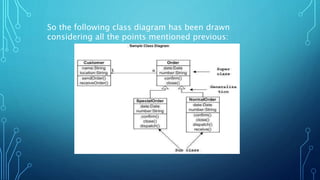
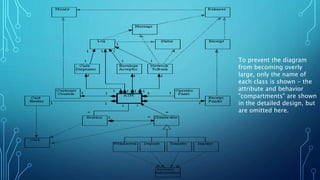
The document presents a class diagrams assignment submitted by a group to Sir Muhammad Tausif, detailing the significance of class diagrams in software engineering. It explains that class diagrams represent the static view of an application, facilitating modeling, visualization, and direct mapping to object-oriented programming languages. The document also emphasizes best practices for drawing class diagrams and illustrates these with examples, such as an ATM system.