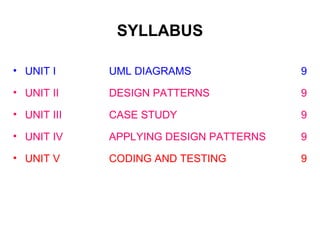
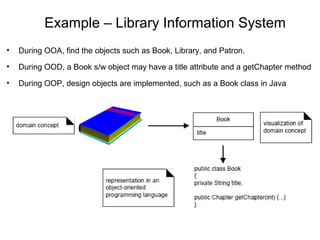
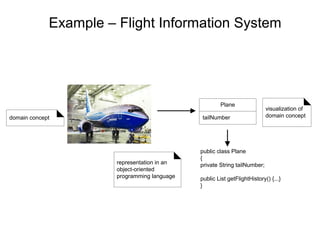
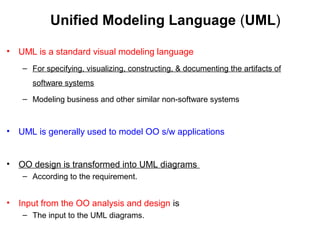
This document provides an overview of the CS6502 Object Oriented Analysis and Design course. The course covers UML design diagrams, design patterns, case studies, applying design patterns, and coding and testing. It discusses the objectives of learning OOAD skills, UML, mapping design to code, and testing techniques. Textbooks and reference materials are also listed. The syllabus outlines five units covering UML diagrams, design patterns, a case study, applying patterns, and coding and testing.