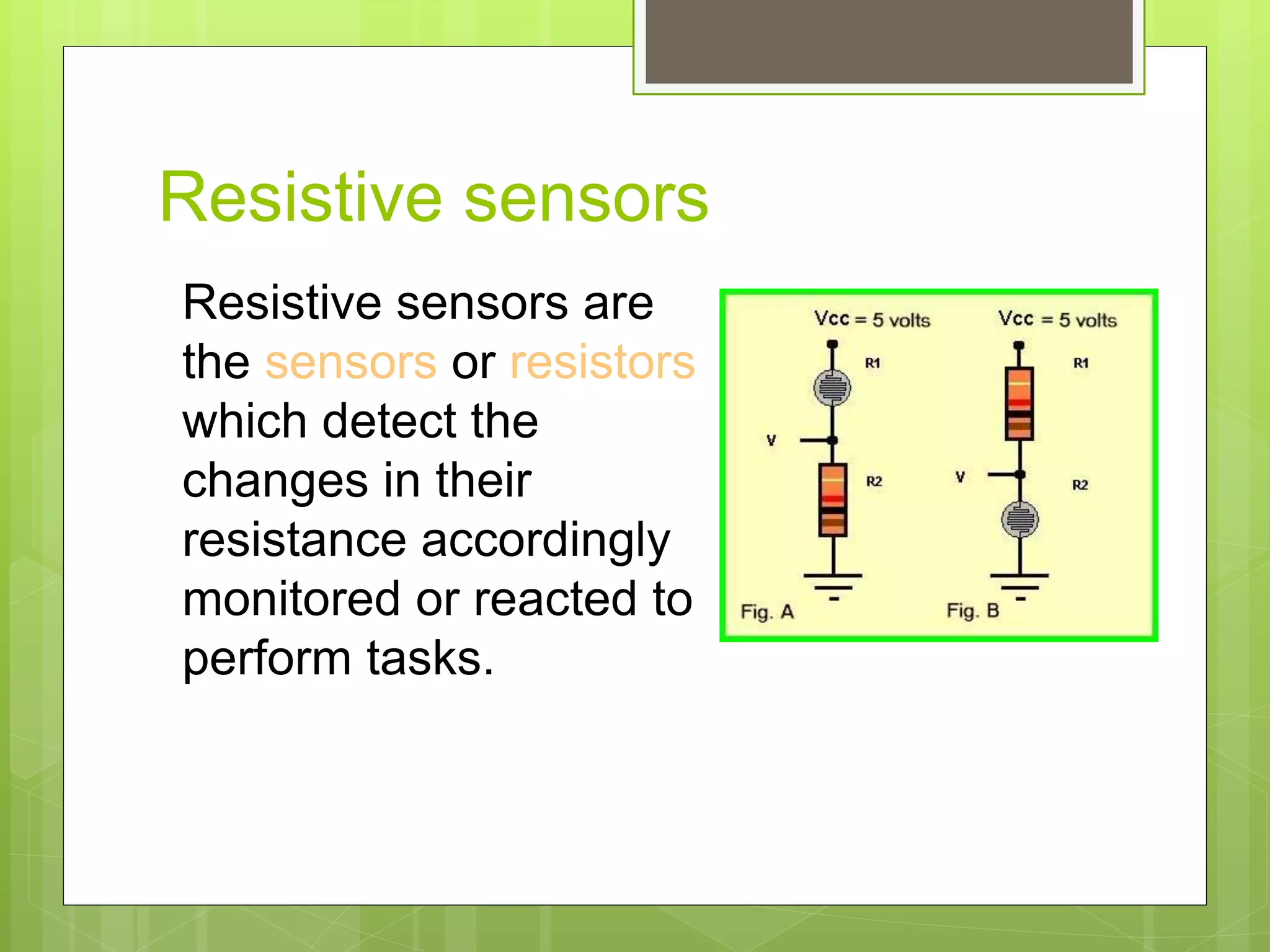
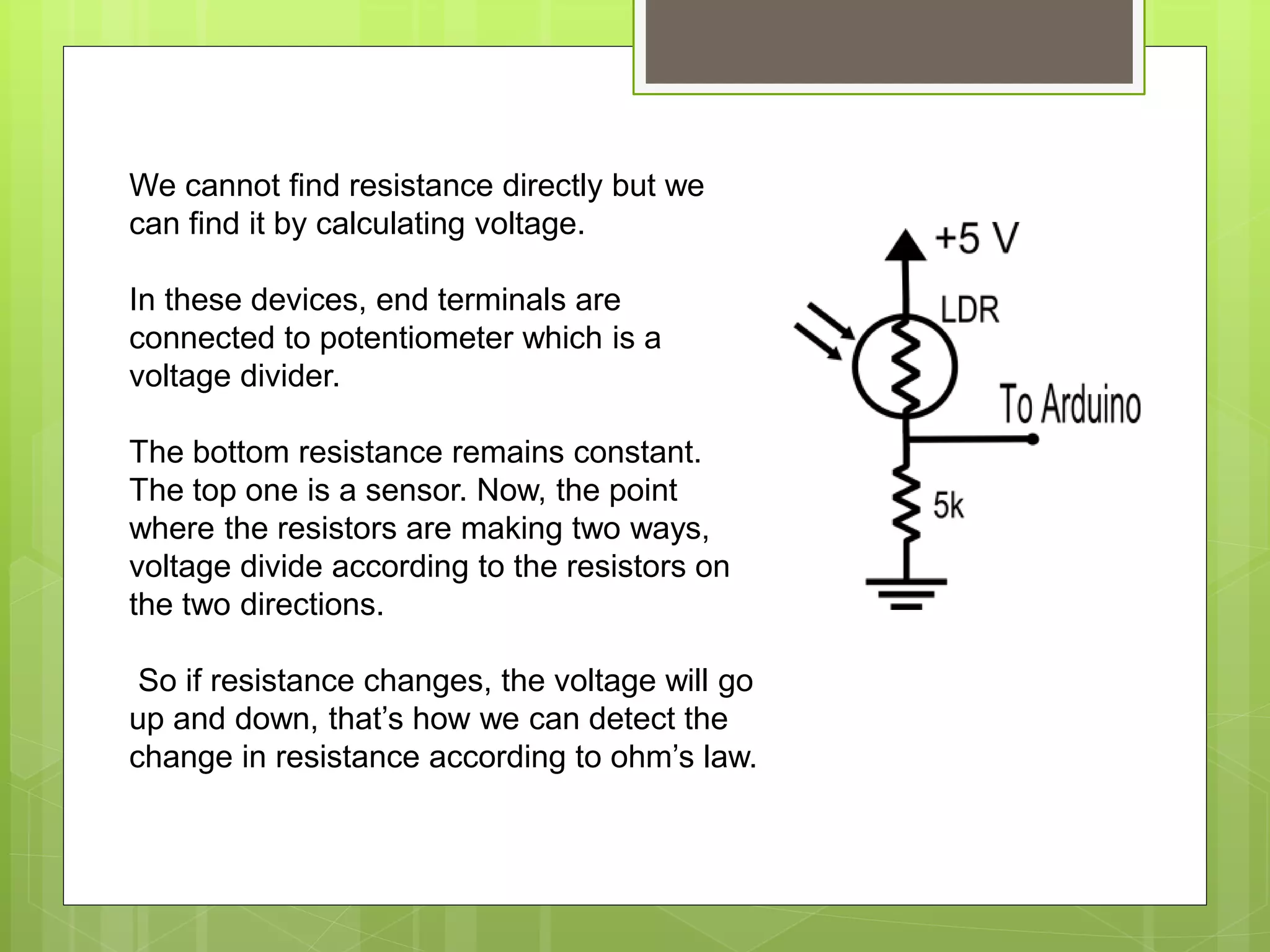
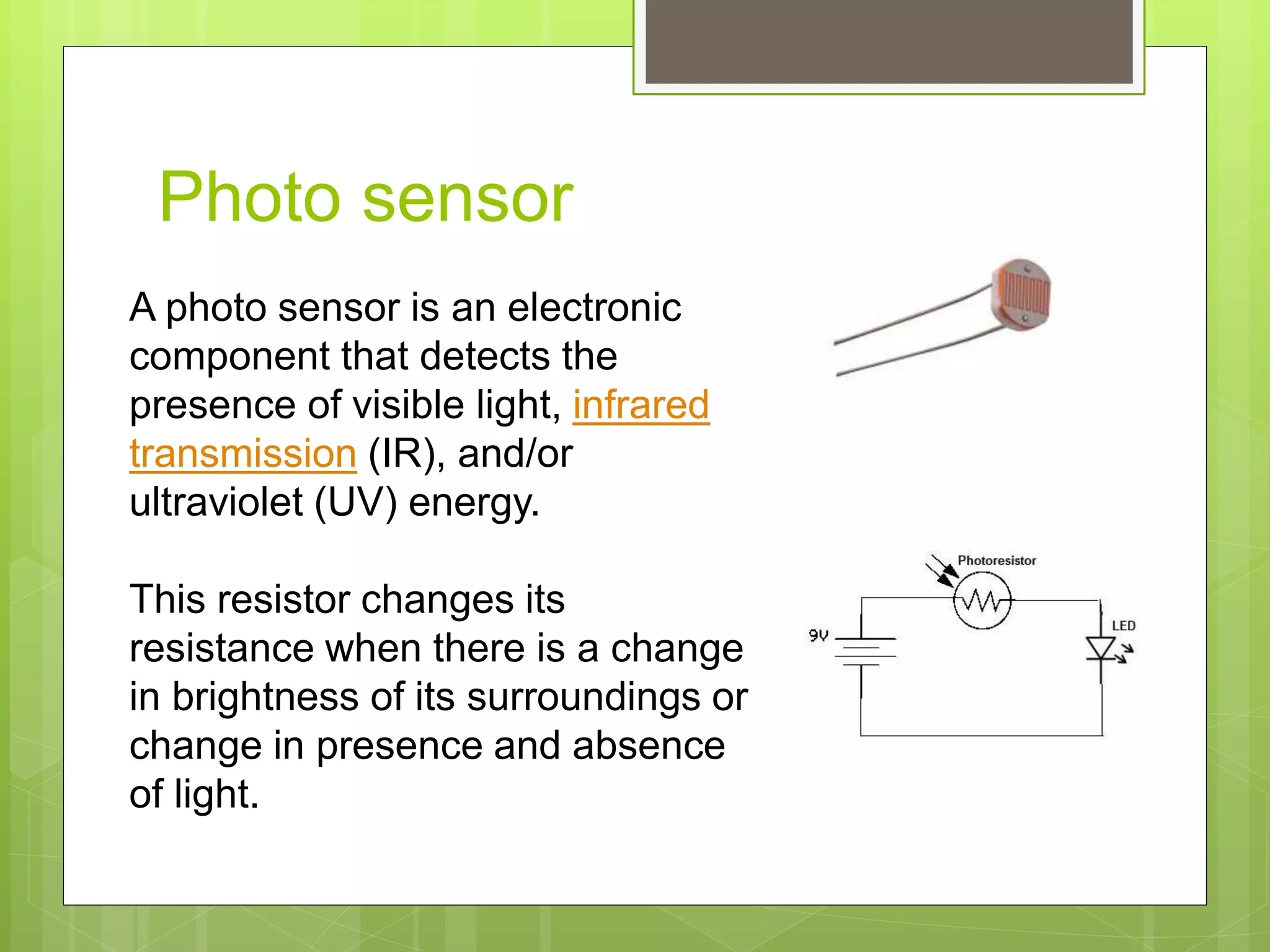
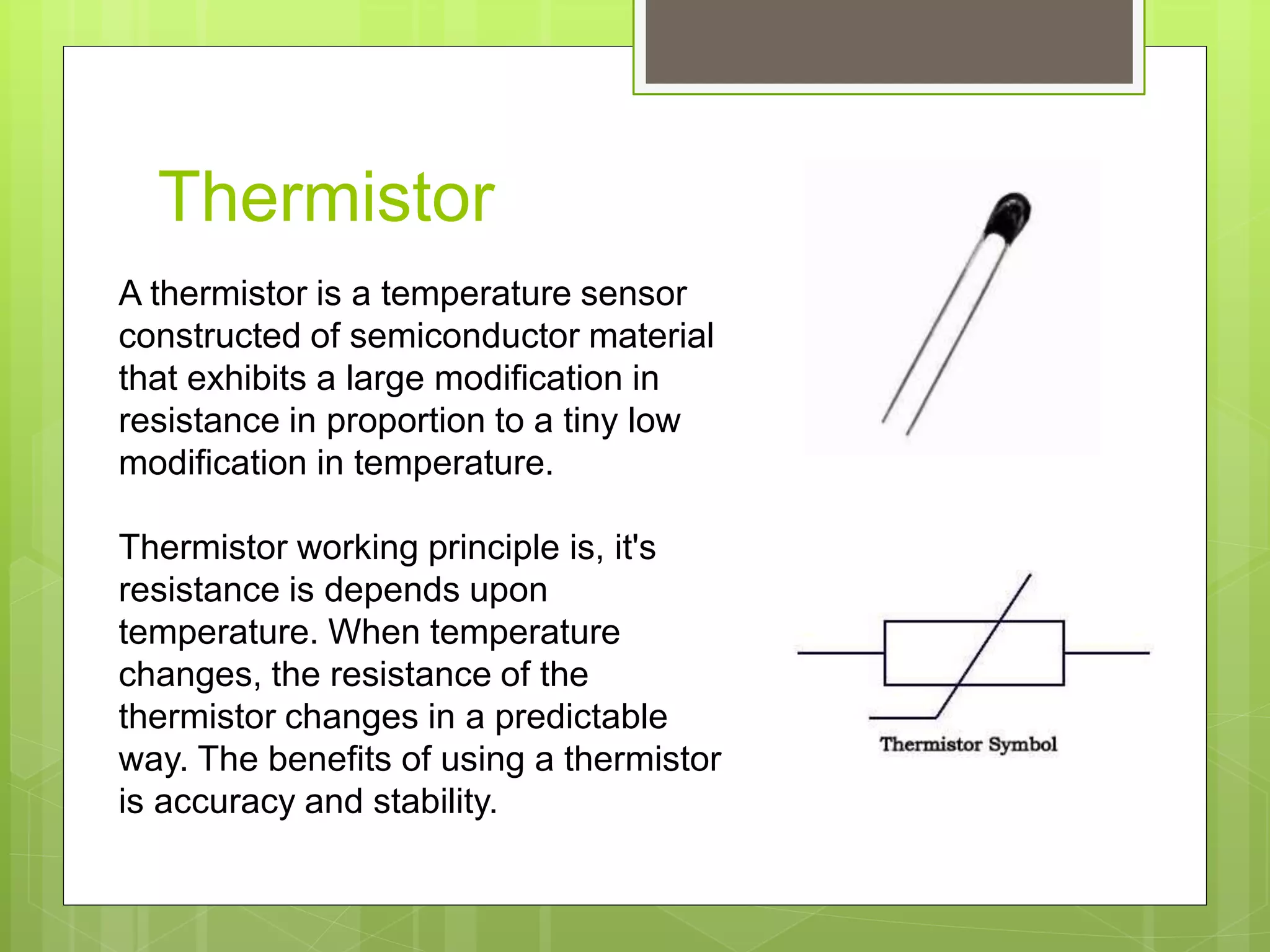
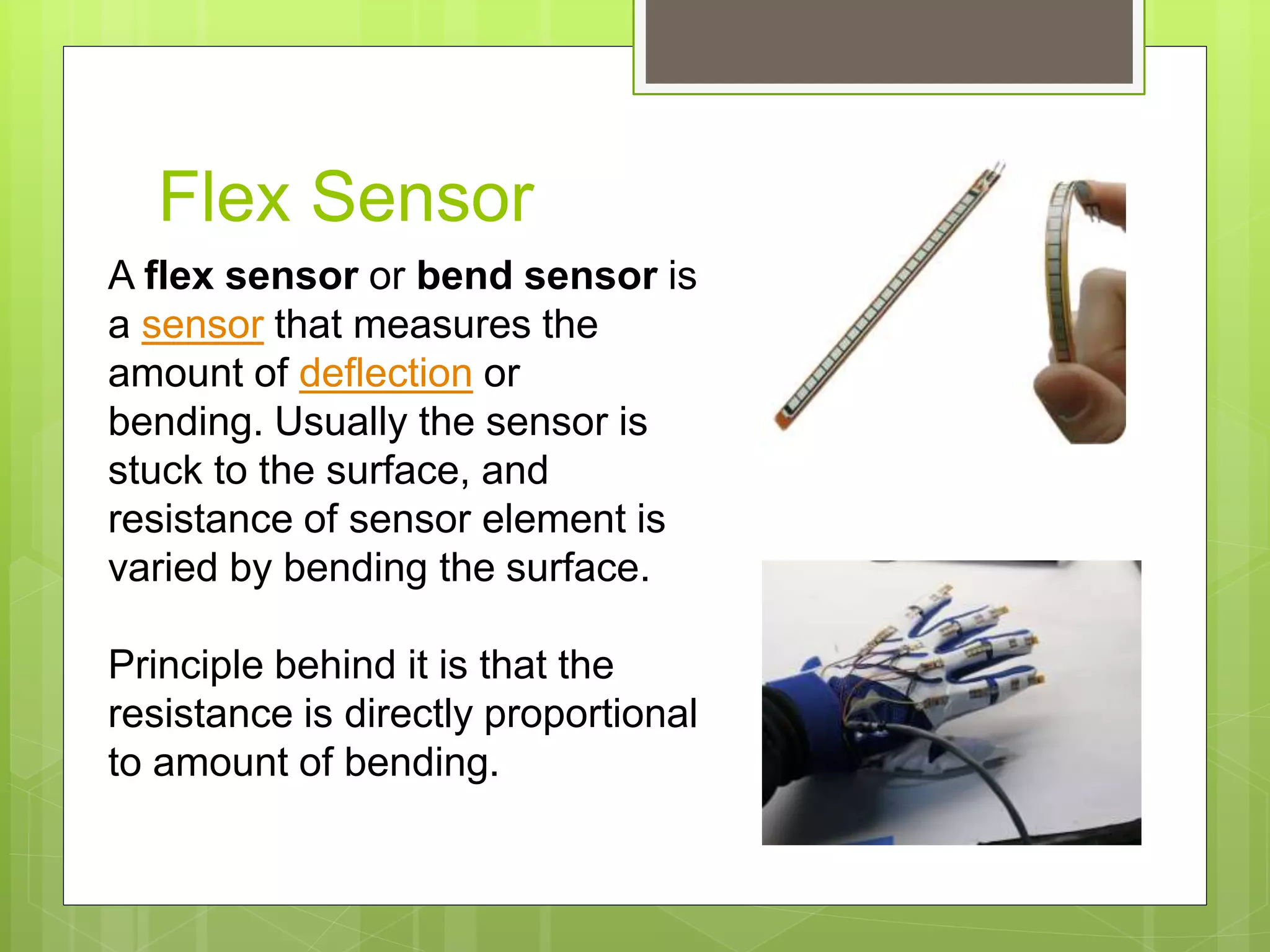
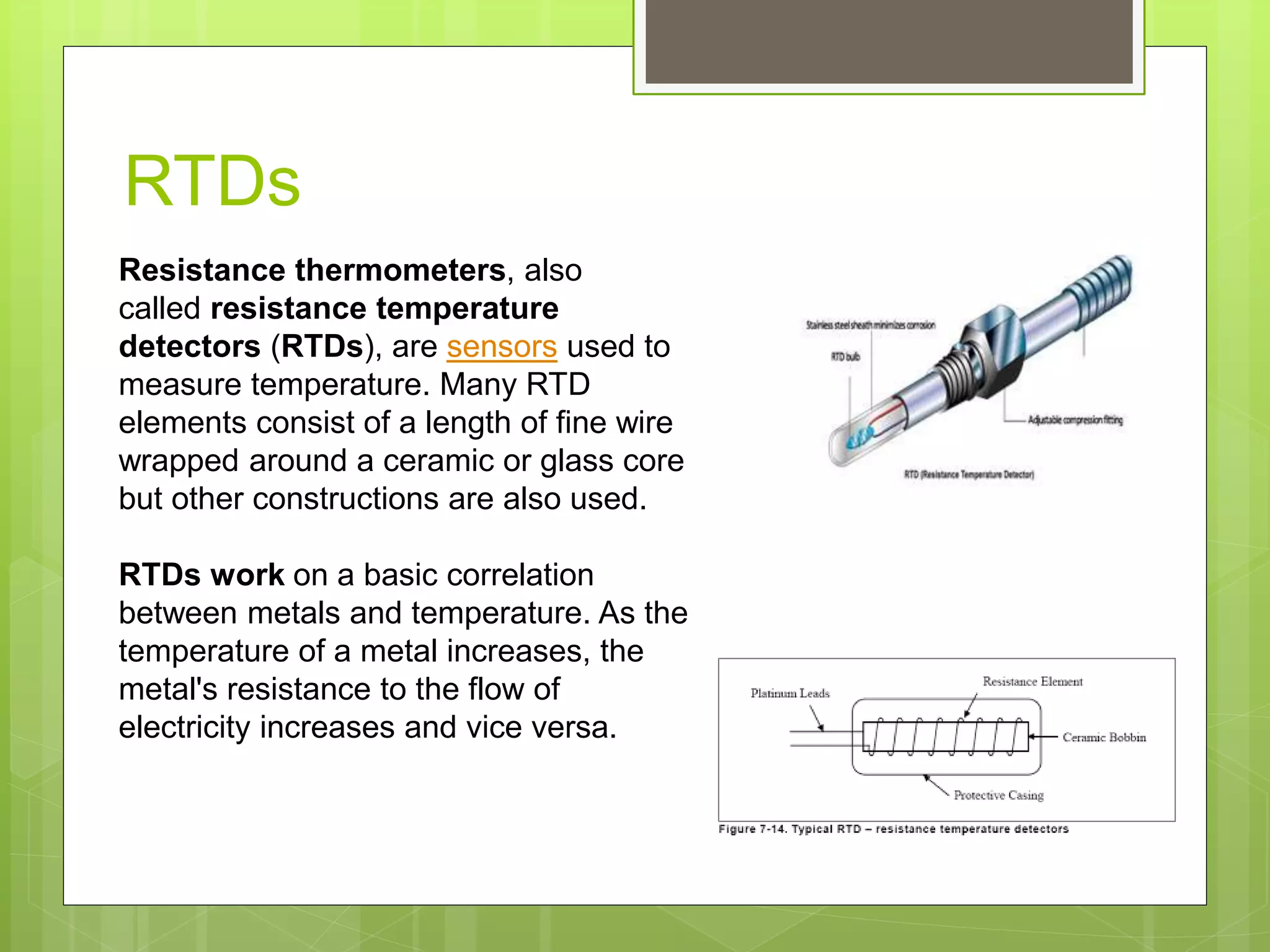
This document discusses resistive sensors and their principle of operation. Resistive sensors detect changes in their resistance which can correspond to changes in factors like temperature, light intensity, pressure, or bending. The document provides examples of common resistive sensors like thermistors, photoresistors, flex sensors, and resistance temperature detectors (RTDs). It explains that these sensors detect environmental changes by measuring changes in electrical resistance through voltage dividers and relating the resistance changes to the measured property based on Ohm's law.