The document discusses temporal databases, which store information about how data changes over time. It covers several key points:
- Temporal databases allow storage of past and future states of data, unlike traditional databases which only store the current state.
- Time can be represented in terms of valid time (when facts were true in the real world) and transaction time (when facts were current in the database). Temporal databases may track one or both dimensions.
- SQL supports temporal data types like DATE, TIME, TIMESTAMP, INTERVAL and PERIOD for representing time values and durations.
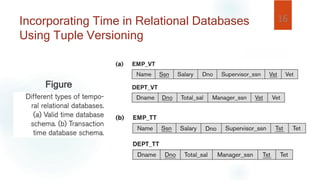
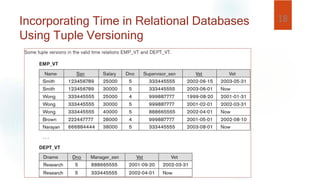
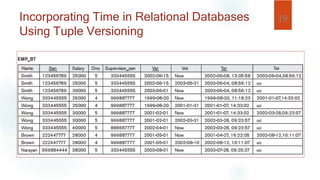
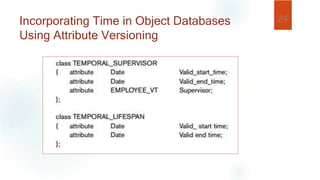
- Temporal information can describe point events or durations. Relational databases incorporate time by adding timestamp attributes, while object databases










![Event Information Versus Duration (or State)
Information
Duration events or facts are associated with a specific time
period in the database;
A time period is represented by its start time and end time
points;
Time period is often interpreted as the set of all time points from
start-time to end-time inclusive in the specified granularity;
For example, employee worked in a company in a company
from August 15, 2003 until November 20, 2008.
The above period is represented as [2003-08-15, 2008-11-20].
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/temporaldatabases-180515183157/85/Temporal-databases-12-320.jpg)