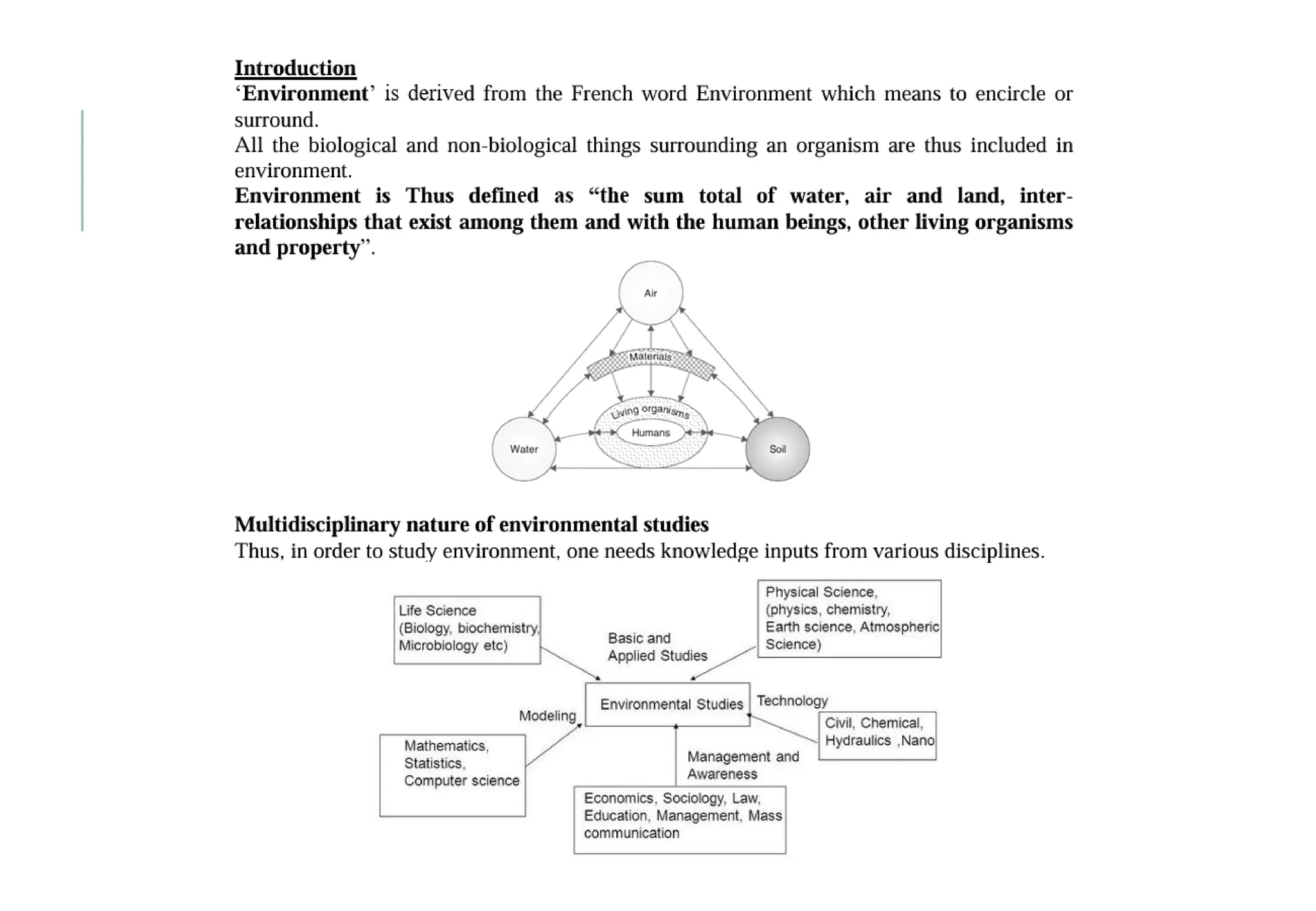
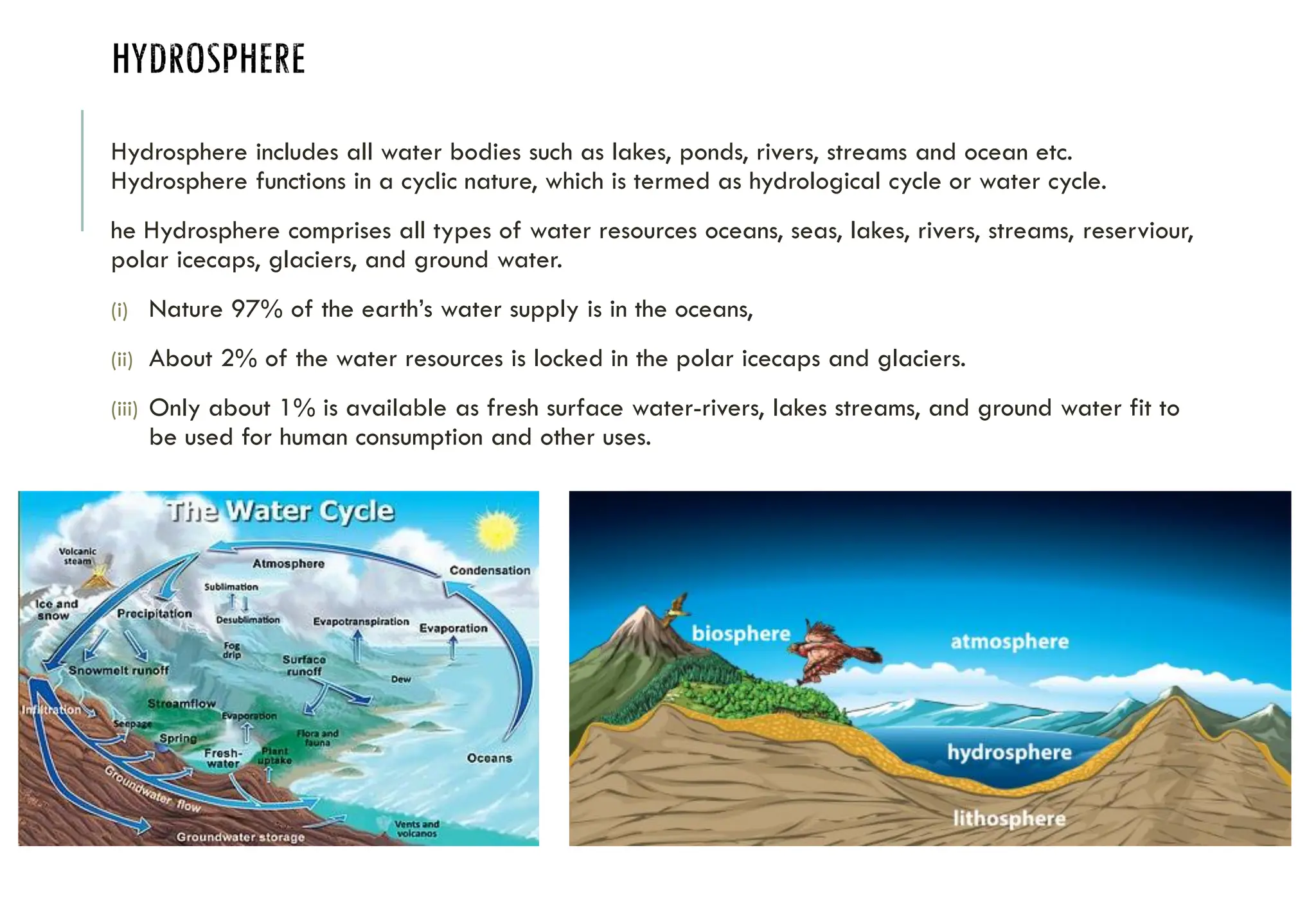
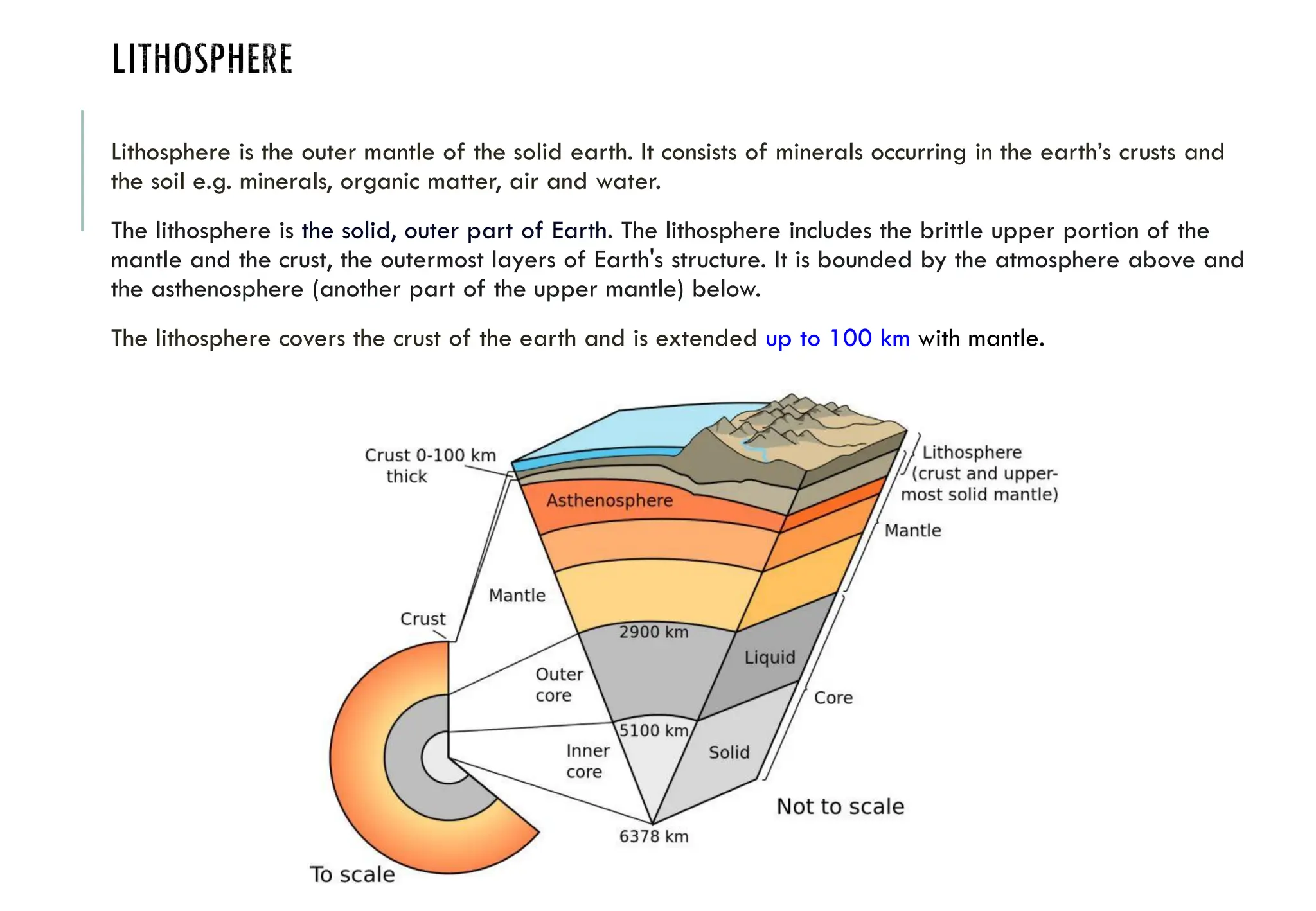
The document outlines the fundamentals of environmental science, covering topics such as the structure and composition of the atmosphere, sources and effects of air pollution, and control measures. It defines the environment, discusses various environmental segments (hydrosphere, lithosphere, biosphere, atmosphere), and distinguishes between natural and man-made environments. Furthermore, it highlights the importance of the environment for resource supply, sustaining life, waste assimilation, and enhancing quality of life.