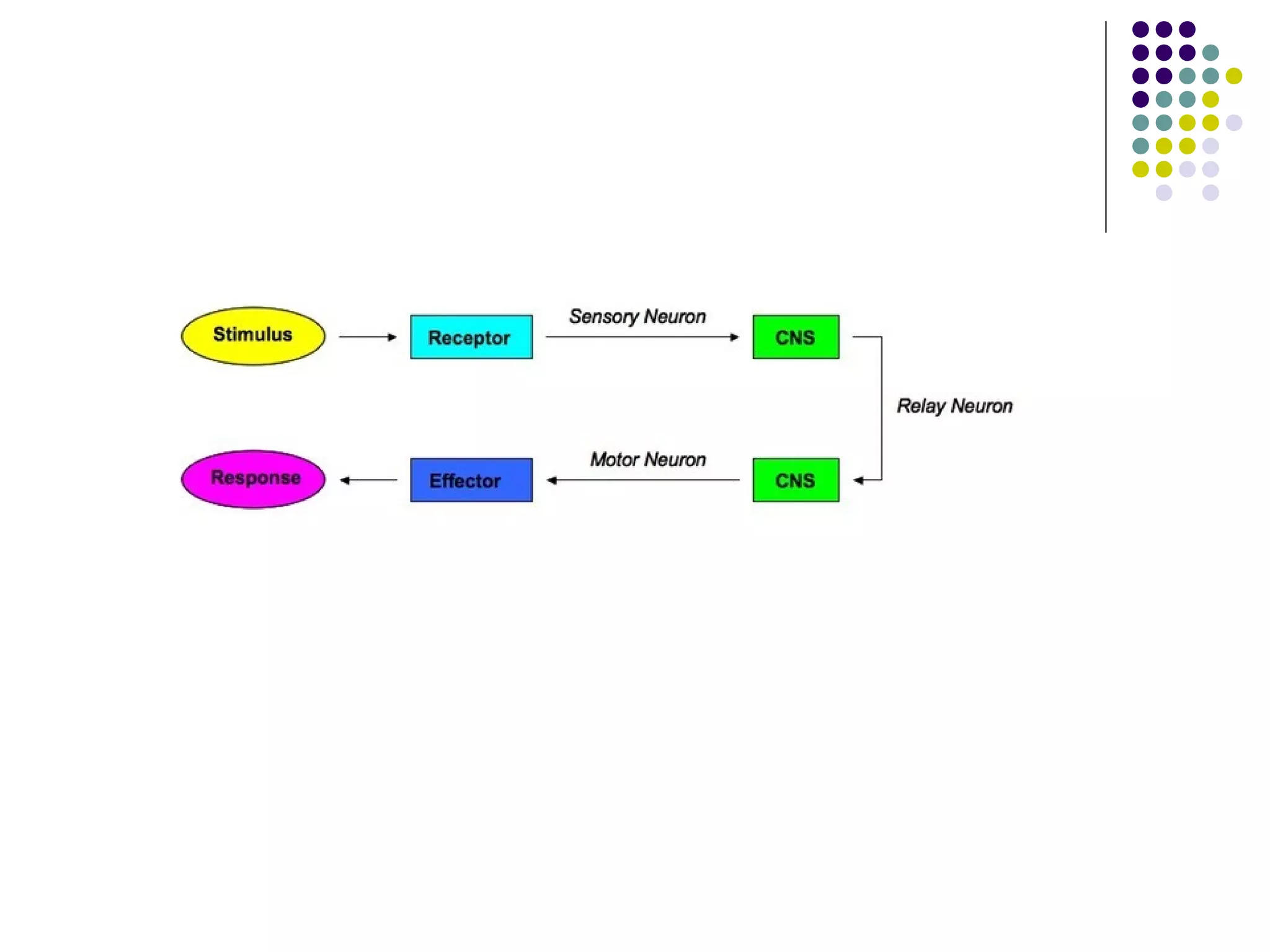
The document discusses motor control theories, specifically reflex theory. Reflex theory proposes that reflexes are the basic building blocks of movement, where a sensory stimulus triggers a stereotypical motor response. However, reflex theory has limitations in explaining voluntary movements, movements without sensory input, fast sequential movements, and the ability to override or modify reflexes. The document also discusses clinical implications of reflex theory and neurofacilitation approaches that were developed based on reflex and hierarchical theories of motor control.