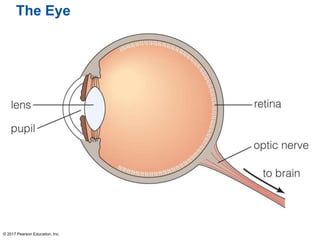
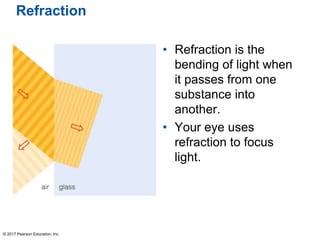
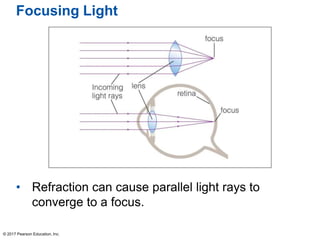
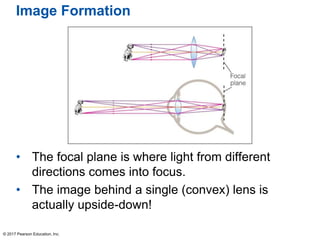
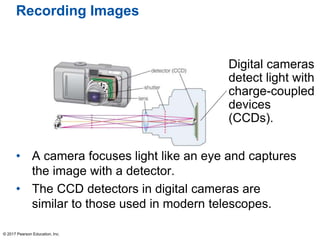
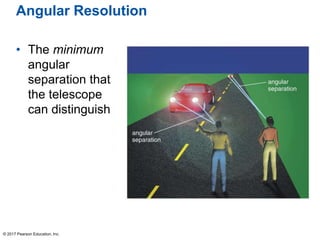
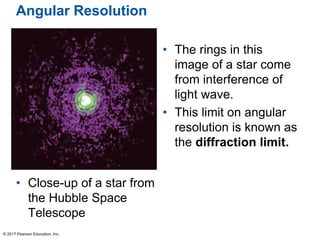
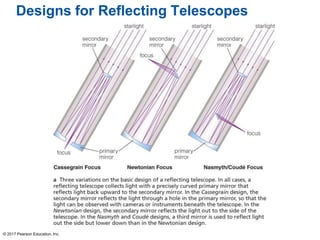
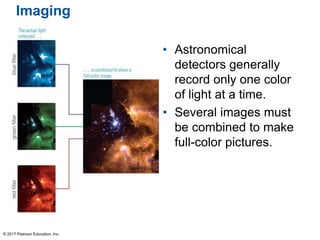
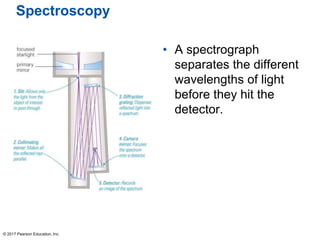
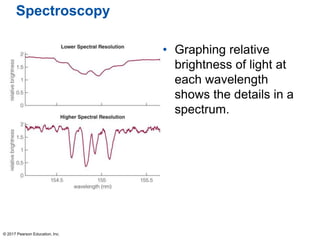
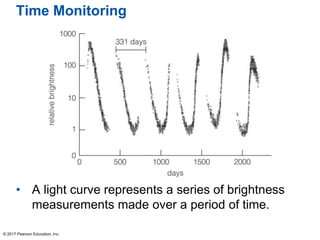
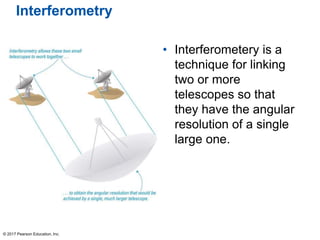
This document summarizes a chapter about telescopes. It discusses how telescopes work by focusing light using lenses or mirrors. The two most important properties of telescopes are their light-collecting area and angular resolution. There are two basic designs: refracting telescopes use lenses while reflecting telescopes use mirrors. Astronomers use telescopes to take images, perform spectroscopy, and monitor light over time. Earth's atmosphere limits ground-based observations so many telescopes are placed in space. Telescopes observe different wavelengths of light by modifying their designs. Multiple telescopes can work together using interferometry to achieve very high angular resolution.