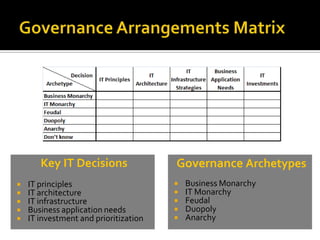
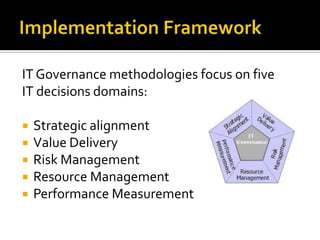
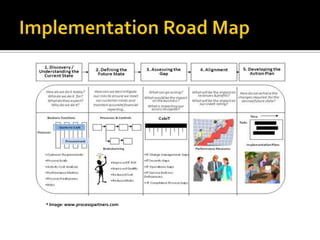
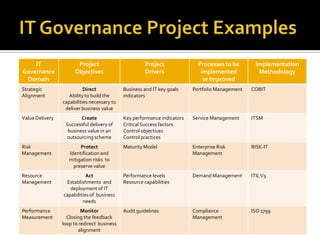
The document outlines the importance of IT governance, its definition, purposes, and benefits for aligning with business strategy and optimizing resource management. It discusses key decision rights and accountability frameworks, risk management, and performance measurement methodologies. Additionally, it references various sources related to IT governance principles and methodologies aimed at enhancing service delivery and managing IT-related risks.