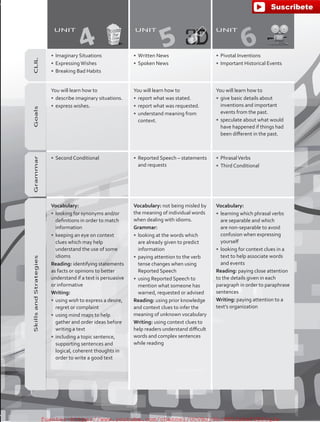
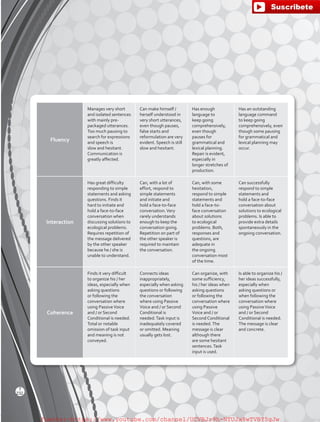
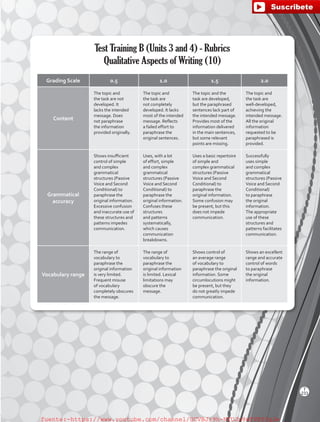
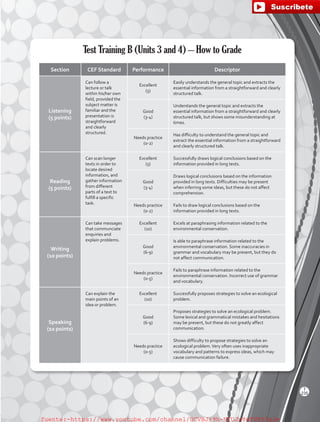
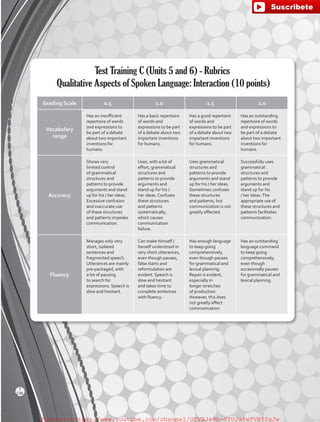
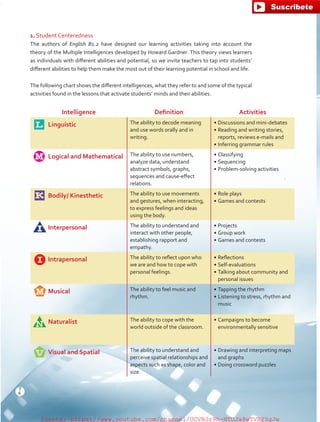
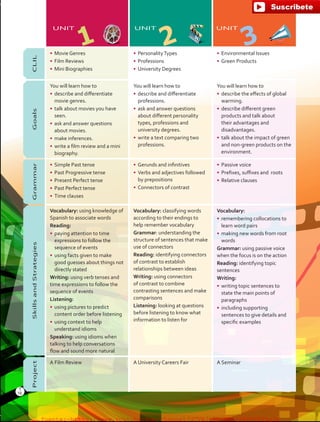
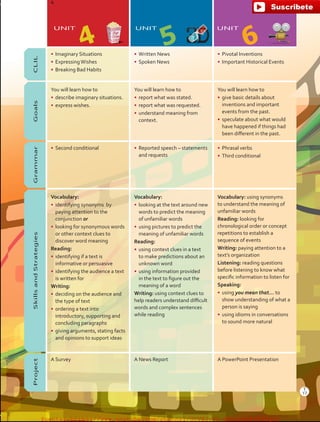
The document outlines the English B1.2 teaching series, aimed at high school students, focusing on fostering language skills through diverse activities that integrate culture, values, and cognitive development. It emphasizes a student-centered approach, with curricula designed around various intelligences and practical applications of language in real-life contexts. Additionally, it details lesson planning, structured around warm-ups, presentations, practice, and applications to enhance student engagement and learning outcomes.






![3. Lesson 3 Reading andWriting
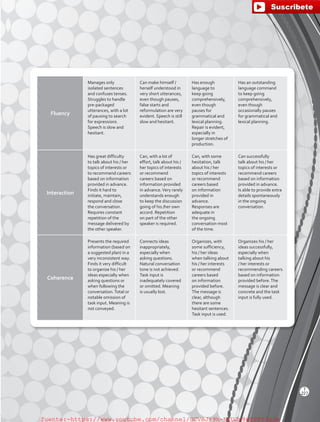
Lesson 3 is entirely devoted to working on the reading process which is subdivided into Pre-Reading,While-Reading
and Post-Reading.These subdivisions are aimed at making students strategic and effective readers.
Pre-Reading Activities
ThepurposeofPre-Readingactivitiesistohelpstudents
get ready to read a text and be better prepared to
understand it. When students preview vocabulary, use
prior knowledge and predict, they feel more motivated
and connected to the text.
While-Reading Activities
While-Readingactivitiesaredesignedtohelpthereader
deal with the text while he or she is actively involved in
comprehension, using strategies like: stopping to think,
re-reading, asking themselves questions, visualizing,
making inferences, underlining or using context clues to
work out meaning.
Post-Reading Activities
Students need to apply some Post-Reading strategies
to achieve a deeper understanding of the text. For this
purpose, they can ask questions, make inferences,
find the main idea, summarize, and hold mini-debates
or discussions. These activities are also aimed at
enhancing readers’ ability to think about what they
read and take a critical position.
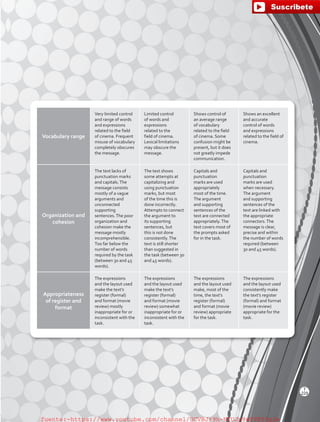
This section also provides students with writing models
and strategies. The idea is to help them determine
writing elements and give form to their ideas in an
organized way. Different strategies help students
generate, organize, connect, rephrase, and develop
their ideas effectively.
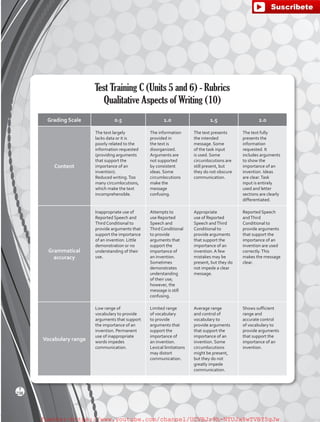
Reading Strategy
Identifying text purpose
Is the text trying to inform or persuade you?The text
type will help determine its purpose and content.
Informative texts try to provide as much factual
information as possible and support its arguments.
Persuasive texts provide some information, but also
try to convince the audience of something by stating
opinions.
Identifying the audience
Determine who the text is written for. This influences
how the content is expressed.
How many times have you said or heard someone say,
“I wish I could stop biting my nails”, or “I wish I didn't
procrastinate so much? Bad habits are extremely
common and people all around the world wish they could
break their bad habits. So, what exactly is a habit? A
habit is something you do consistently, over and over again
. It generally doesn't require thinking. A bad habit is
simply a behavior pattern which is considered negative.
Common examples include: procrastination, fidgeting,
overspending, nail-biting, and so forth. According to
some psychologists, breaking bad habits should be one of
your top priorities in life . At first, it may be challenging
to break a bad habit.You will need a lot of self-discipline,
but it will get easier. Here are 5 easy steps for changing
bad habits:
Key Expressions
Cold turkey: the sudden and complete cessation
of a bad habit
Fidgeting: small movements through nervousness
or impatience
Do the trick: bring the desired results
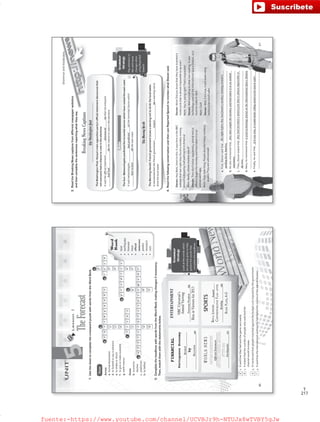
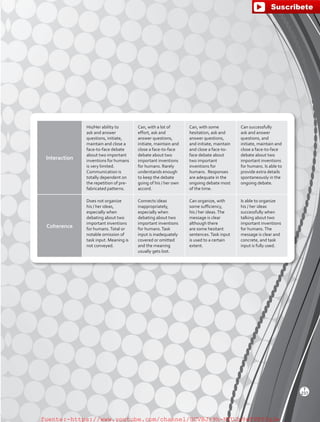
1. Conduct a survey of your classmates to find out how many people have the following bad habits.
Lesson 3
BreakingBadHabits
Bad Habit biting your fingernails
spending more money
than you should
procrastinating
having any other bad
habit you want to change
Number of
Classmates
2. Read and determine if the italicized sentences
are facts [F] or opinions [O]. Then, answer the
questions.
Awareness: You must become aware of your habits .
What is this habit exactly? How is this bad habit affecting
you? How is it affecting others? For example, overspending
might also have negative effects on your family.
Wanting to Change: You must decide that breaking the
bad habit is a worthy goal. You must be convinced that a
change is worth the effort involved.
Commitment:You must be determined to do whatever it
takes to break the bad habit so that you can be in better
control of your life. You have to make a decision that “no
matter what” you will do what is required to change the
habit.
F
52
Writing Strategy
Who is the text written for?Will it be persuasive orinformative?
Order your text into anintroductory paragraph,supporting paragraphs anda conclusion.
Remember to givearguments, stating factsand opinions to supportyour ideas.
4. Think of a bad habit that you have and write a short text on how to break it.
Introduction
(What is the bad habit?)
Supporting paragraph 1(Negative influences)
Supporting paragraph 2(How to break the habit)
Conclusion
(Your commitment to breaking the bad habit)
• Analyze the answers collected in thesurvey, and represent them on a graph
showing percentages. Organize theresults for a PowerPoint presentation.
E.g. 65% of the people interviewed said
they would build a shelter using trees and
build a fire for warmth.
Project Stage 3
Reading and Writing
Consistent Action: It is important to focus on changing just
one habit at a time. Take consistent daily actions to break
the bad habit. Try doing the process one step at a time rather
than trying to do it all at once . However, it is important
to note that everyone is different and some people are able
to change a habit by going cold turkey while others prefer a
gradual change .
Perseverance: Breaking bad habits is not easy. There might
be times when you question whether it is worth it . You
may say to yourself that breaking the bad habit is too
difficult. You need to regularly visualize the rewards for
following through and the costs of not following through on
breaking bad habits. Get support from others who also want
to make changes in their lives and read about people who
have been successful in breaking bad habits.Now, you are armed with a 5-step process for breaking bad
habits or other conditions that require changing. If you
have an addiction to something such as video games, these
steps alone may not be enough.You may require additional
professional help or a support group, but for most cases this
5-step process will do the trick!
a. You need self-discipline tobreak a bad habit.
true
false
doesn't mention
b. Bad habits are not verycommon.
true
false
doesn't mention
c. Bad habits are morecommon than good habits.
true
false
doesn't mention
3. Go over the reading strategy and answer the questions below.
a. What type of text is this? Give reasons for your answer.
an informative text
a persuasive text
both
Why?
b. Who is the text written for? Give reasons for your answer.
general public
educators
scientists
Why?
53
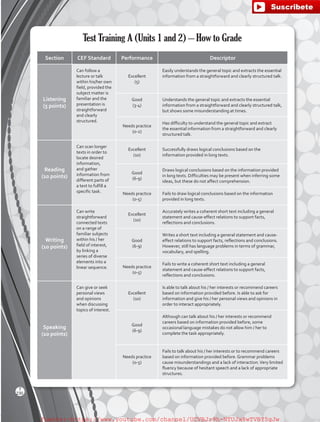
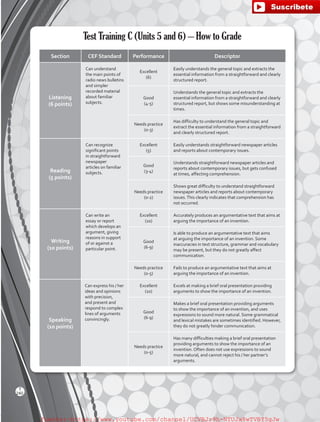
11
T
11
T
fuente:-https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCVBJr9h-NTUJx8wTVBY5gJwfuente:-https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCVBJr9h-NTUJx8wTVBY5gJw](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/libroresueltoenglishb1-180505195858/85/Book-English-Techaer-B1-2-compressed-9-320.jpg)


























































































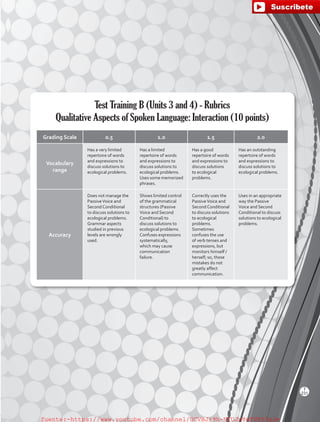
![Reading Strategy
Identifying text purpose
Is the text trying to inform or persuade you?The text
type will help determine its purpose and content.
Informative texts try to provide as much factual
information as possible and support its arguments.
Persuasive texts provide some information, but also
try to convince the audience of something by stating
opinions.
Identifying the audience
Determine who the text is written for.This influences
how the content is expressed.
How many times have you said or heard someone say,
“I wish I could stop biting my nails”, or “I wish I didn't
procrastinate so much? Bad habits are extremely
common and people all around the world wish they could
break their bad habits. So, what exactly is a habit? A
habit is something you do consistently, over and over again
. It generally doesn't require thinking. A bad habit is
simply a behavior pattern which is considered negative.
Common examples include: procrastination, fidgeting,
overspending, nail-biting, and so forth. According to
some psychologists, breaking bad habits should be one of
your top priorities in life .At first, it may be challenging
to break a bad habit.You will need a lot of self-discipline,
but it will get easier. Here are 5 easy steps for changing
bad habits:
Key Expressions
Cold turkey: the sudden and complete cessation
of a bad habit
Fidgeting: small movements through nervousness
or impatience
Do the trick: bring the desired results
1. Conduct a survey of your classmates to find out how many people have the following bad habits.
Lesson 3
BreakingBadHabits
Bad Habit biting your fingernails
spending more money
than you should
procrastinating
having any other bad
habit you want to change
Number of
Classmates
2. Read and determine if the italicized sentences
are facts [F] or opinions [O]. Then, answer the
questions.
Awareness: You must become aware of your habits .
What is this habit exactly? How is this bad habit affecting
you? How is it affecting others? For example,overspending
might also have negative effects on your family.
Wanting to Change: You must decide that breaking the
bad habit is a worthy goal. You must be convinced that a
change is worth the effort involved.
Commitment:You must be determined to do whatever it
takes to break the bad habit so that you can be in better
control of your life. You have to make a decision that “no
matter what” you will do what is required to change the
habit.
F
52
O
F
Answers may vary.
fuente:-https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCVBJr9h-NTUJx8wTVBY5gJwfuente:-https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCVBJr9h-NTUJx8wTVBY5gJw](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/libroresueltoenglishb1-180505195858/85/Book-English-Techaer-B1-2-compressed-108-320.jpg)