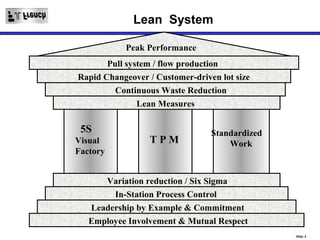
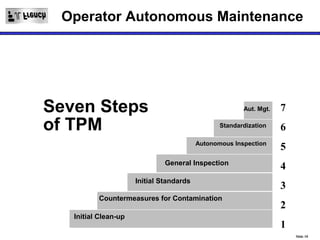
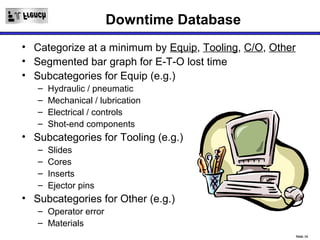
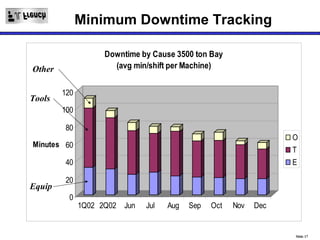
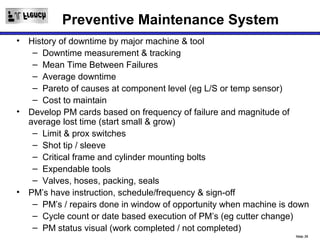
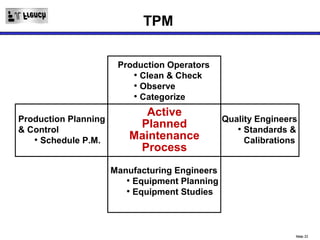
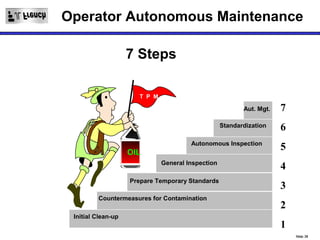
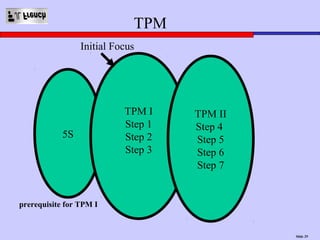
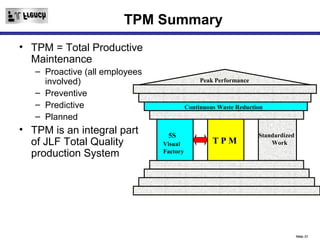
TPM is a Lean initiative that aims to optimize equipment effectiveness through proactive, preventative, and predictive maintenance involving all employees. It starts with 5S and visual controls to make problems visible. A comprehensive downtime database tracks causes to predict and prevent issues through planned preventative maintenance. Operators expand their role in early problem detection through autonomous maintenance checks and problem solving. The goal is reducing waste like defects and downtime through continuous improvement.