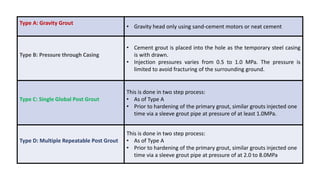
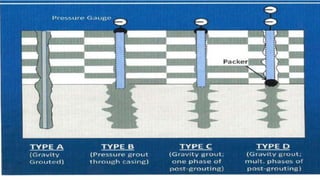
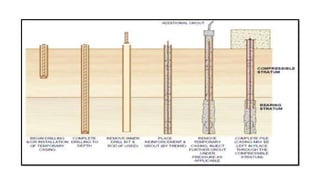
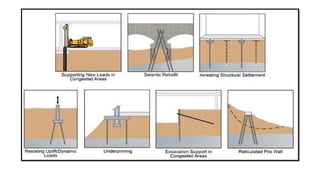
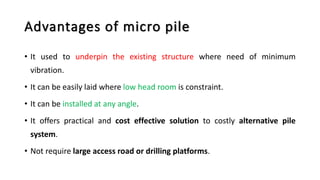
Micro-piles, developed in the 1950s in Italy, are small diameter, drilled, and grouted piles used to support foundations against static and seismic loads, especially in challenging conditions like uneven settlement and restricted spaces. The document discusses various construction types, applications, and advantages of micro-piles, including their use in underpinning damaged structures and providing slope stabilization. A case study illustrates the implementation of micro-piles for bridge foundations in a remote, glacier-prone area where traditional foundation methods were impractical.