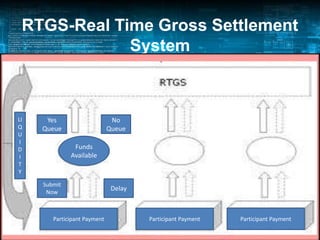
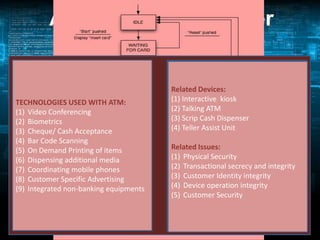
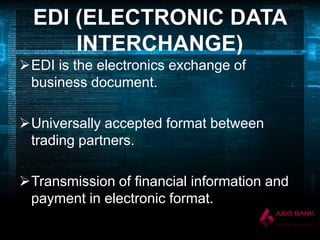
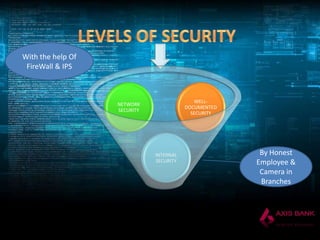
The document discusses the impact of technology on banking. It explains how technology has revolutionized every core banking function such as supervision, regulation, currency management, and financial stability. It highlights how the widespread adoption of technology has made banks interested in utilizing it. Some key technologies discussed include ATMs, core banking solutions, electronic banking, mobile banking, internet banking, ECS, RTGS, e-cheques, POS, telebanking, and EDI. The document also covers challenges in implementing these technologies and the implications of IT in banking.