneered by researchers examining how organizations are social and require cooperation. Quantitative approaches focused on concepts like total quality management and process improvement. Contemporary approaches include systems theory analyzing organizations as interconnected parts and the contingency approach stating there is no universal best way to manage due to different organizational situations.