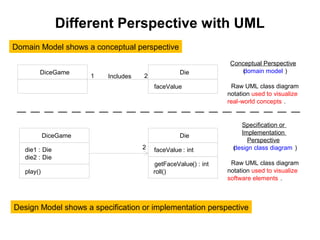
The document introduces UML (Unified Modeling Language) diagrams which are used to visualize, specify, construct and document software systems and business processes. It discusses the main UML diagram types - use case diagrams, class diagrams, interaction diagrams, state diagrams and activity diagrams. It also explains that UML can be used at different levels of detail from informal sketches to detailed blueprints and executable specifications. UML supports object-oriented software design and can model concepts, software specifications or implementations depending on the perspective.