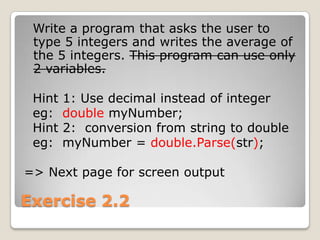
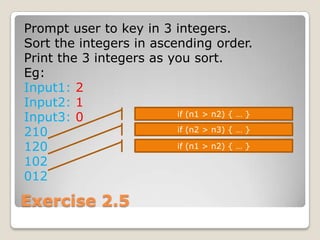
The document provides an introduction to variables in C#, including value types like integers and reference types like objects. It discusses defining and assigning values to variables, and differences between static and non-static classes. Examples show creating a basic console application in C# and getting input from the user via arguments or keyboard. Exercises guide practicing variable usage, type conversion, and writing simple programs to calculate averages and swap values.

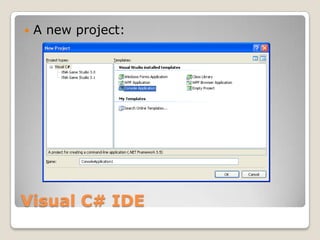








![Understanding Program.csusing System;namespace ConsoleApplication1{ class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { } }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spfchapter02-100416092320-phpapp01/85/SPF-Getting-Started-Console-Program-13-320.jpg)
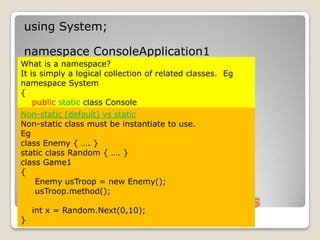
![Understanding Program.csusing System;namespace ConsoleApplication1{ class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { } }}What is a namespace?It is simply a logical collection of related classes. Egnamespace System{publicstatic class Console { …. // with properties and methods } class xxxx { …. // with properties and methods }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spfchapter02-100416092320-phpapp01/85/SPF-Getting-Started-Console-Program-14-320.jpg)
![Understanding Program.csusing System;namespace ConsoleApplication1{ class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { } }}What is a namespace?It is simply a logical collection of related classes. Egnamespace System{publicstatic class Console { …. // with properties and methods } class xxxx { …. // with properties and methods }}Access Modifiers – on class, its properties and methodsTypes: public, private, protectedpublic: Access is not restricted.private: Access is limited to the containing type.protected: Access is limited to the containing class or types derived from the containing class.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spfchapter02-100416092320-phpapp01/85/SPF-Getting-Started-Console-Program-15-320.jpg)
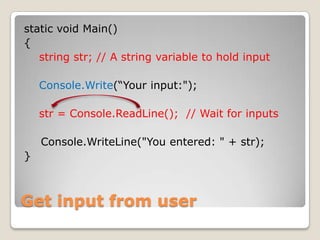
![Understanding Program.csusing System;namespace ConsoleApplication1{ class Program {static void Main(string[] args) { } }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spfchapter02-100416092320-phpapp01/85/SPF-Getting-Started-Console-Program-17-320.jpg)
![Understanding Program.csusing System;namespace ConsoleApplication1{ class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { } }}Inside a namespace, may contain internal namespace.namespace System{ namespace Data { …. // with classes & their properties and methods }}OR combine with a “.”Namespace System.Data{ …. // with classes & their properties and methods}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spfchapter02-100416092320-phpapp01/85/SPF-Getting-Started-Console-Program-18-320.jpg)


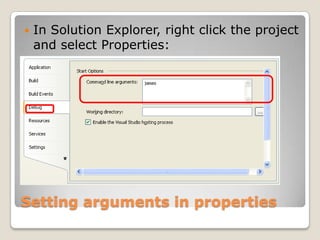
![Main(string[] args)string[] args // string array // with name argsGetting inputs from commandlineConsole.WriteLine("Hello " + args[0]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spfchapter02-100416092320-phpapp01/85/SPF-Getting-Started-Console-Program-22-320.jpg)




![Guided Hands onLaunch Visual Studio 2008 – C#Create a new console projectAdd the following line into main(..)Console.WriteLine("Hello " + args[0]);Add argument “James“Build and run](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spfchapter02-100416092320-phpapp01/85/SPF-Getting-Started-Console-Program-28-320.jpg)










