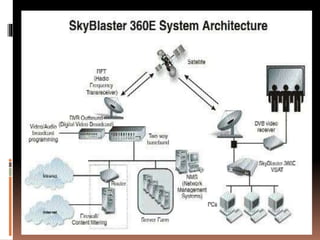
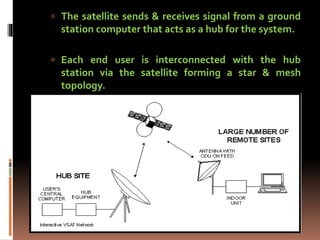
This document discusses different types of internet connectivity. It describes gateway access, dial-up connection, leased connection, DSL, cable modem connection, and VSAT. Gateway access provides limited internet access through a local network. Dial-up uses modems to connect over phone lines. Leased connections offer dedicated, high-speed access. DSL and cable modems utilize existing phone and cable infrastructure. VSAT uses small satellite terminals for connectivity.