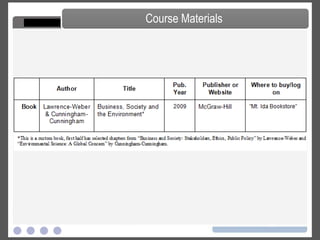
This document outlines the course structure and content for a Business, Society & Environment course. It includes:
- An introduction to the topics of global warming, skepticism about climate change, and businesses' role in society through video clips.
- A definition of sustainable development as meeting present needs without compromising future generations' ability to meet their own needs.
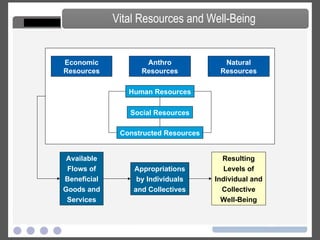
- An overview of the course objectives to study the impacts of business on resources and describe systems to influence these impacts.
- A course map listing topics like corporate social responsibility, the environment, renewable energy, and waste management that will be covered.
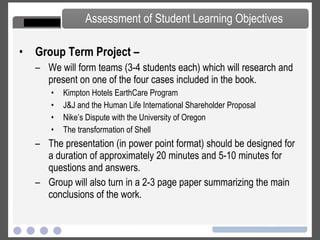
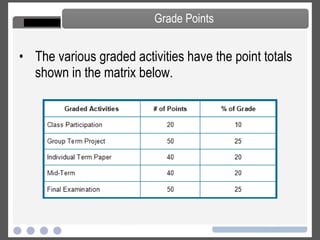
- Details on group and individual assignments, midterm and final exams, and grading criteria.