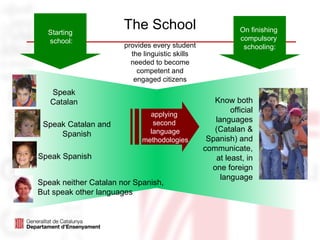
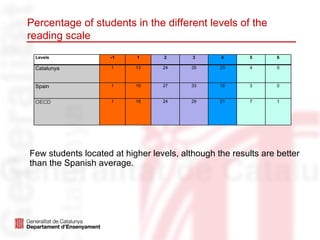
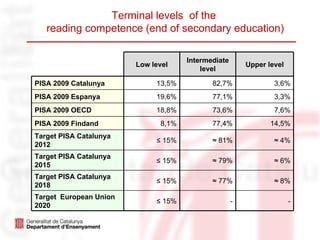
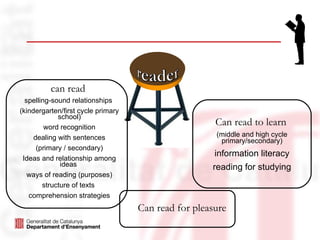
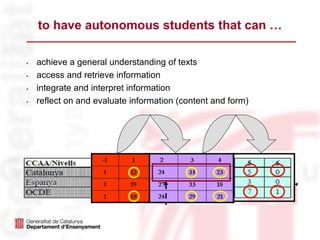
The document outlines the language education policies in the Catalan educational system, emphasizing the importance of teaching Catalan, Spanish, and at least one foreign language to promote multilingualism and social cohesion. It highlights initiatives to improve reading competencies as central to academic success and lifelong learning, alongside strategic educational goals to enhance both teaching methodologies and student engagement in reading. The plan aims to involve families and communities in fostering reading habits and to personalize the educational process for maximizing student performance.