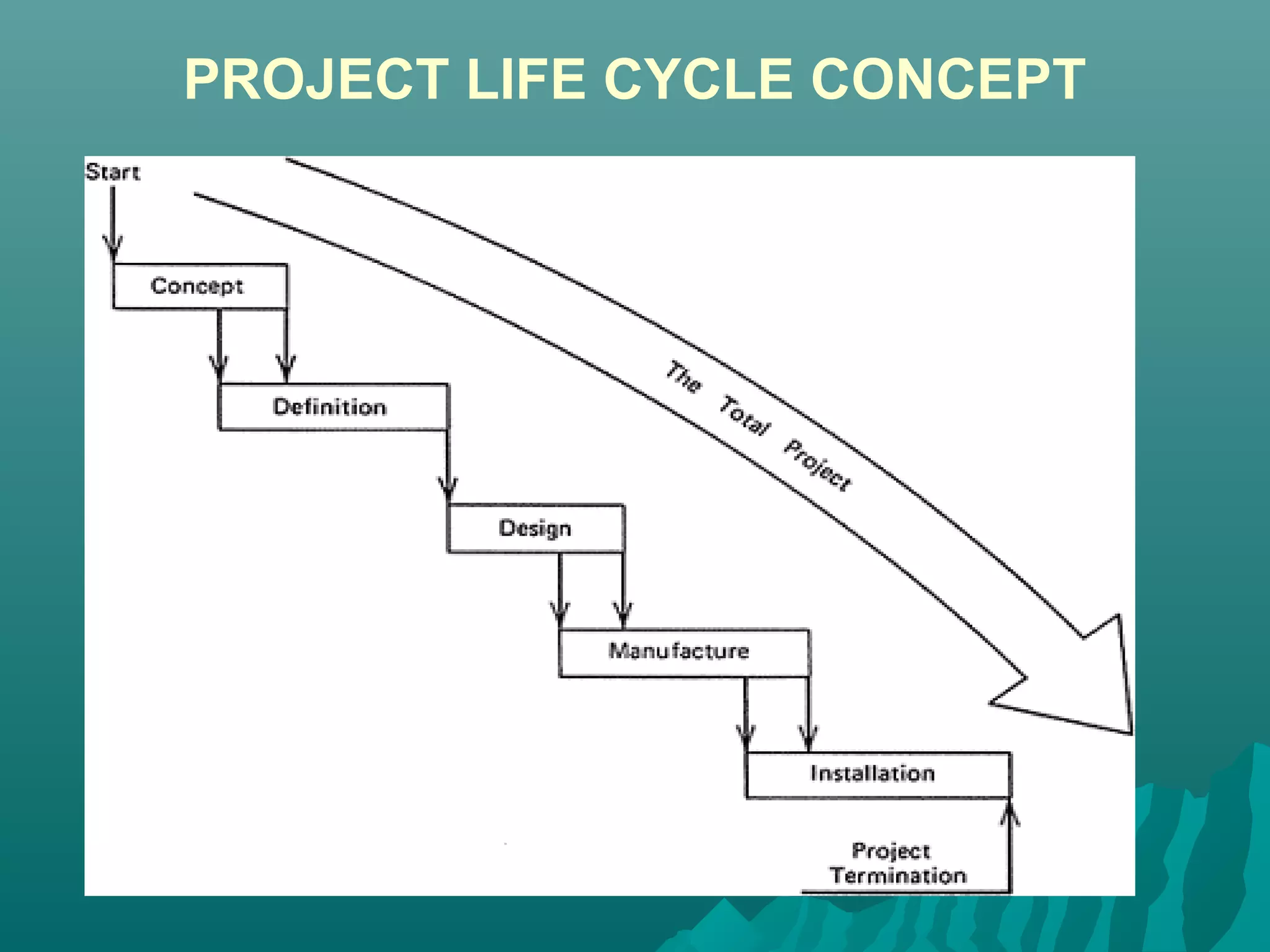
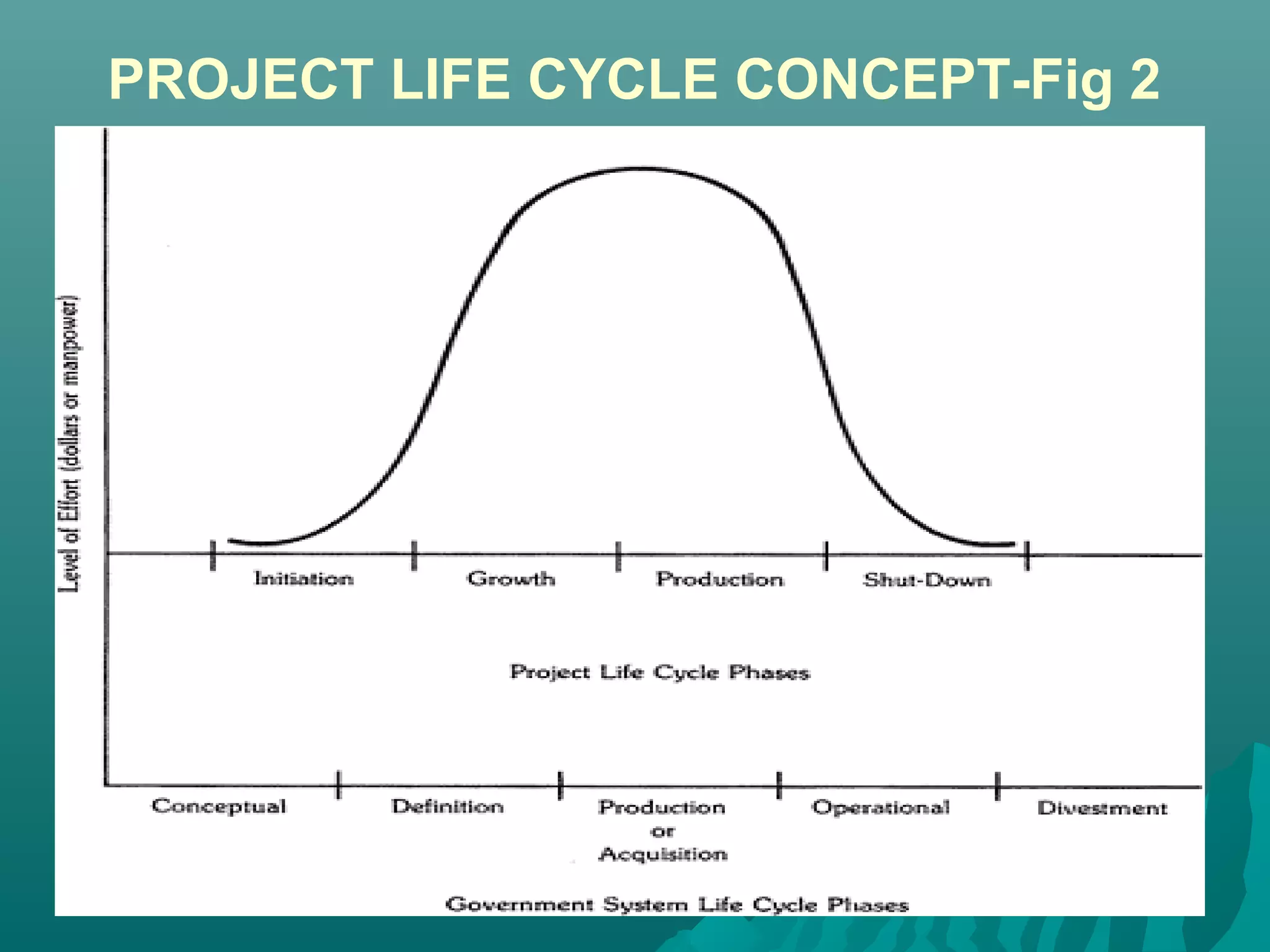
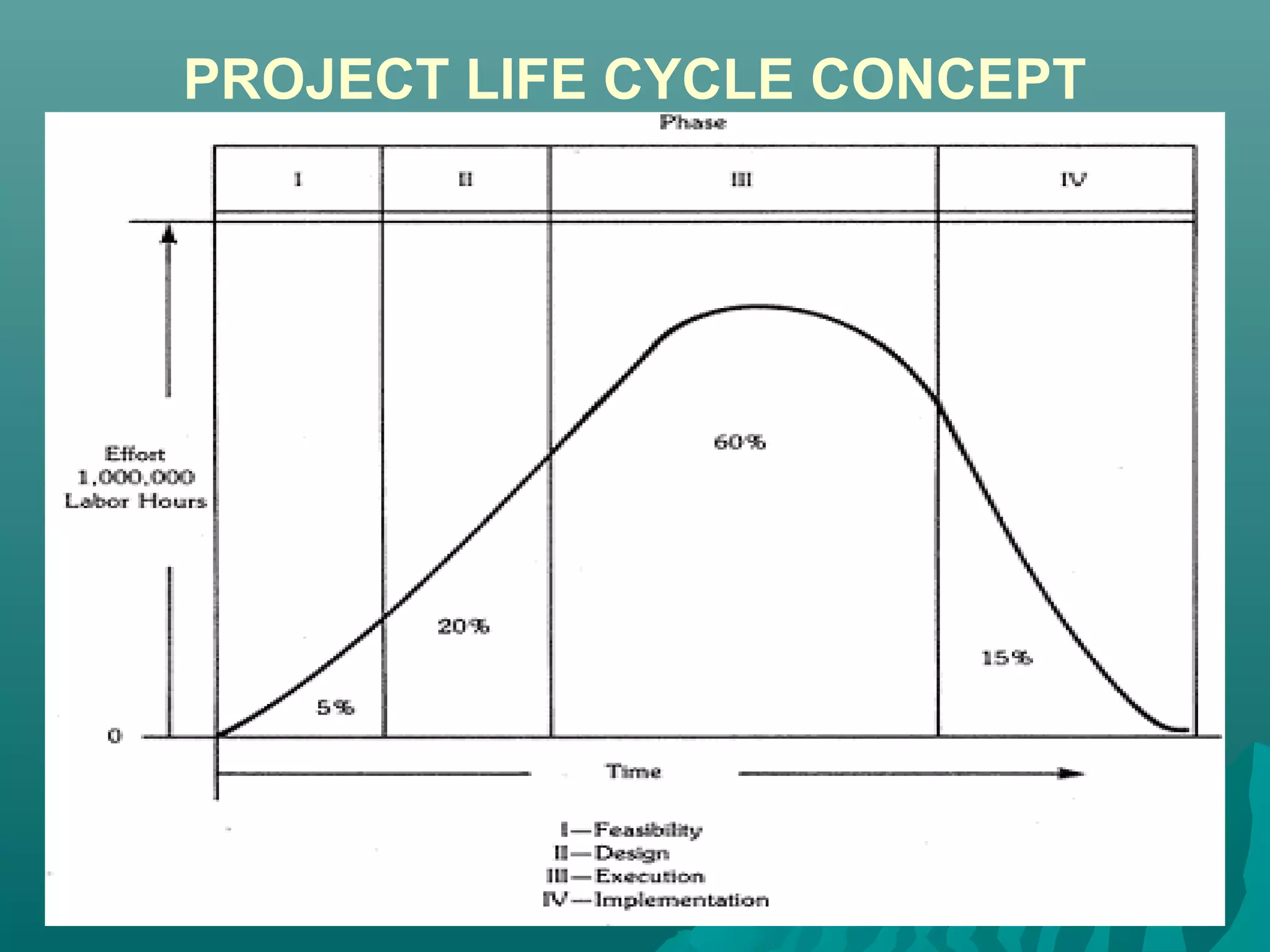
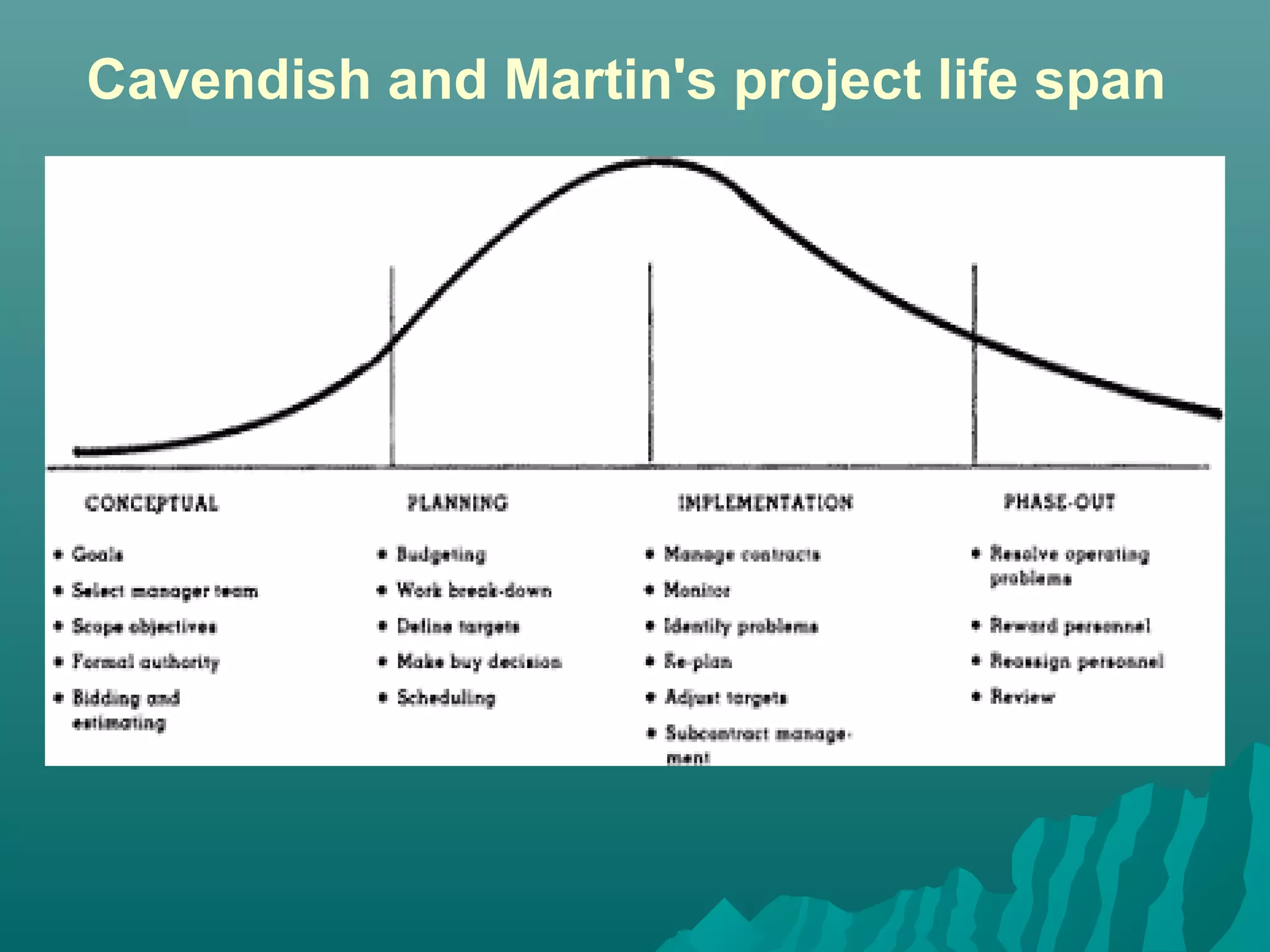
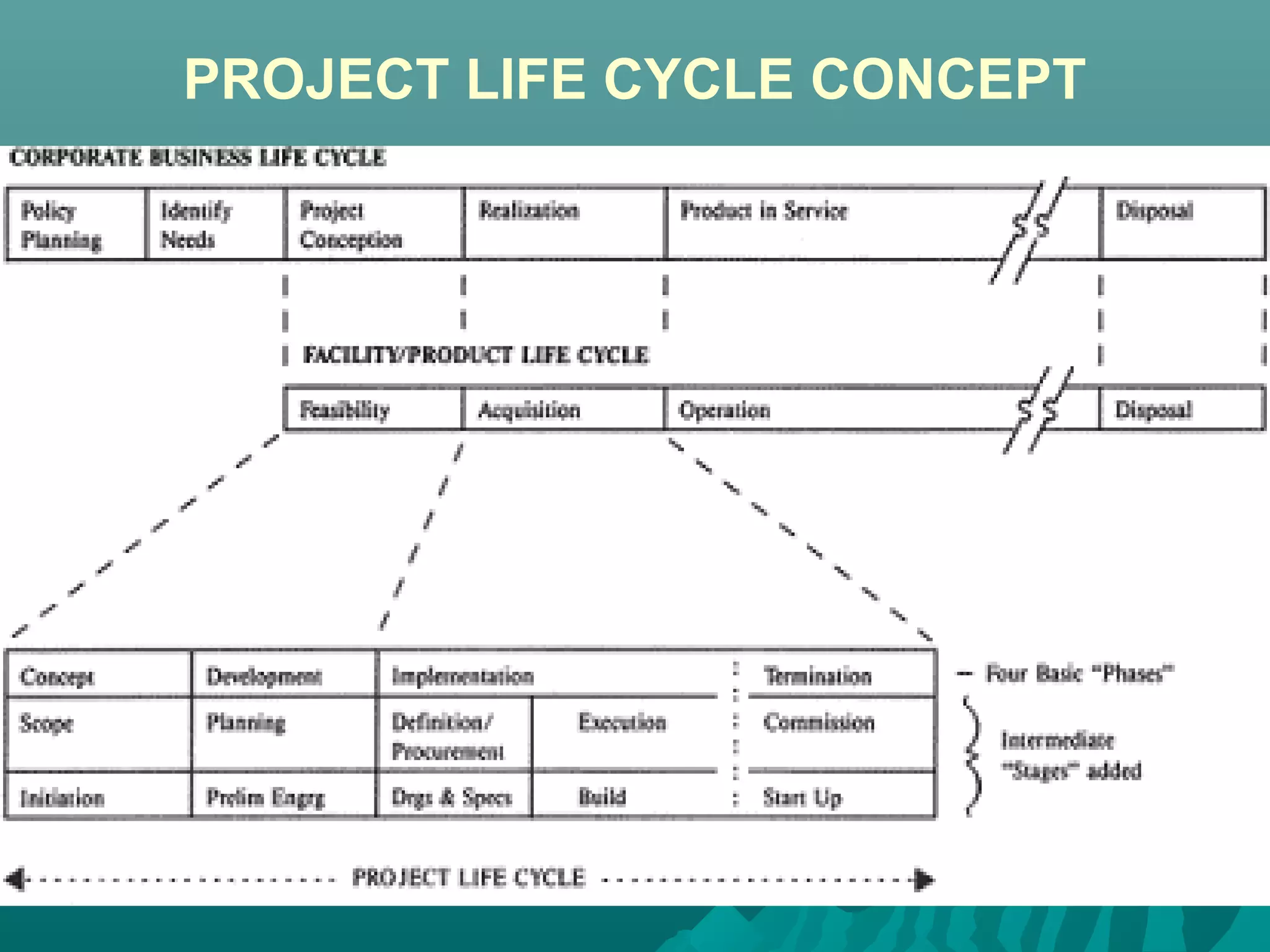
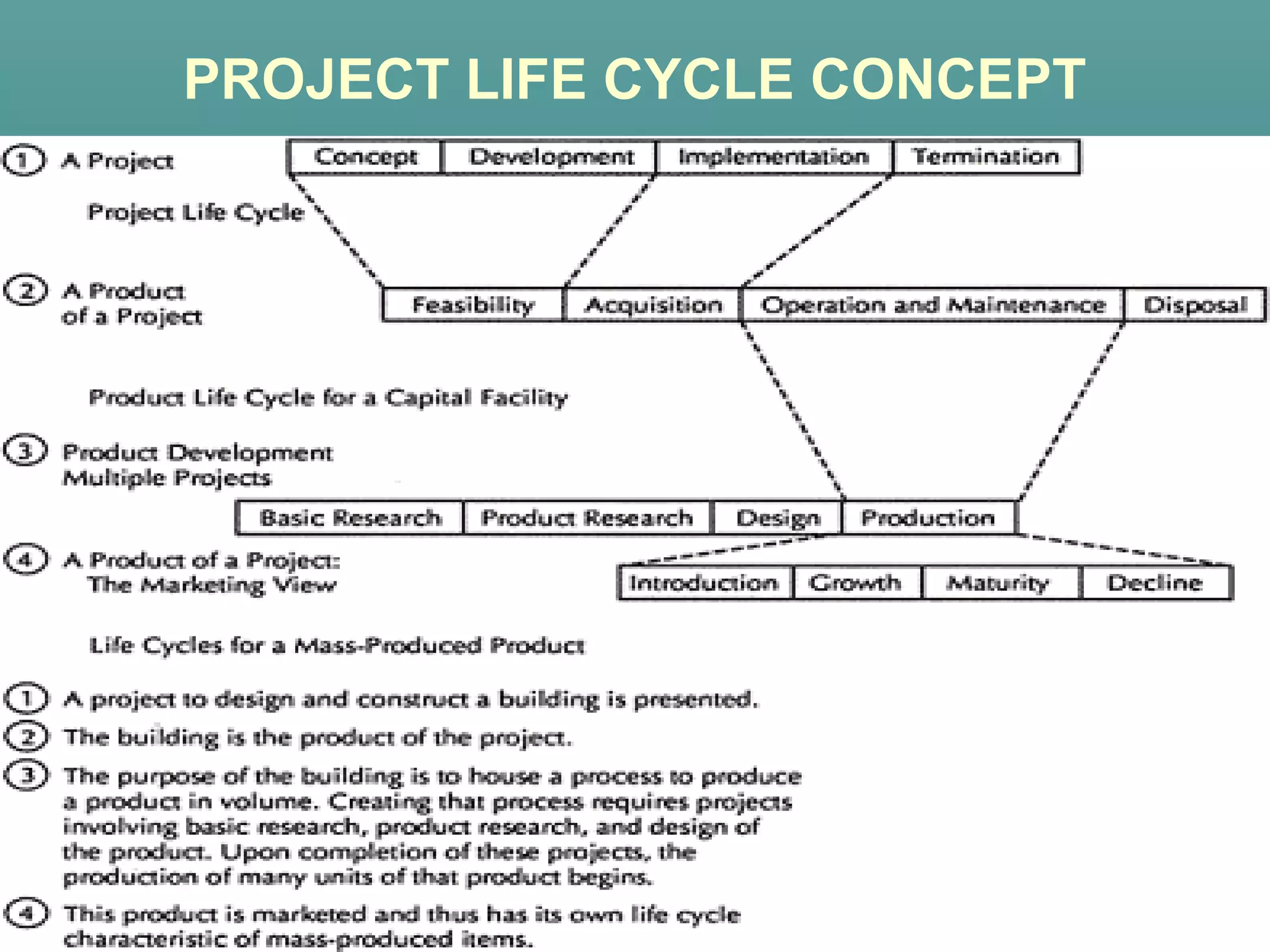
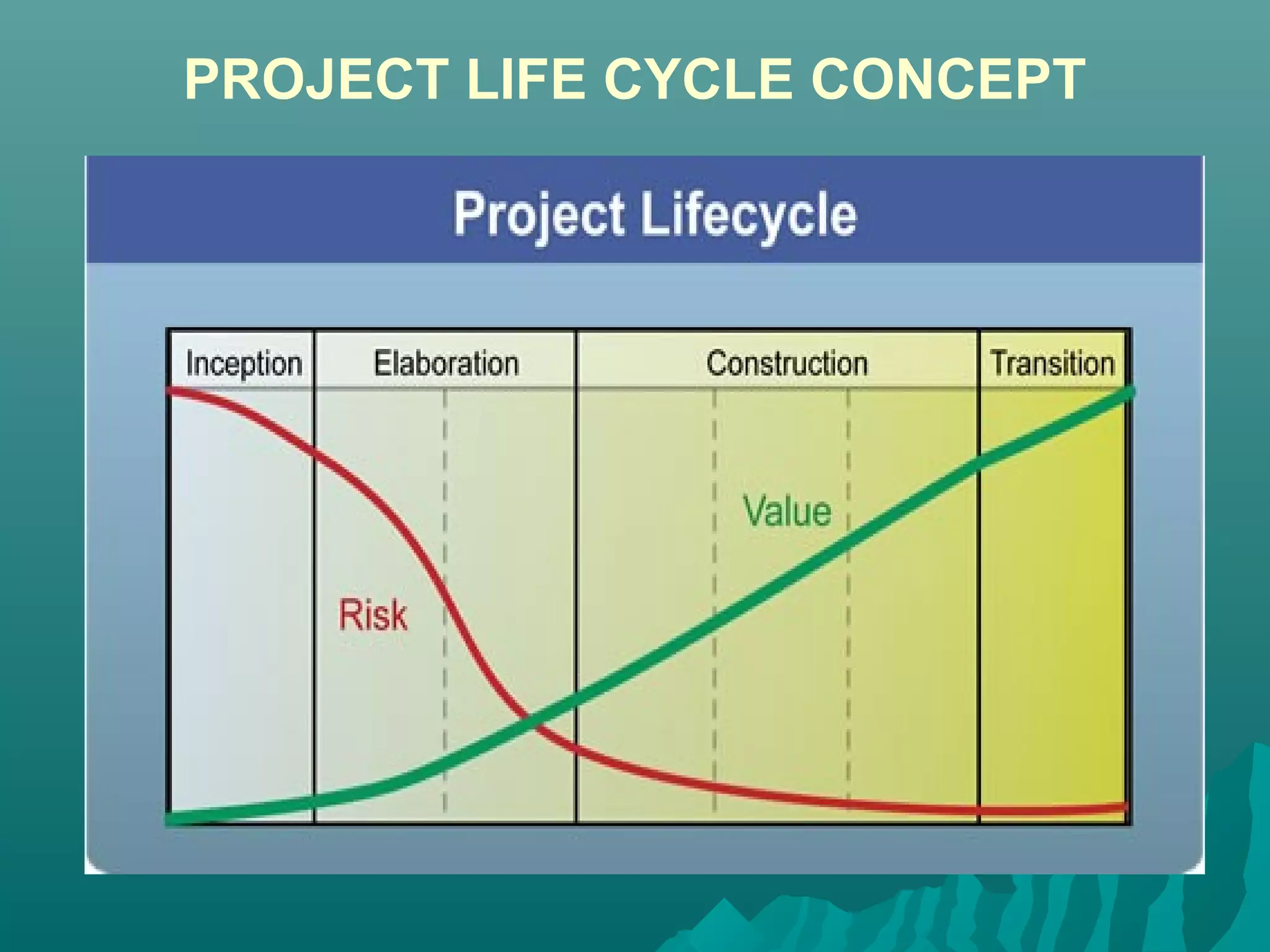
The document discusses the project life cycle concept. It states that a project passes through several distinct phases from inception to completion, with identifiable start and end points. These phases include concept, definition, design, development, application, and post-completion. Resources, people, skills, and organizations involved change throughout the phases. Major reviews occur at the end of each phase to authorize proceeding to the next phase or canceling the project. The life cycle provides a framework for budgeting, staffing, resource allocation, milestones, and reviews.