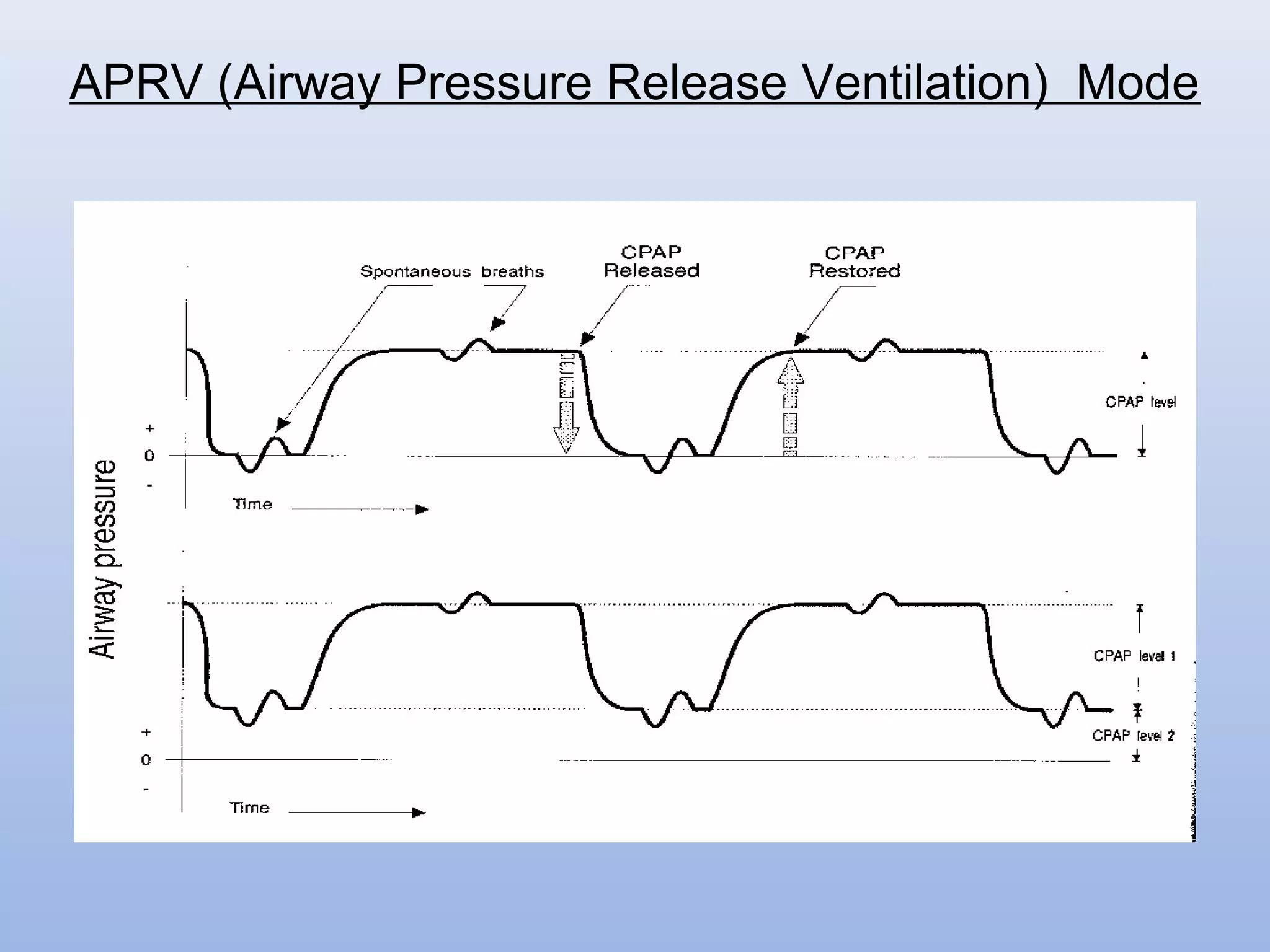
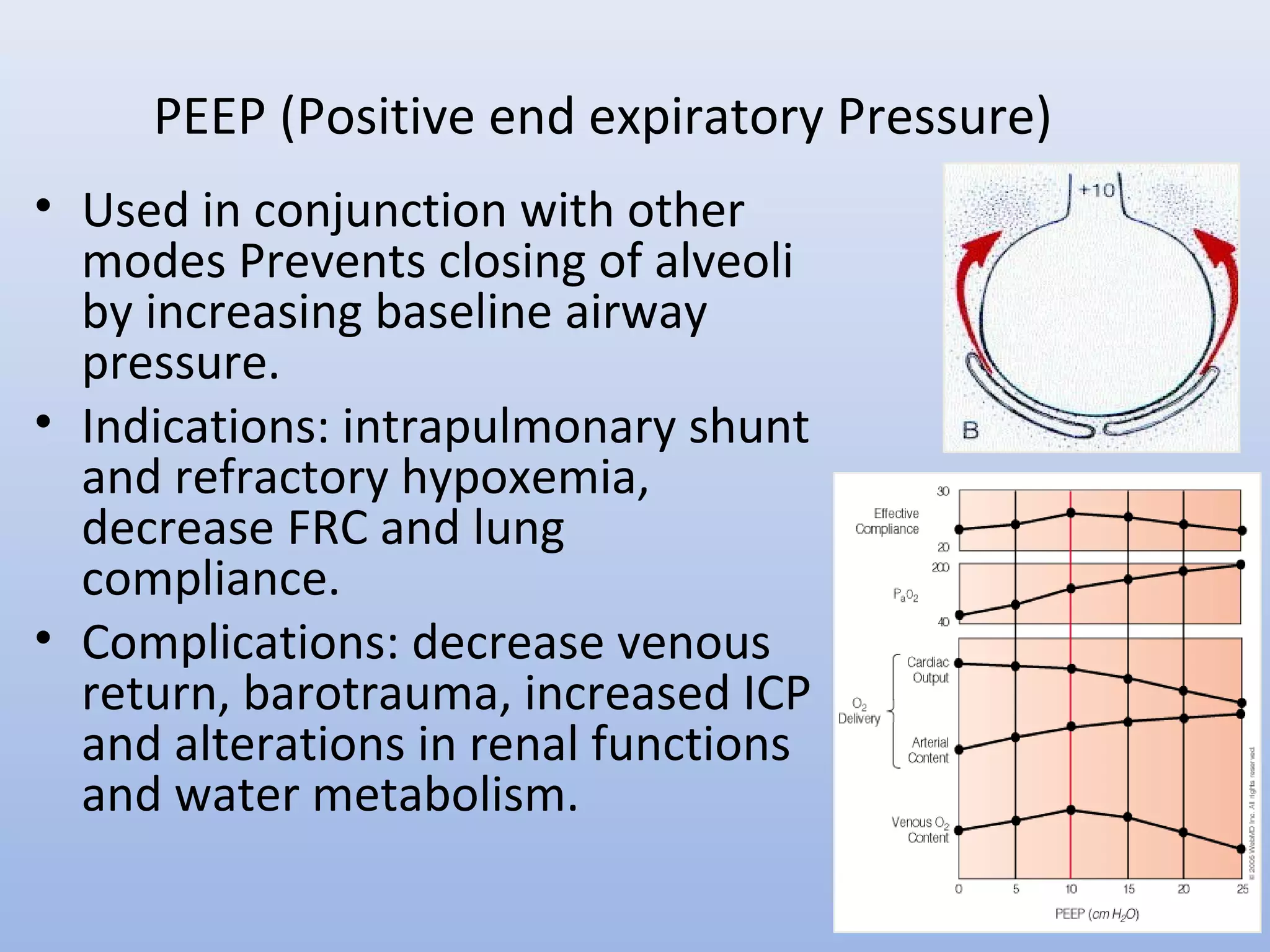
Mechanical ventilation is used widely in patient care from initial injury through hospital transport, surgery, intensive care, and intermediate care. Various modes of ventilation have been developed to support patient breathing including controlled mandatory modes like CMV that do not allow spontaneous breathing and supported modes like PSV that augment patient effort. Key parameters monitored include pressures, volumes, and gas exchange. Complications can include barotrauma, decreased cardiac output, and pneumonia. Weaning protocols gradually reduce ventilator support as the underlying condition improves and respiratory function is adequate.