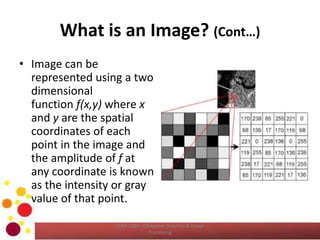
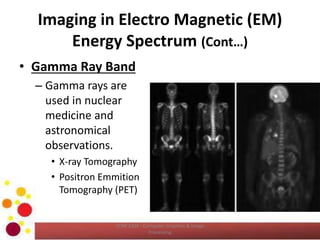
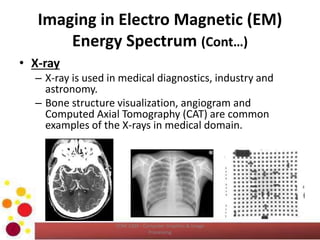
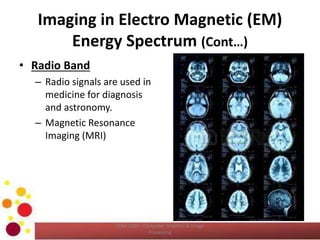
The document outlines an introductory lecture on computer graphics, image processing, and computer vision, focusing on the definition of images, the significance of digital image processing, and the role of computer vision in extracting information from visual data. It discusses various image sources, particularly within the electromagnetic energy spectrum, and emphasizes the components of image processing systems. Learning outcomes include the ability to describe and compare concepts related to images and their processing applications.