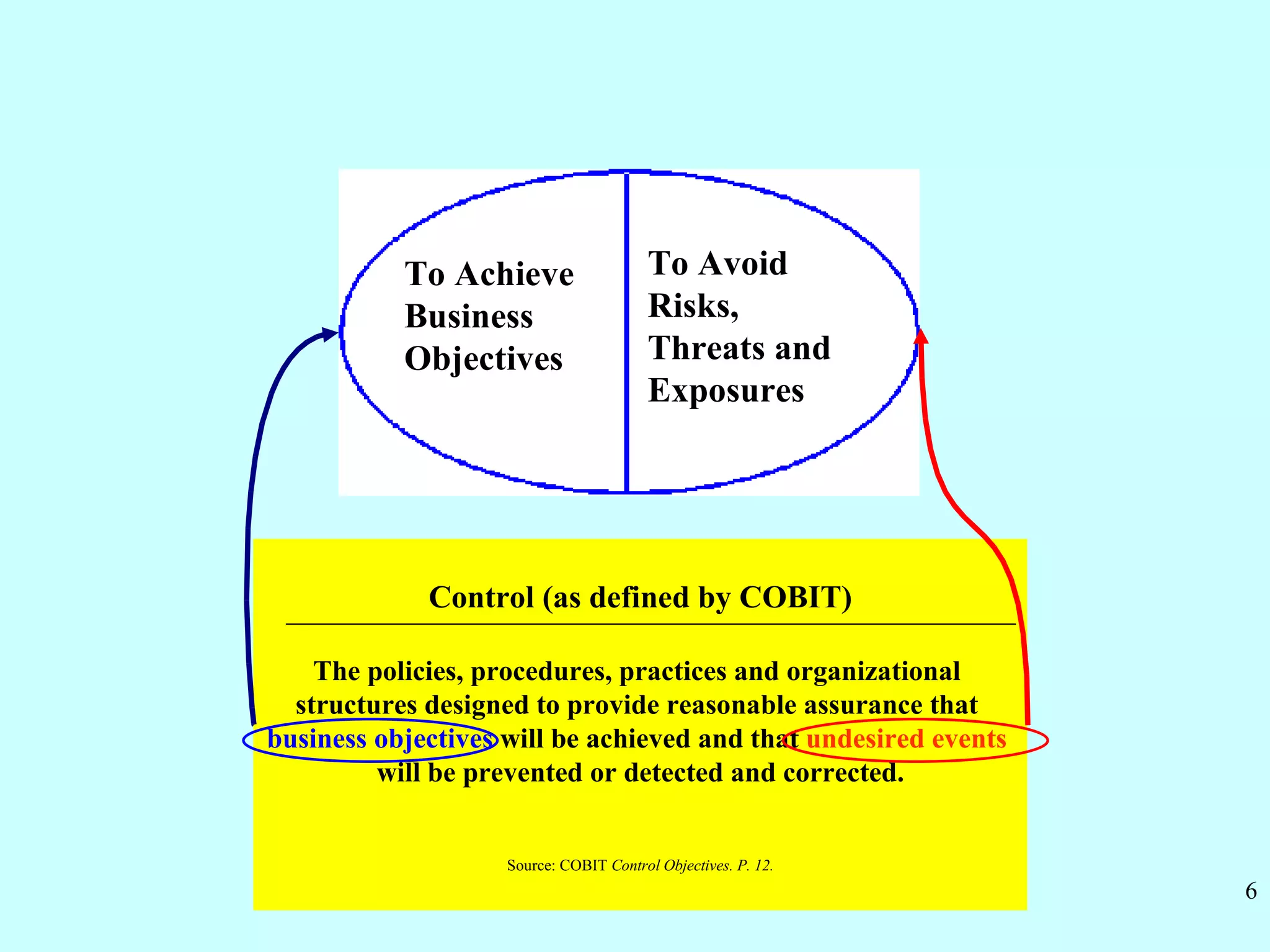
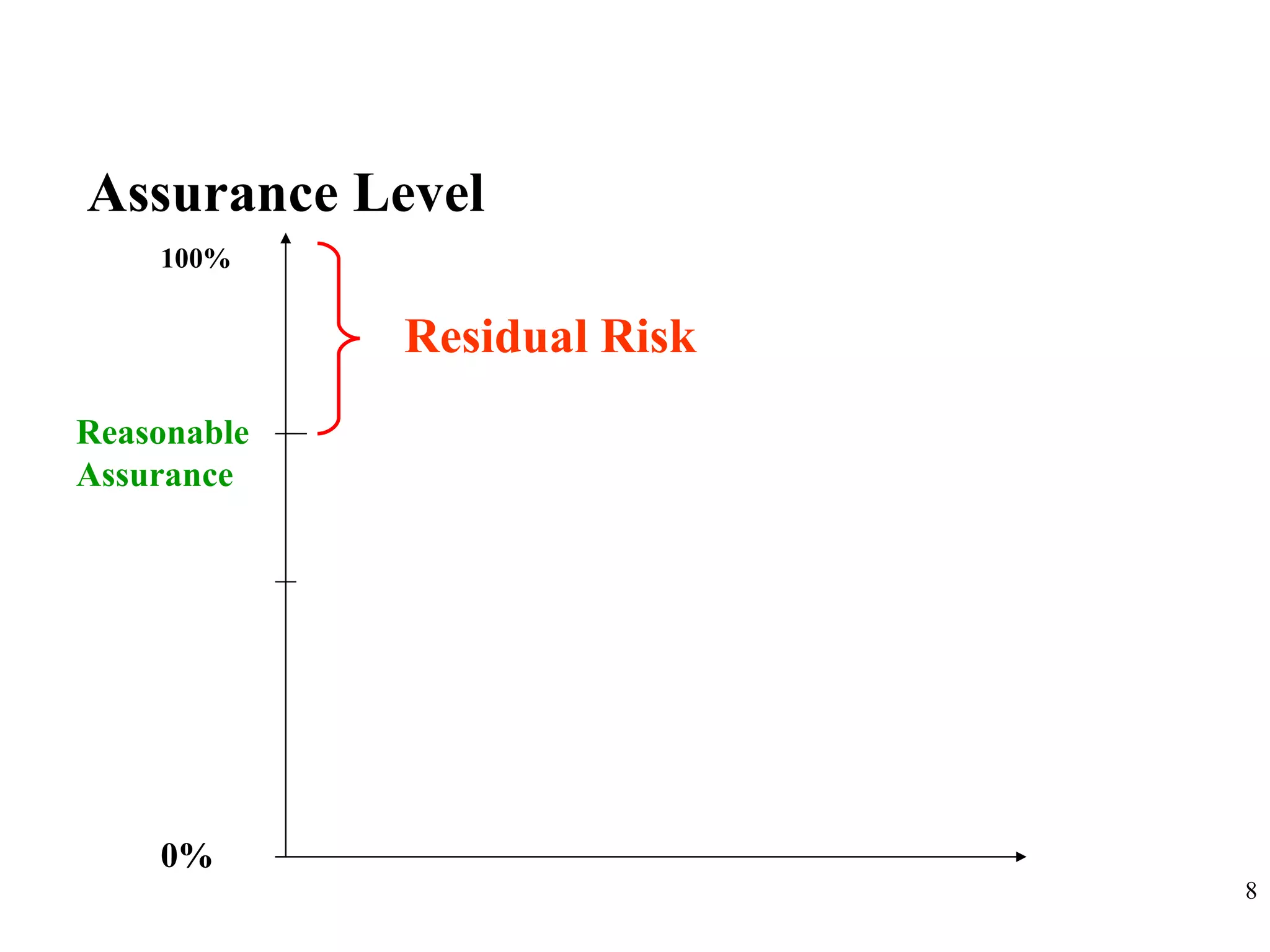
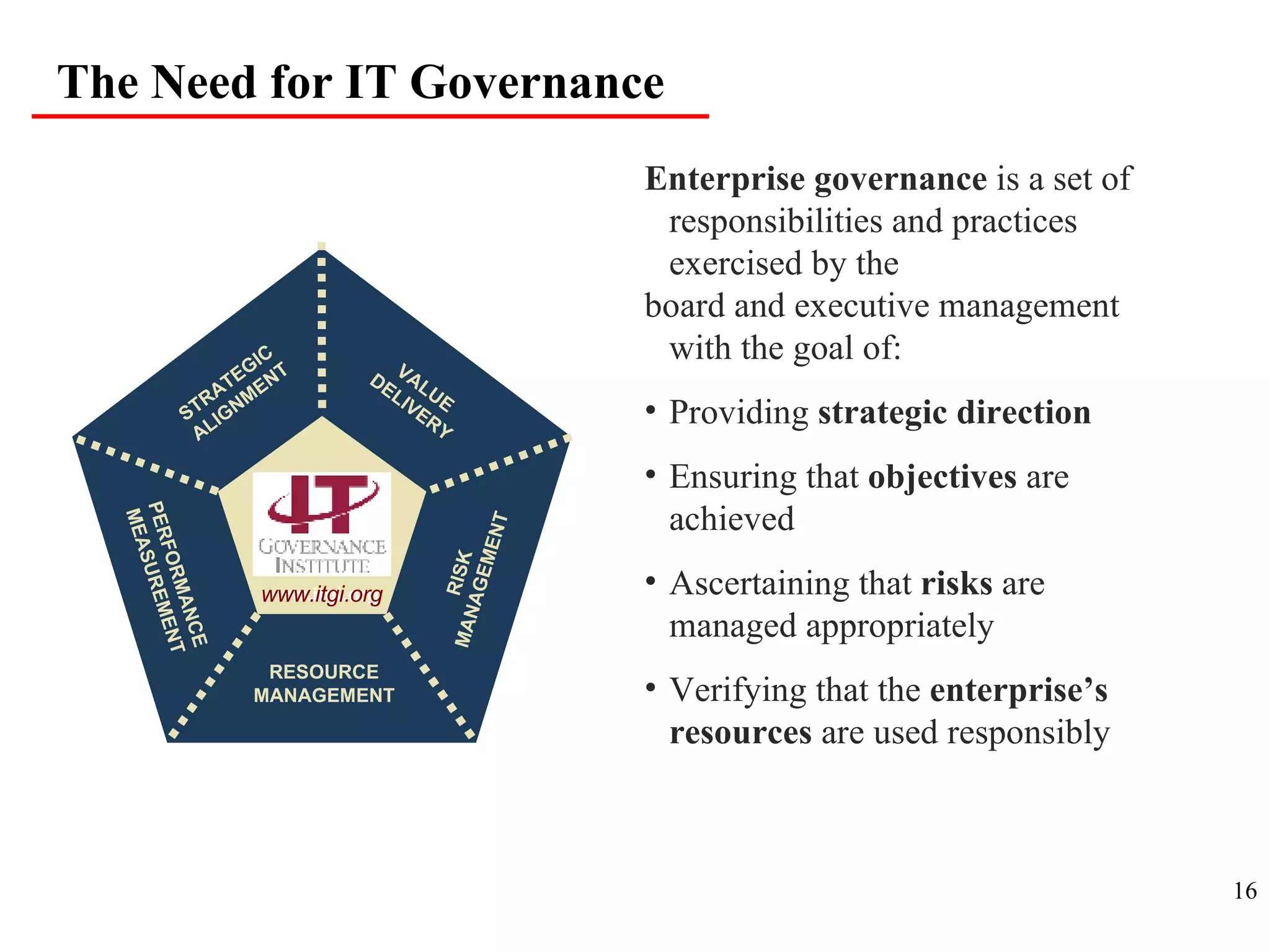
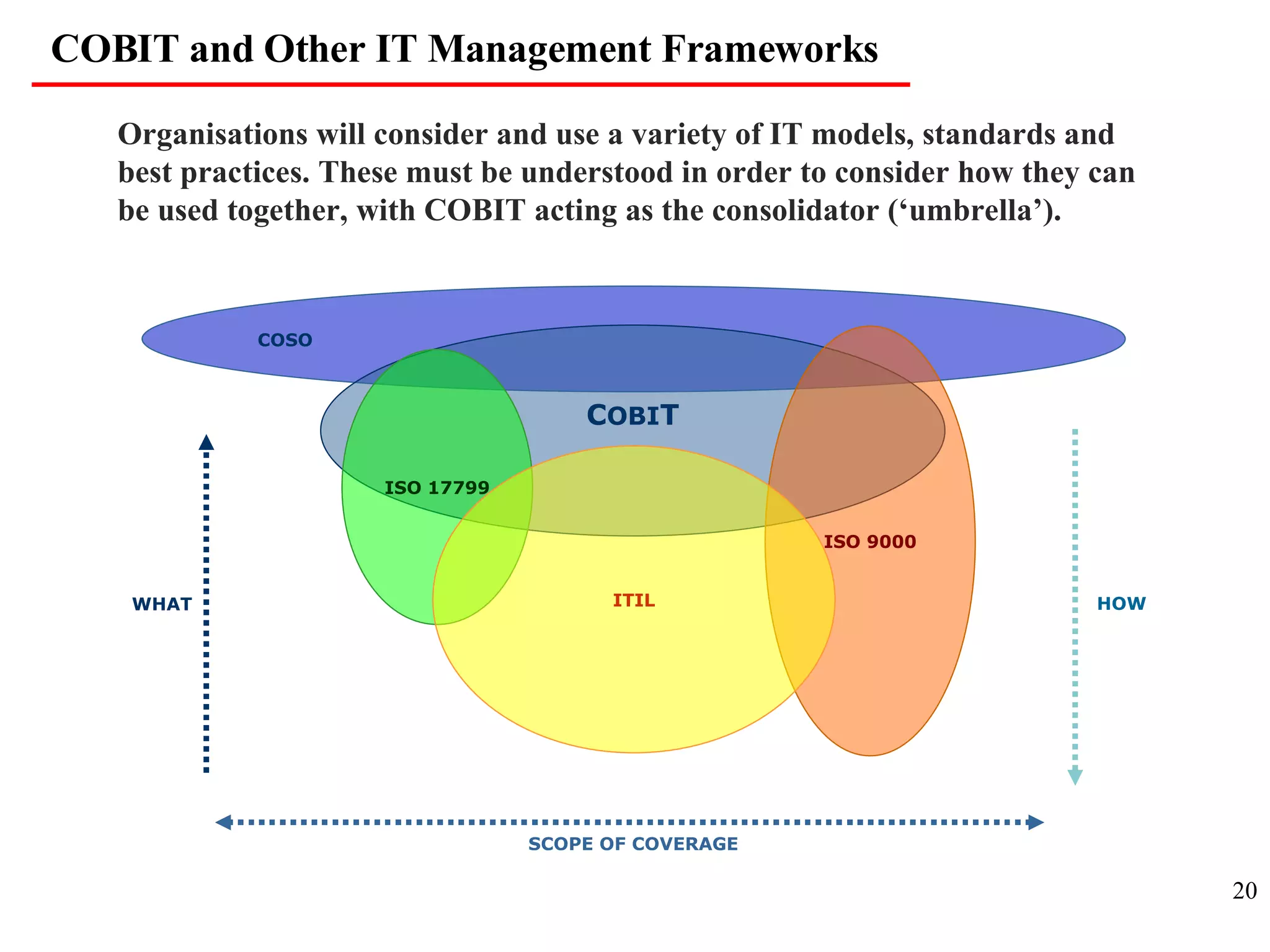
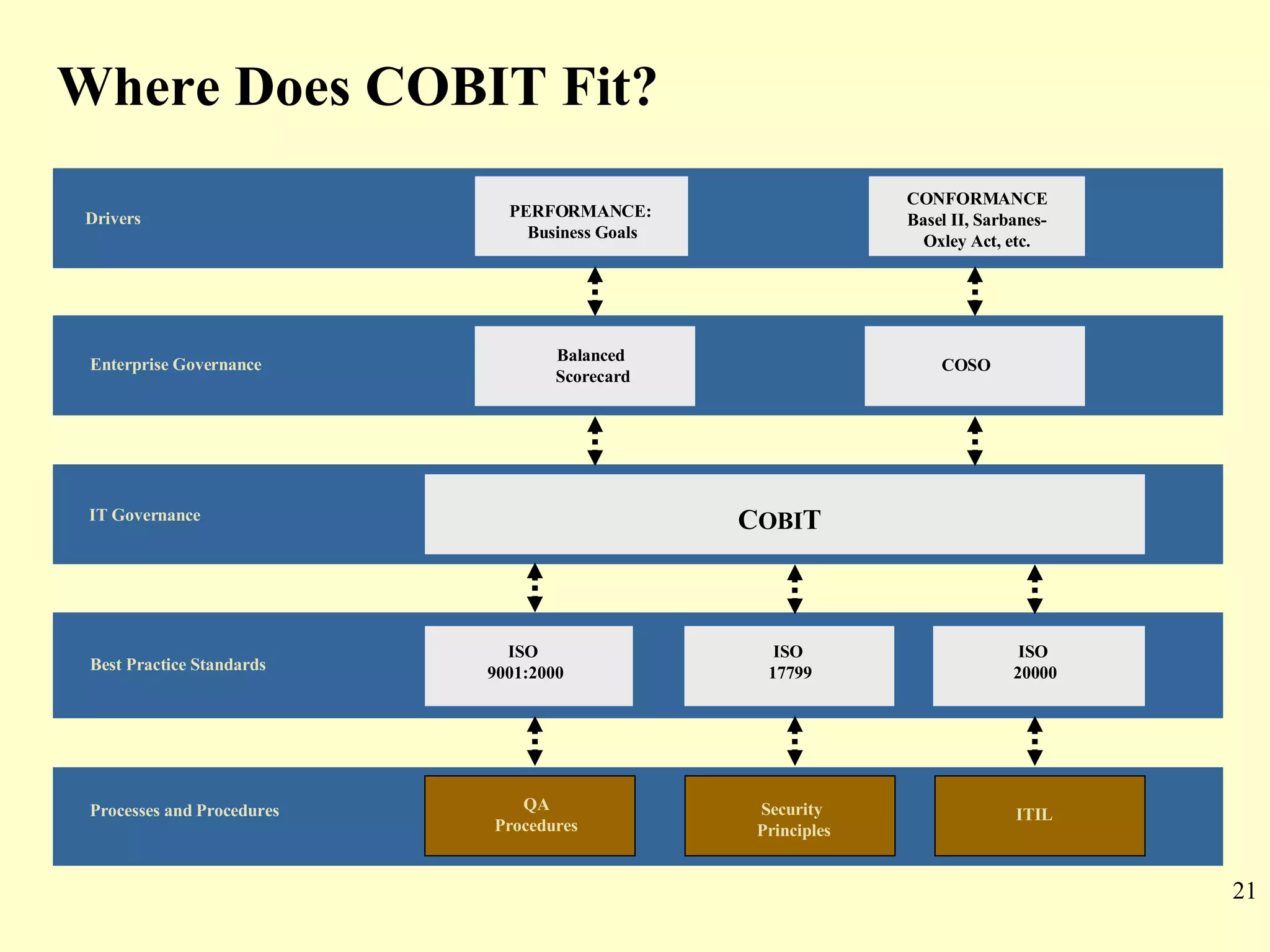
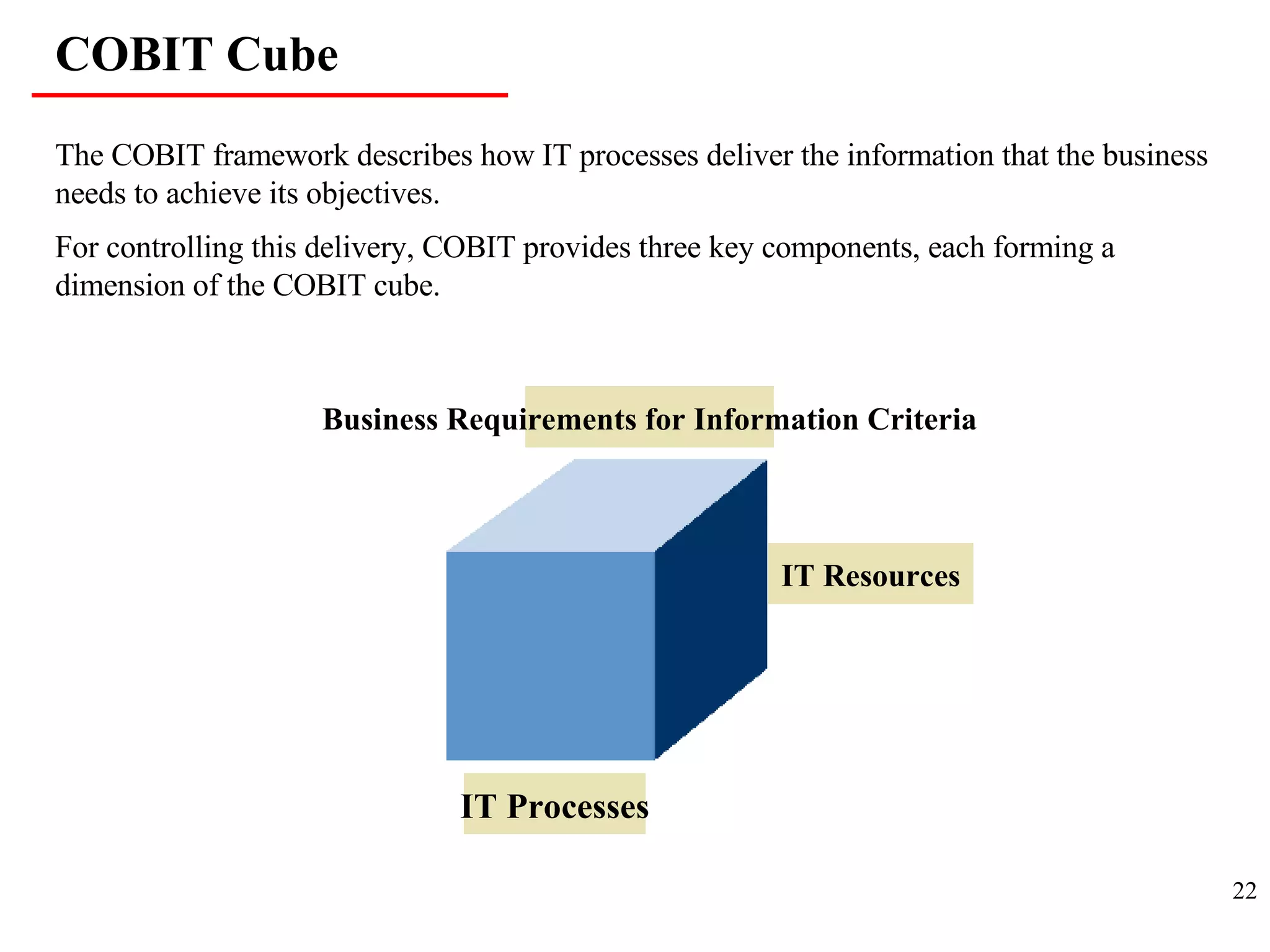
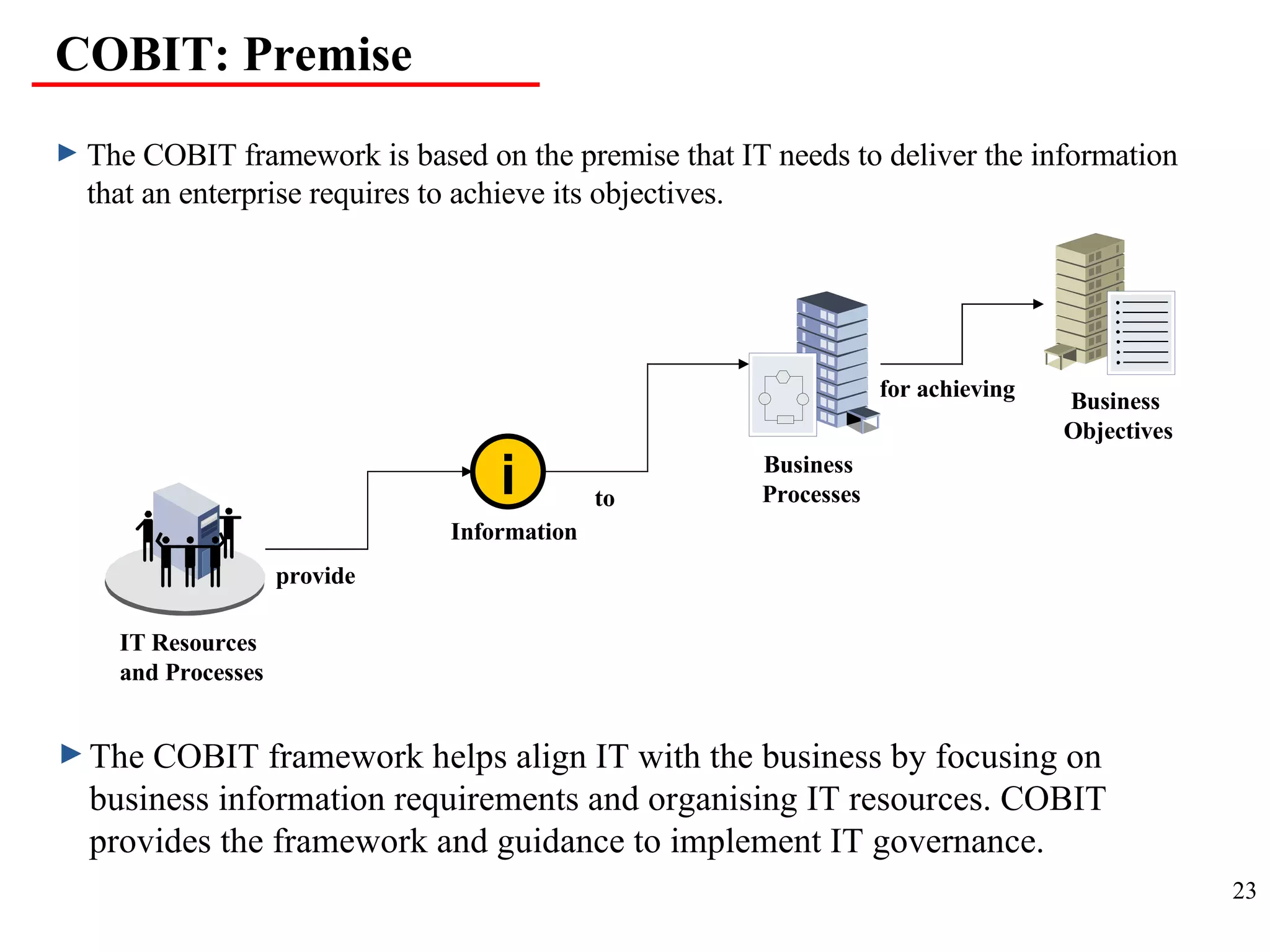
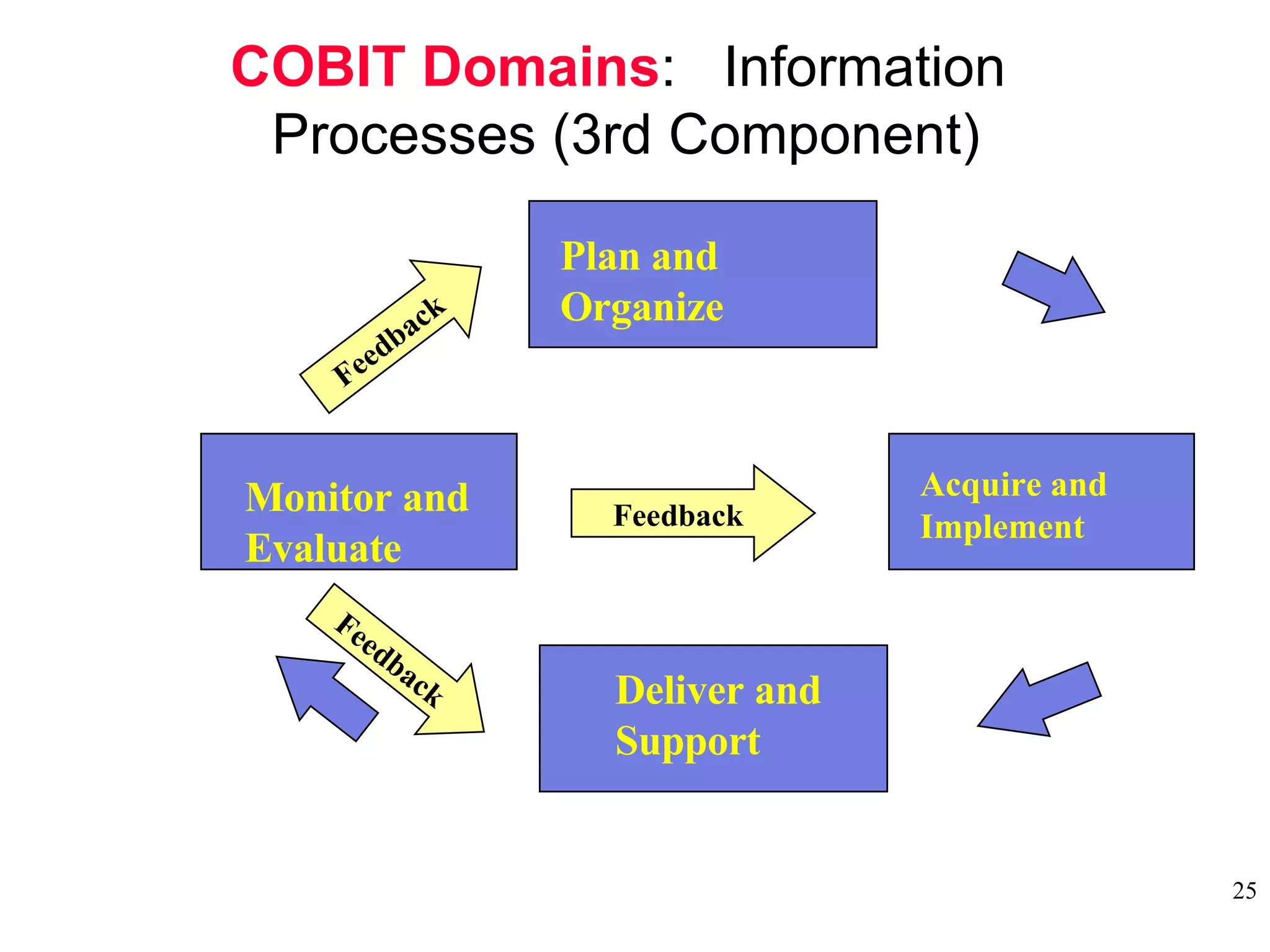
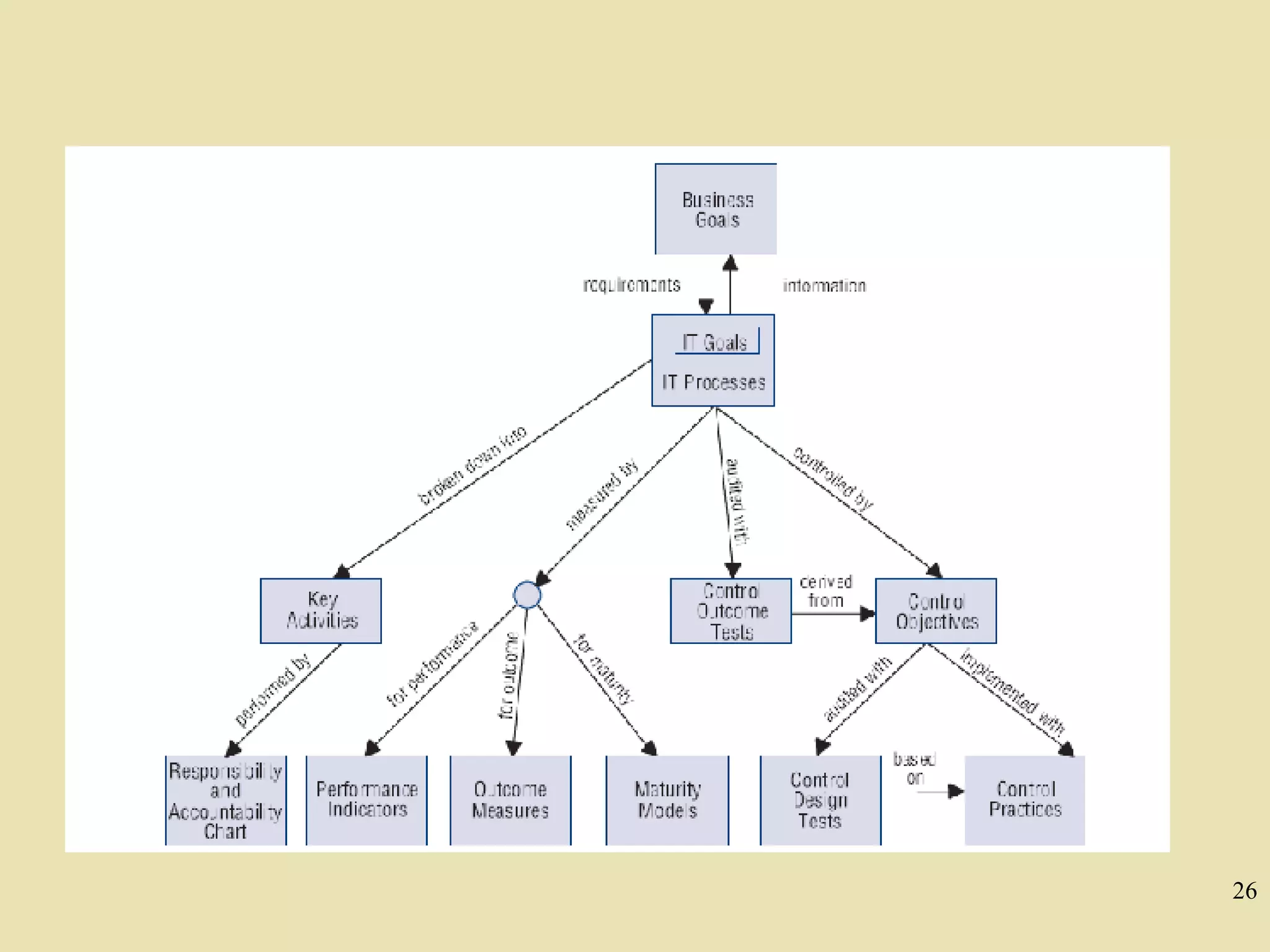
CobiT 4.1 is an authoritative, up-to-date set of generally accepted IT control objectives and practices for business and IT managers. It provides a framework for IT governance and is aimed at ensuring information integrity, security, and availability. CobiT promotes the understanding that IT resources need to be managed through key processes in order to deliver the information required for organizations to achieve their objectives.

















![CobiT is Easily Available Freely downloadable from: www.isaca.org If you need guidance or training contact us [email_address] or [email_address] Thank You](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accountability-corbit-overview-06262007-119730586988998-2/75/Accountability-Corbit-Overview-06262007-27-2048.jpg)