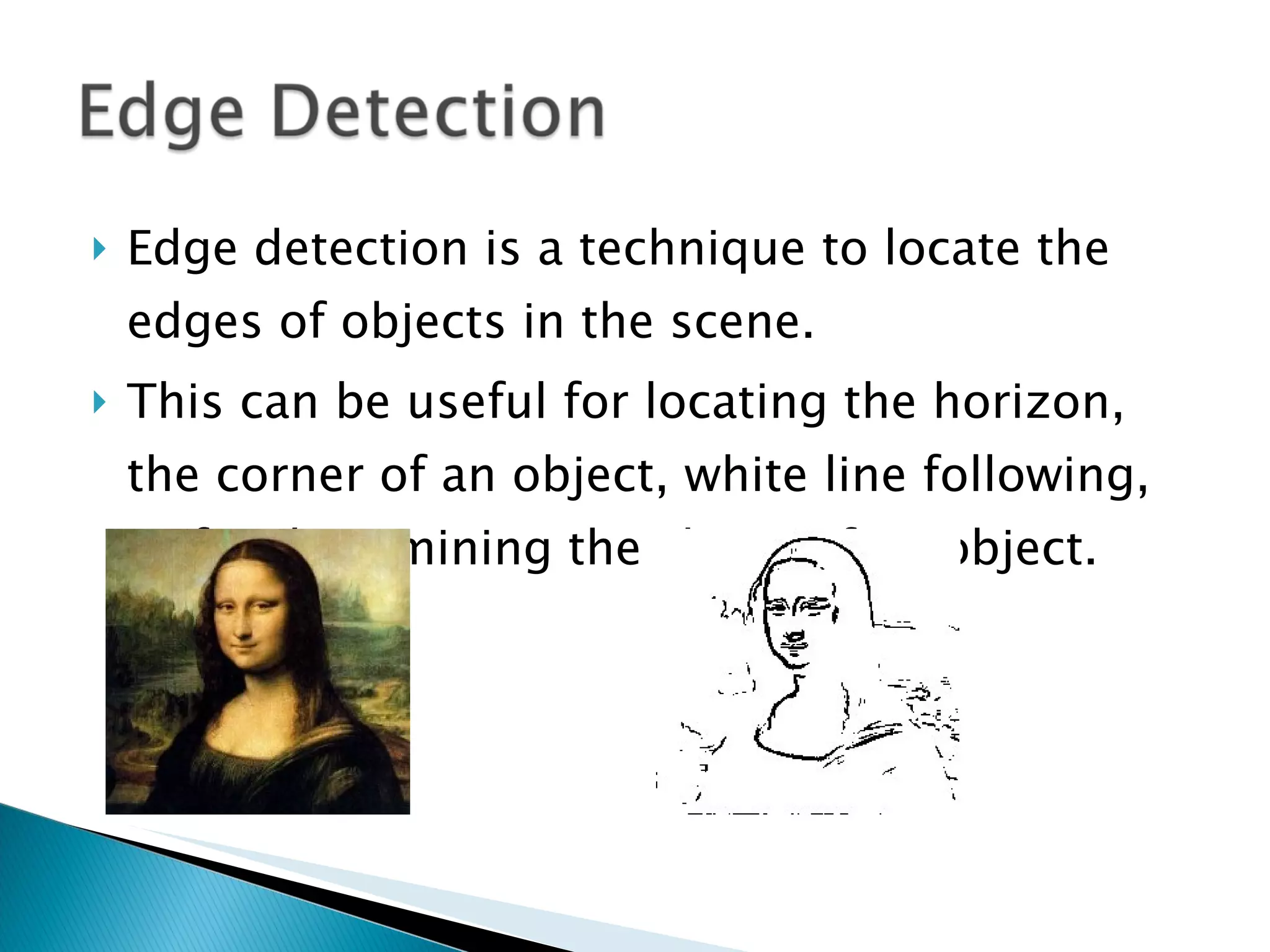
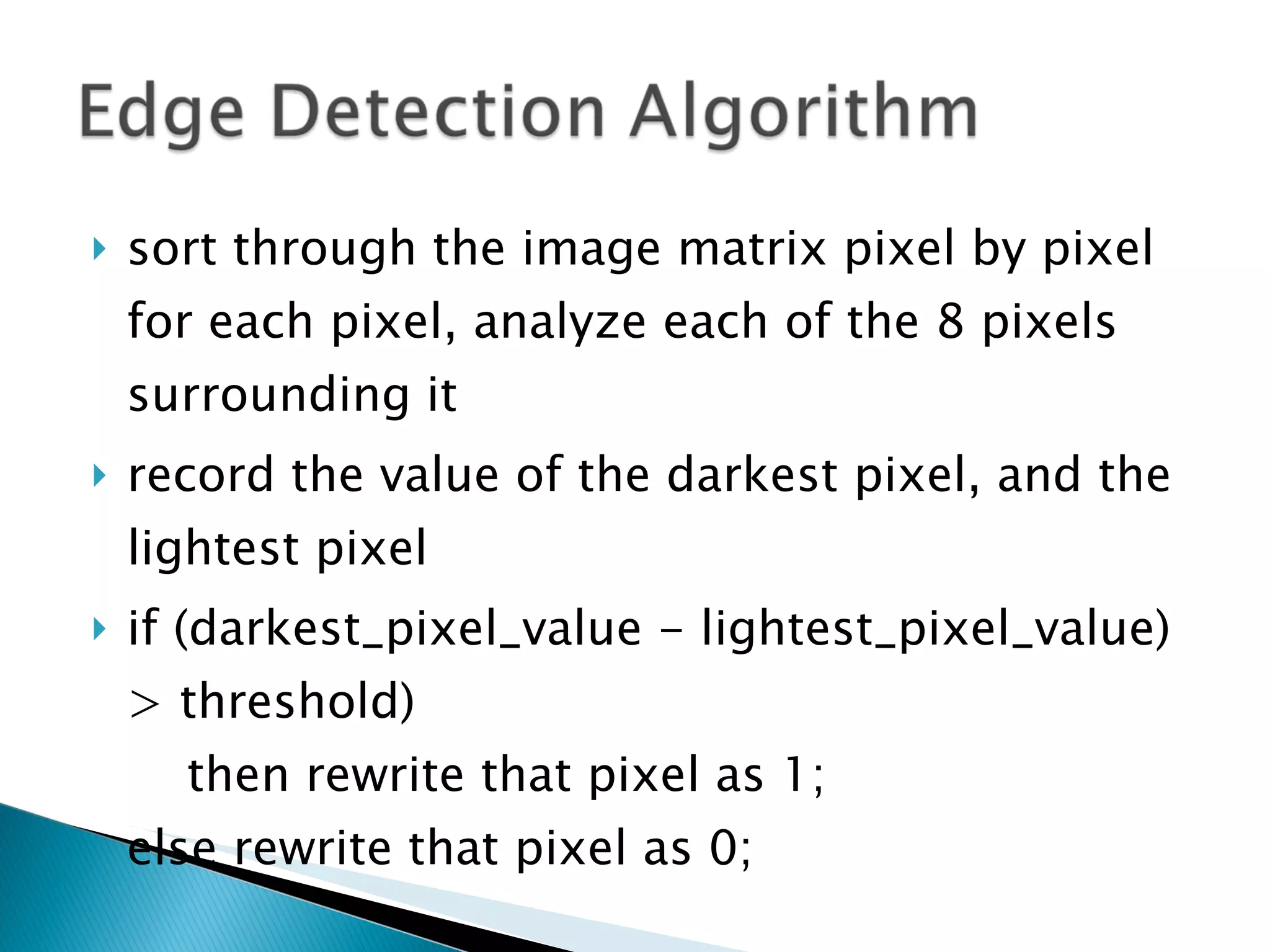
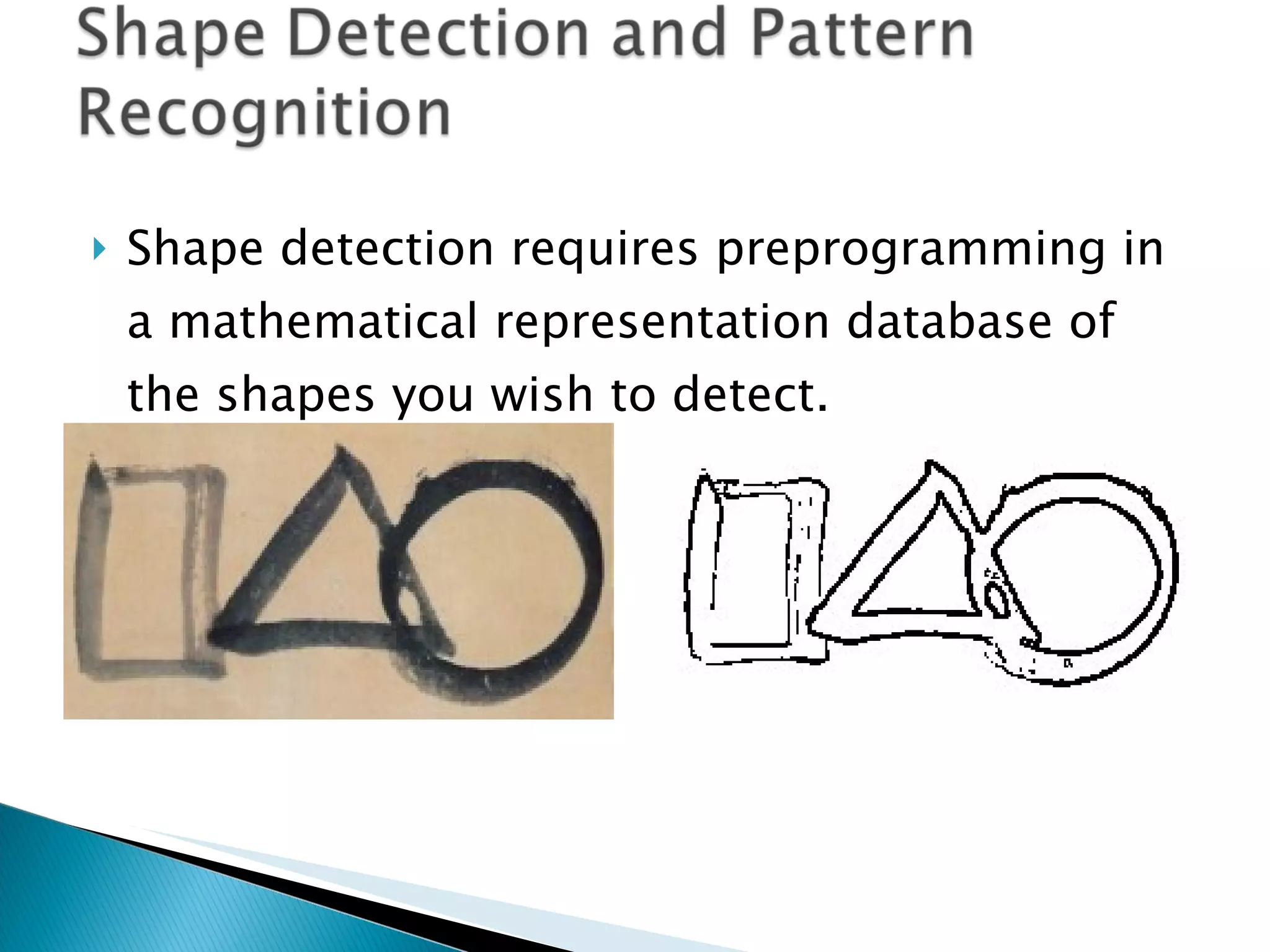
Computer vision analyzes real-world images while machine vision uses simplified images. Edge detection locates object edges by analyzing pixel values. Shape detection identifies shapes by counting continuous edges and measuring angles between lines. Motion detection compares pixel positions between frames to detect motion if the pixel mass changes significantly. Optical flow analyzes pixel intensity changes between images to determine motion vectors without identifying objects. Aerial robot altitude can be estimated from a downward camera by analyzing pixel velocity, as higher altitude results in slower apparent ground motion.