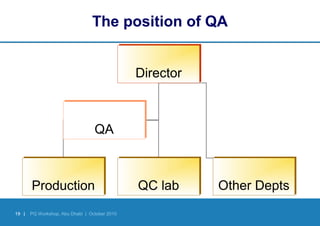
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) provide quality assurance guidelines for manufacturing medicines safely, effectively and consistently. GMP involves defining and documenting manufacturing processes, training personnel, validating equipment and facilities, controlling materials, documenting procedures, and inspecting to ensure compliance. Following GMP helps ensure medicines are produced and controlled according to their marketing authorization and quality standards through all stages of manufacture.