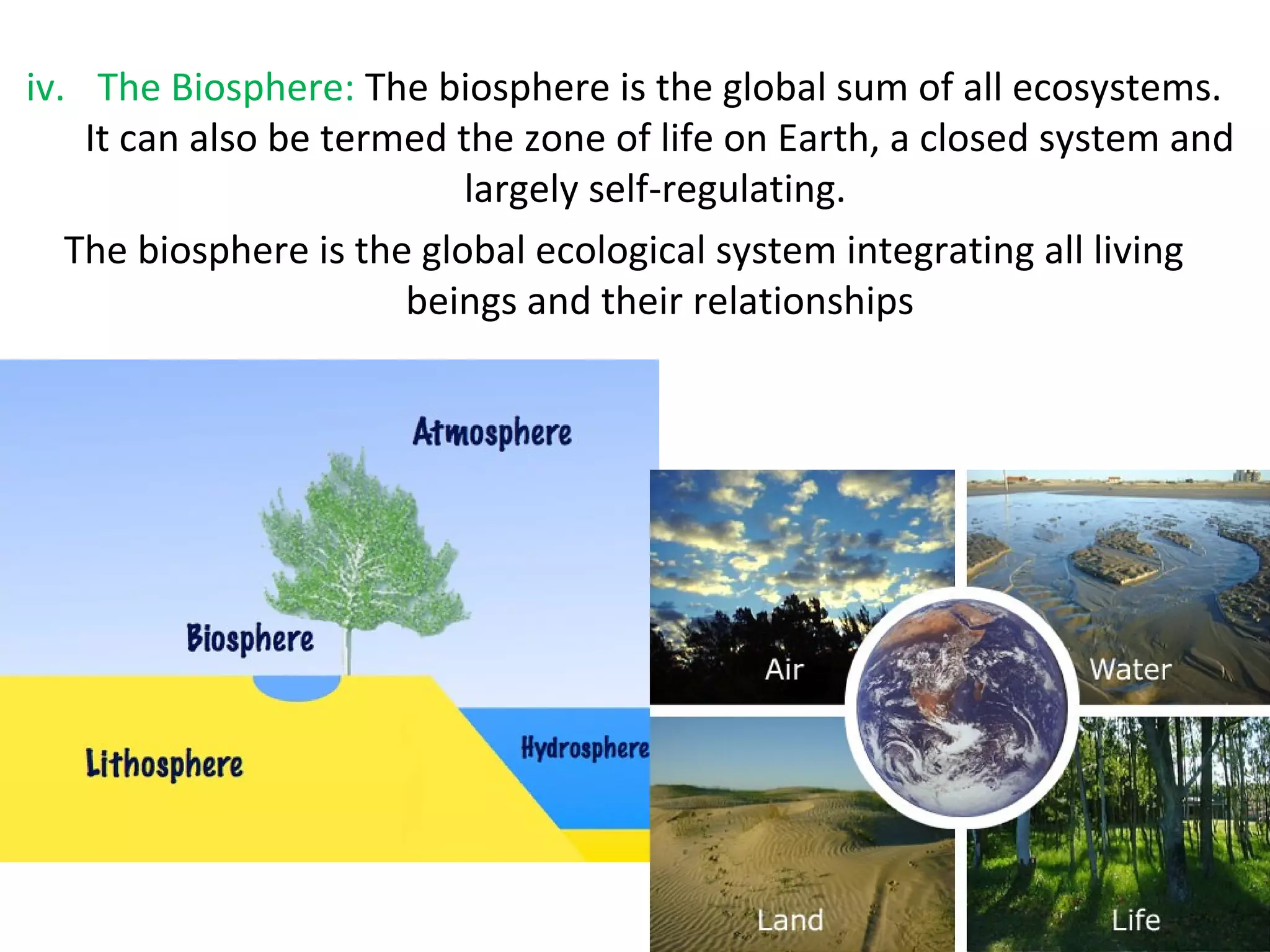
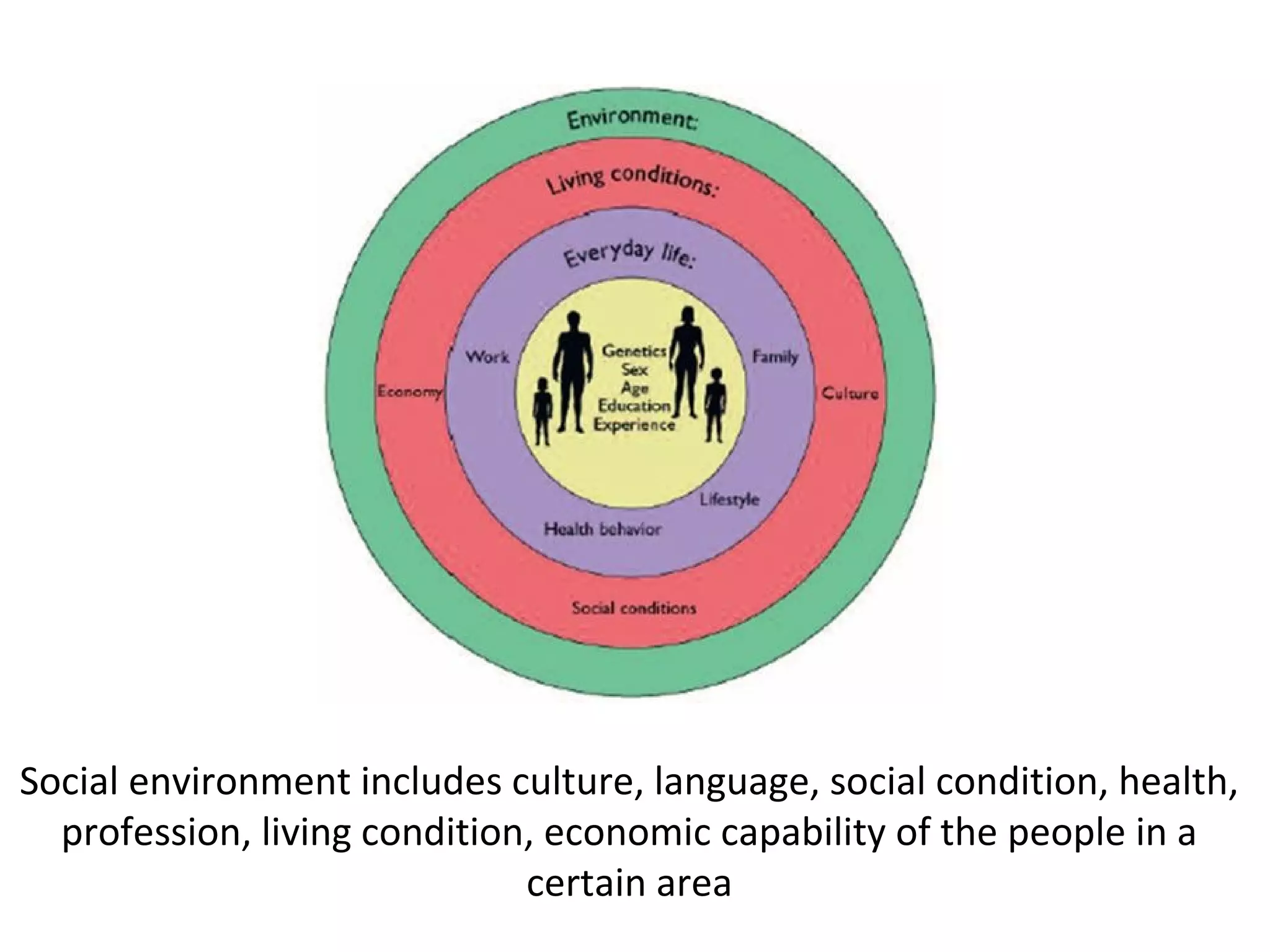
This document discusses different types of environments. It defines environment as the sum of all surroundings, including natural forces and living things. Environments can be categorized as built, natural, or social. The built environment refers to human-made surroundings like buildings and infrastructure. The natural environment includes living and non-living things found naturally on Earth, like various rock layers, bodies of water, the atmosphere, and biosphere. The social environment is the physical and cultural setting where people interact, including factors like culture, communication, social status, health, and economic conditions.