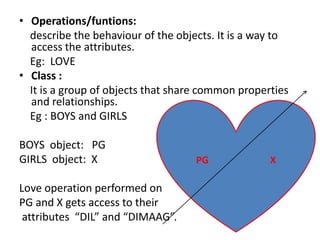
Object oriented architecture organizes software around discrete objects that incorporate both data structures and behavior. This contrasts with procedural approaches that emphasize "doing" things rather than data. Objects have identifiable characteristics and behaviors, and are instances of classes. Classes group objects that share common properties and relationships. Key principles of object oriented architecture include identification, classification, polymorphism, inheritance, and abstraction. Object oriented methodology for ERP uses the Object Modeling Technique which involves problem analysis, system design, object design, and implementation. OMT uses three models - the object model describing system objects and relationships, the dynamic model describing system changes over time, and the functional model describing data value transformations.