Embed presentation
Downloaded 34 times
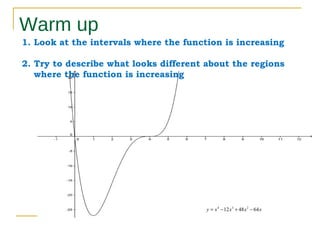





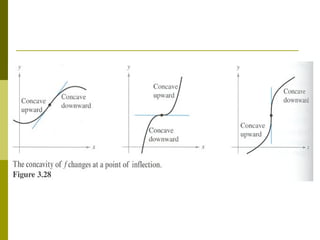



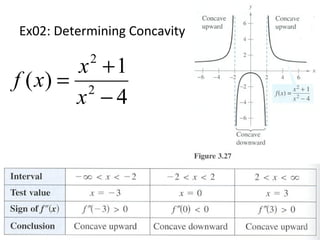
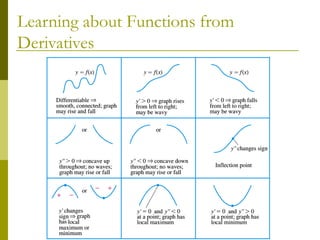

This document discusses using concavity and derivatives to understand the behavior of functions. It defines concavity as: - Concave up when the second derivative is positive, meaning the graph acceleration is positive. - Concave down when the second derivative is negative, meaning the graph acceleration is negative. Inflection points occur when the concavity changes, meaning the second derivative equals zero or is undefined. The document provides examples of using derivatives to determine concavity and find inflection points of functions.











