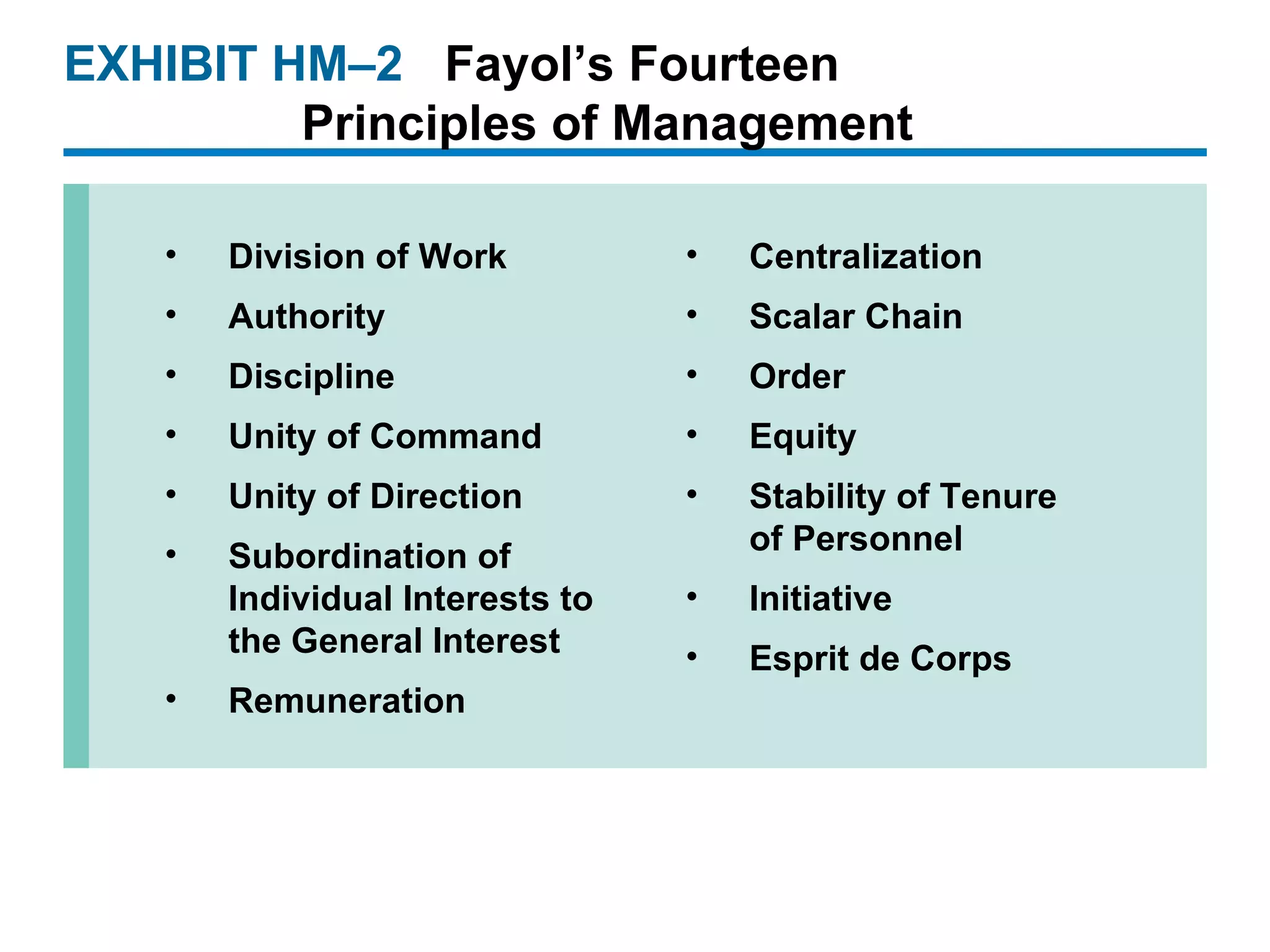
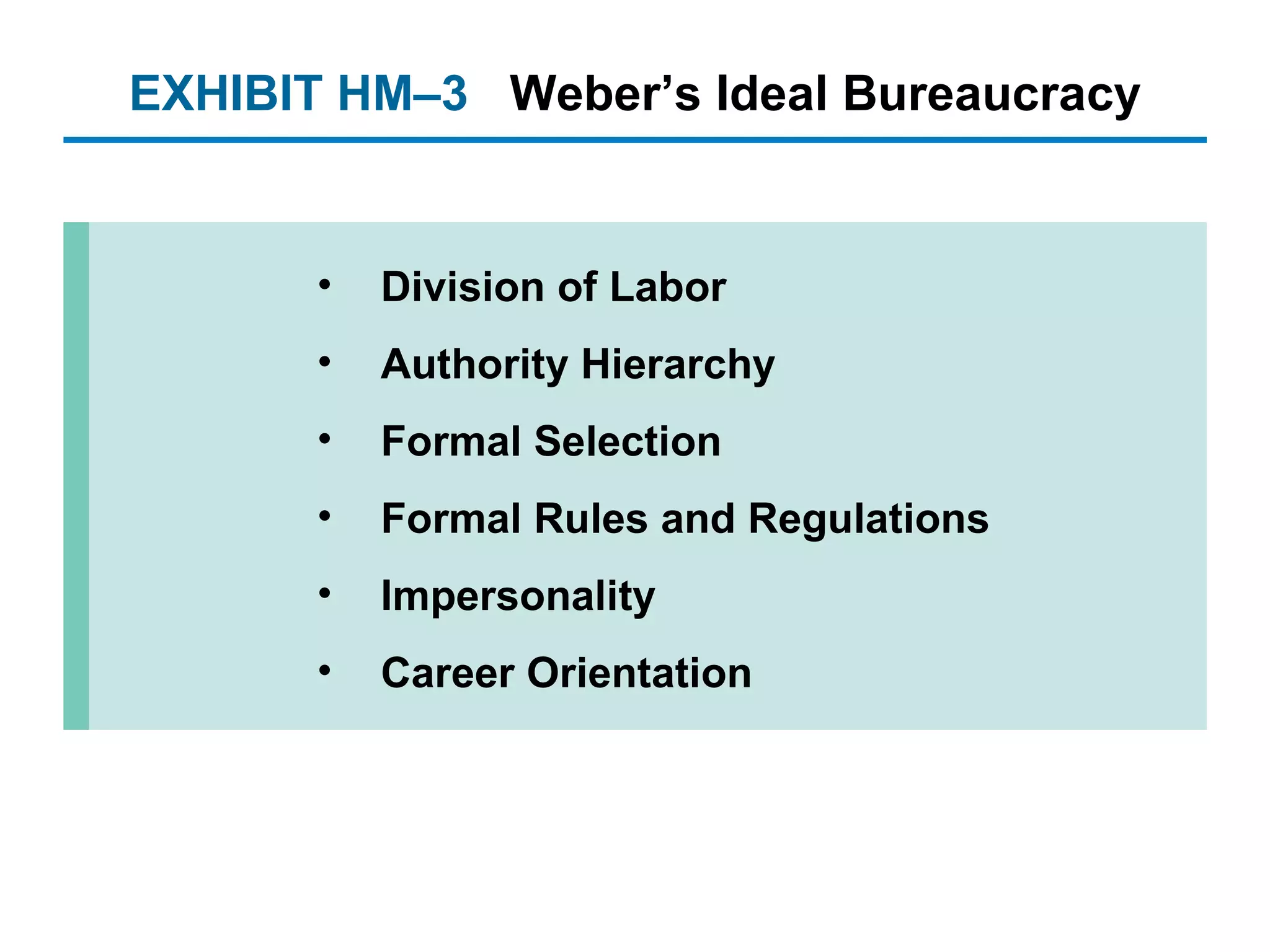
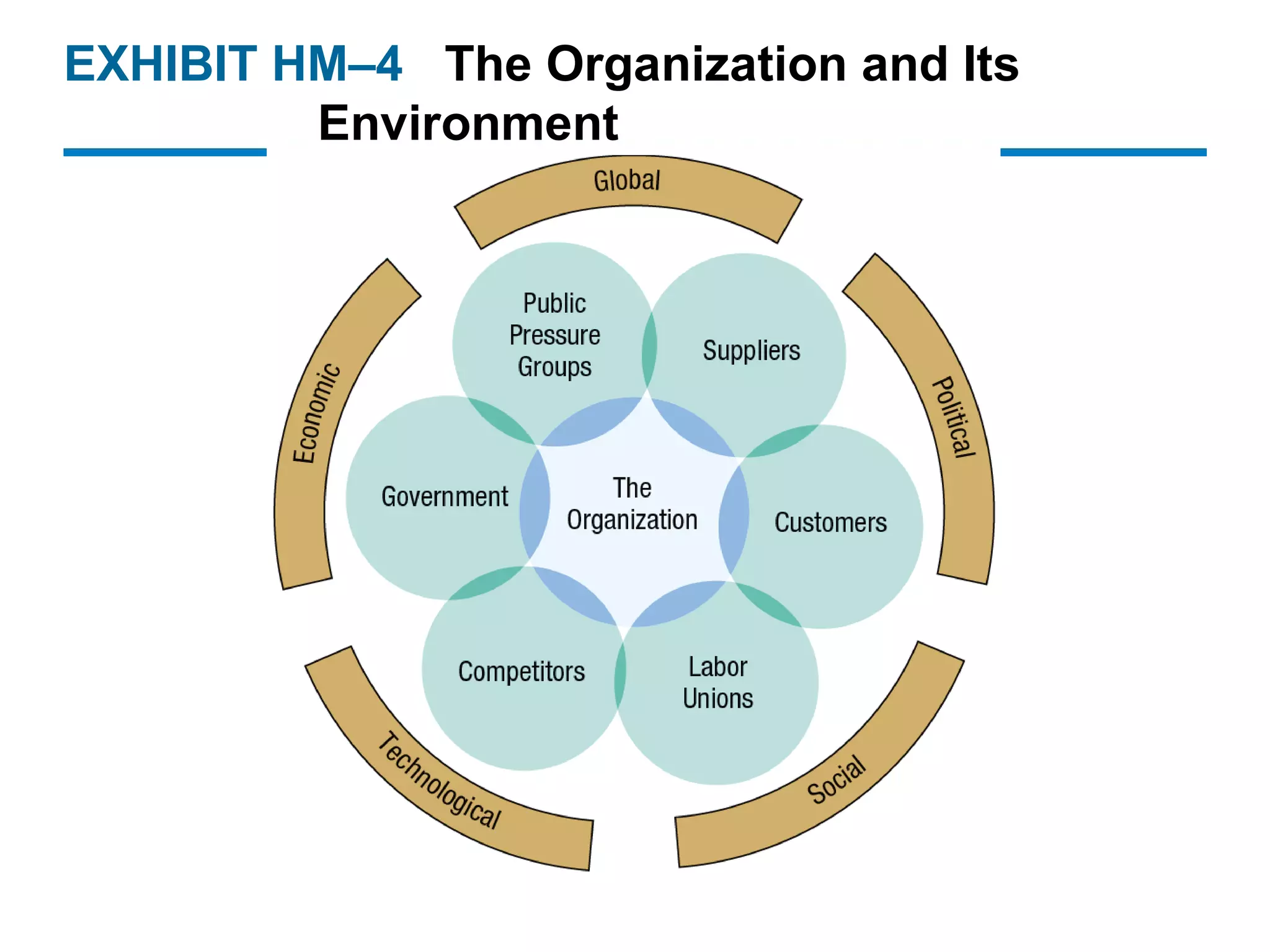
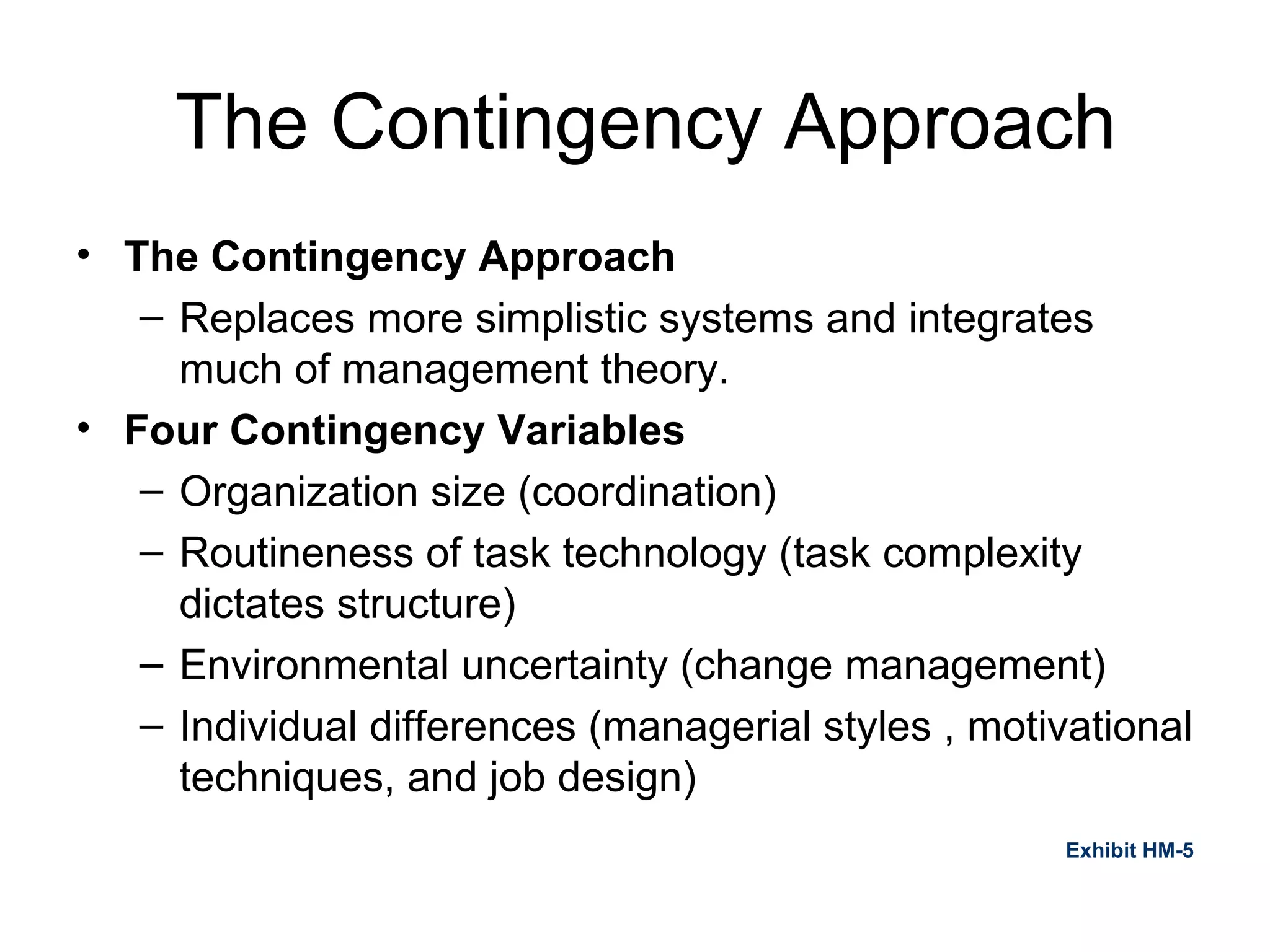
The document provides an overview of the historical roots and evolution of modern management practices from ancient times to the present. It discusses influential early thinkers like Adam Smith and developments like the Industrial Revolution that shaped new management approaches. Major 20th century frameworks are also summarized, including scientific management, bureaucracy theory, human relations movement, and contingency theory.