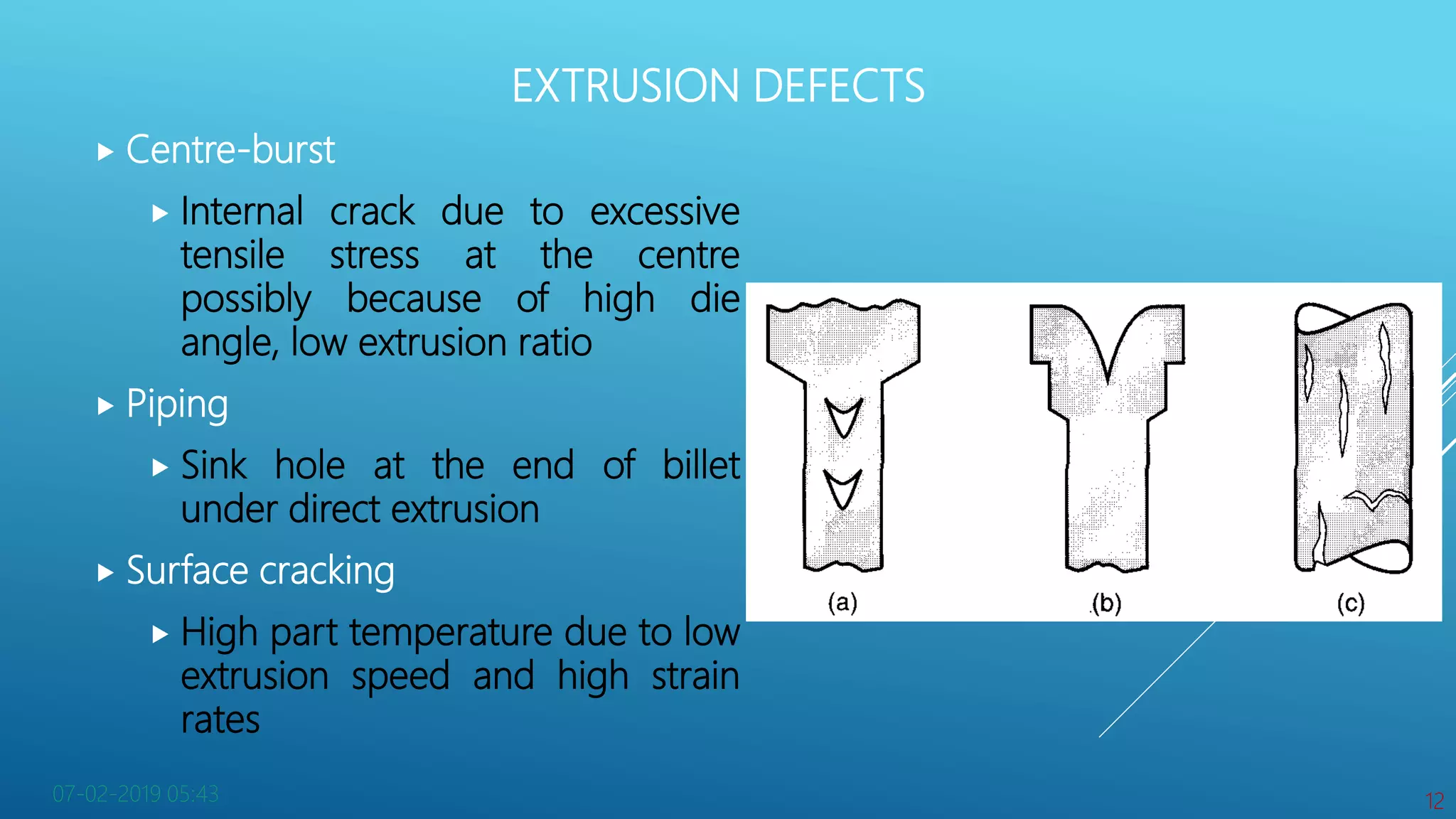
This document discusses the manufacturing process of extrusion. Extrusion is a compression forming process that forces metal to flow through a die opening to produce a desired cross-sectional shape. There are two main types of extrusion: direct extrusion where the ram forces the billet through the die, and indirect extrusion where the die is mounted to the ram. Extrusion can be performed hot or cold, and defects may occur such as center-bursting or piping due to excessive stresses during the process. Variations on extrusion include impact extrusion for discrete parts and hydrostatic extrusion which uses pressurized liquid to reduce friction.