1) Environmental economics studies the relationship between the environment and economic development to ensure the environment is not impaired by economic activity.
2) The environment provides material resources, waste treatment, life support services, and recreational benefits to humans.
3) The material balance model shows that in the economy, the total raw materials input from the environment equals the total waste output.
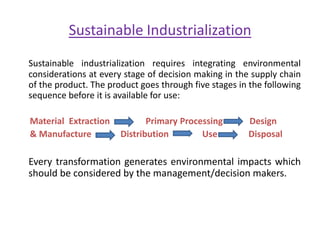
4) Sustainable development aims to meet current needs without compromising the environment for future generations. Tools like pollution taxes and industrial efficiency can promote sustainable development.