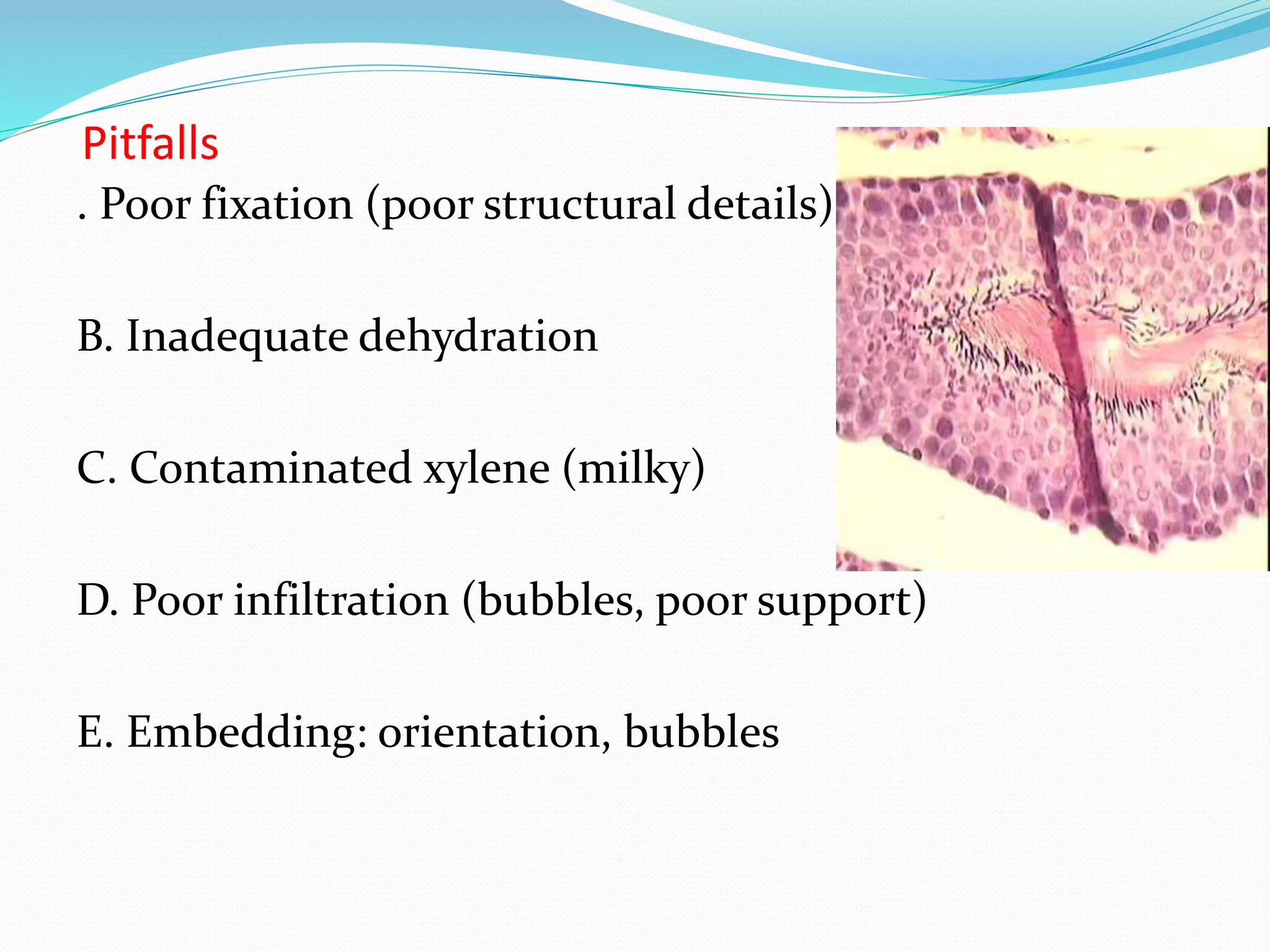
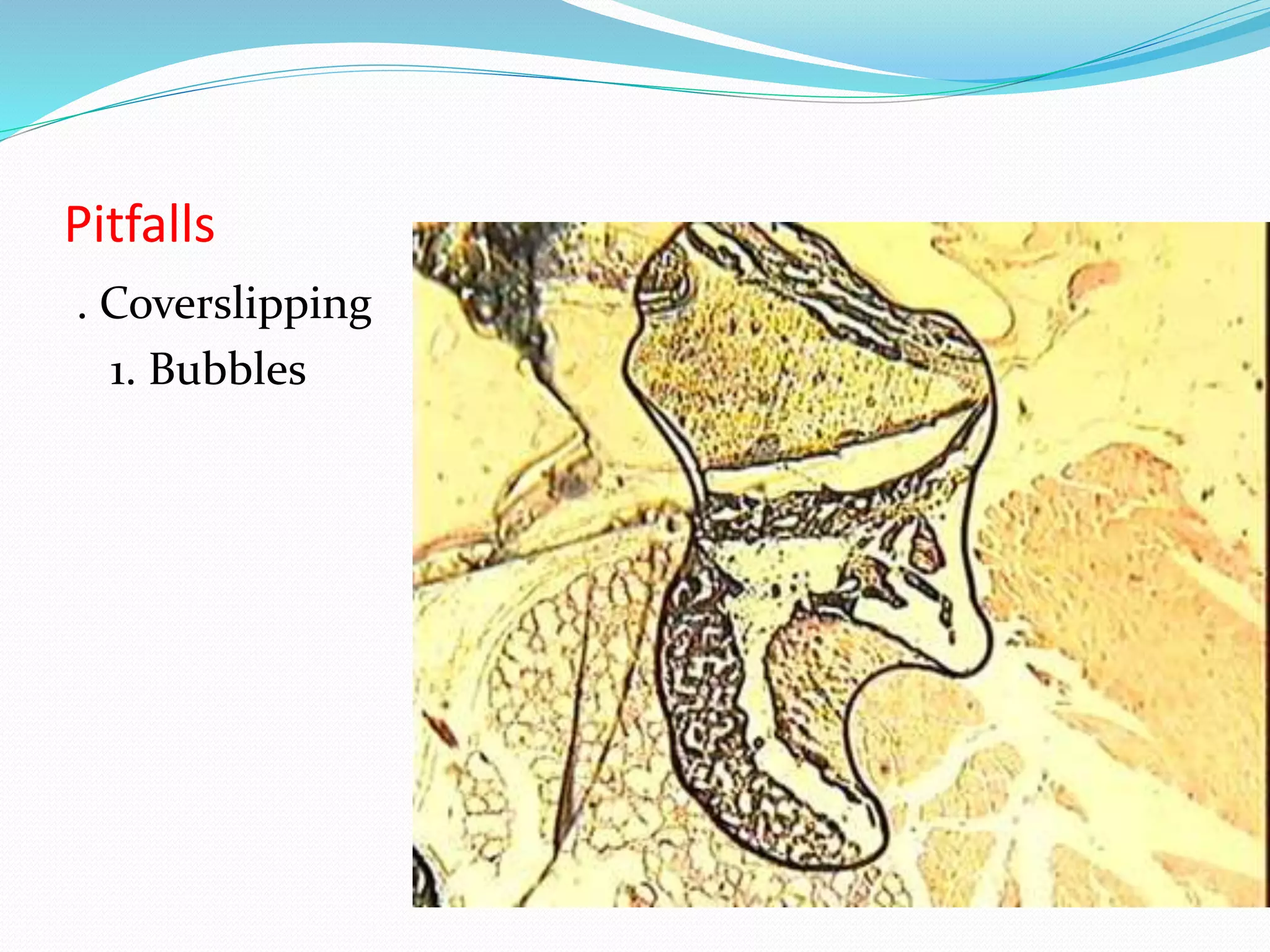
This document summarizes the key steps in the tissue preparation process:
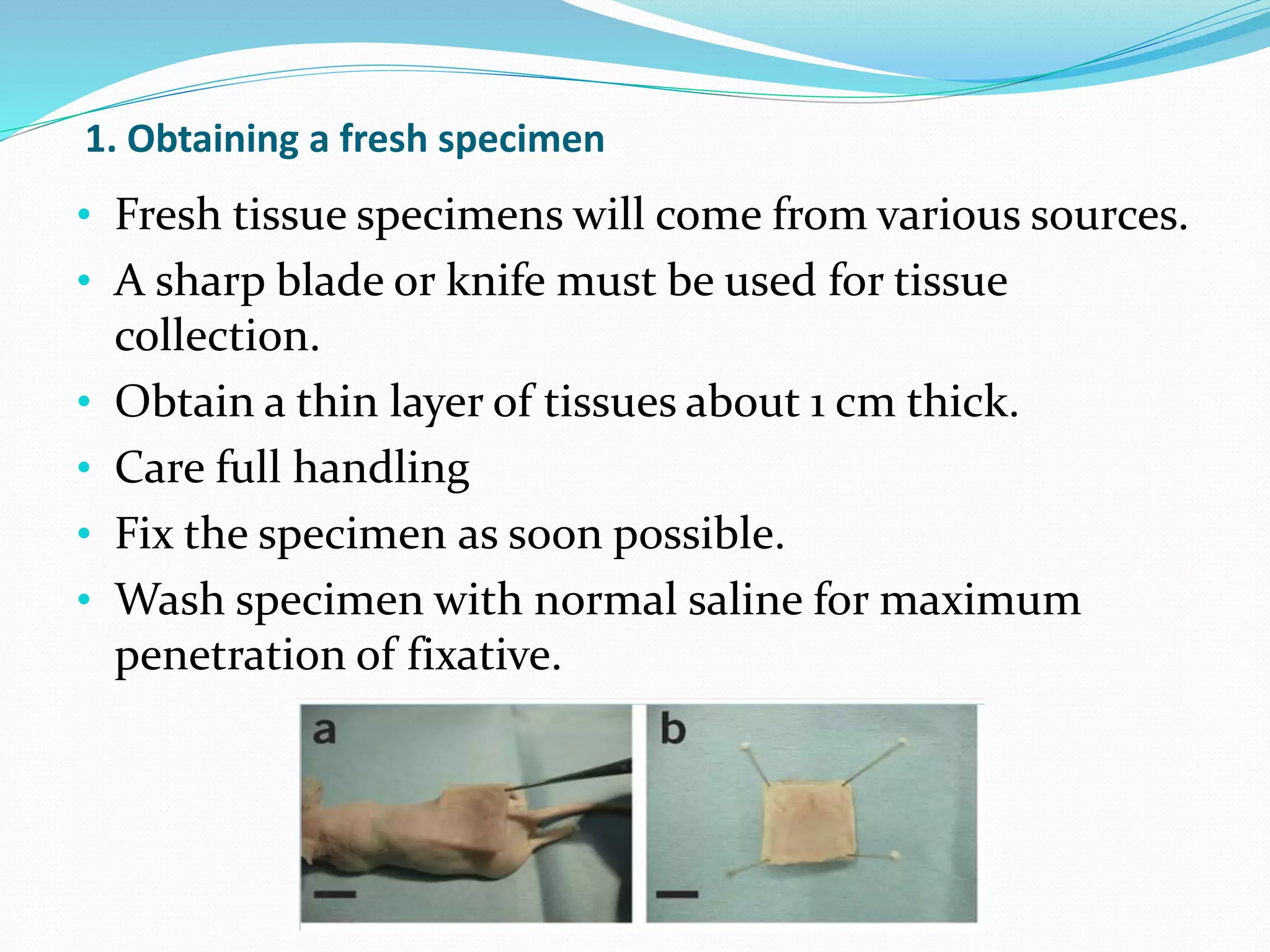
1) Obtaining a fresh specimen and fixing it to maintain its structure.
2) Dehydrating the tissue using increasing concentrations of alcohol.
3) Clearing the tissue using a solvent like xylene to remove alcohol.
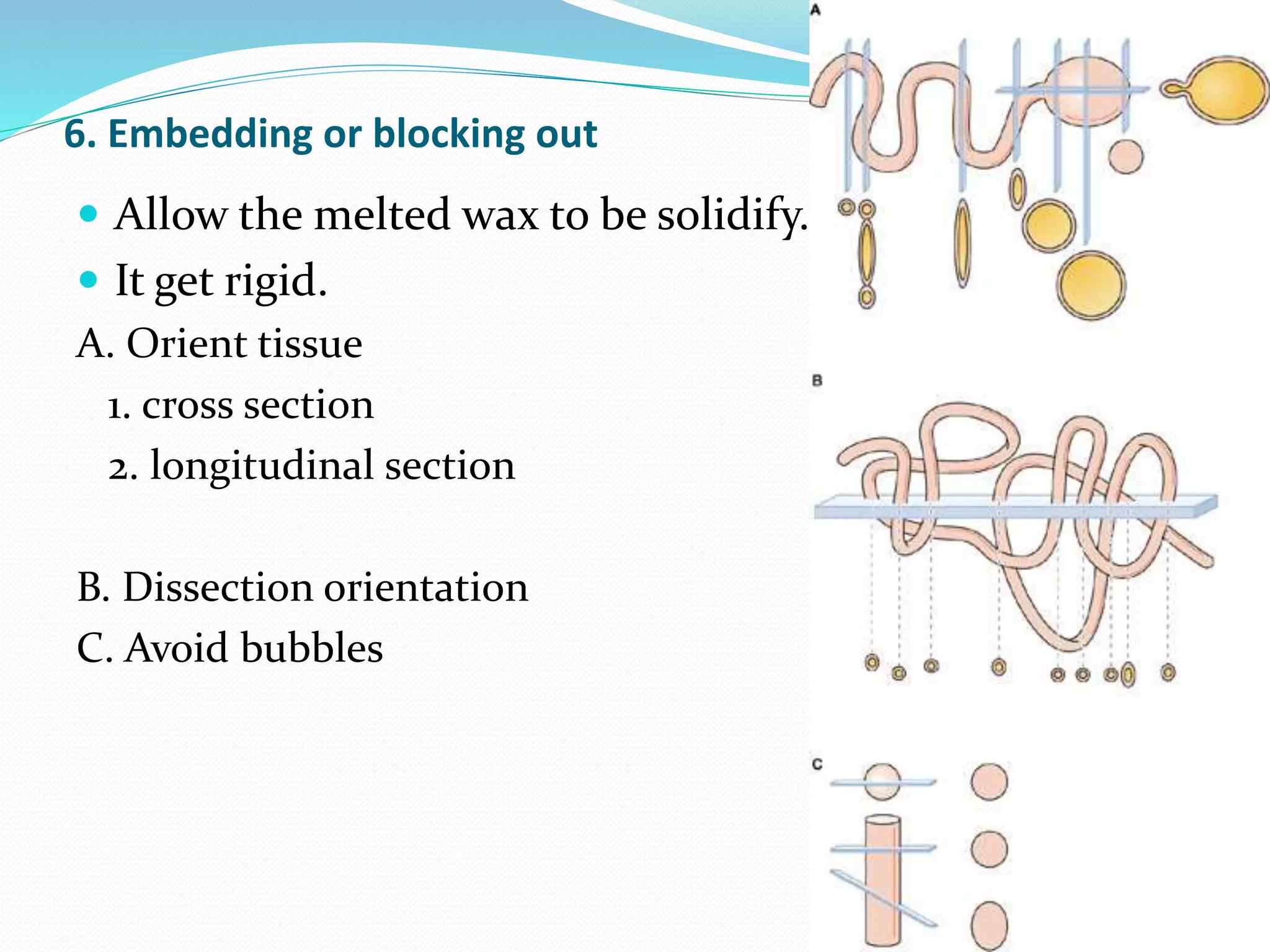
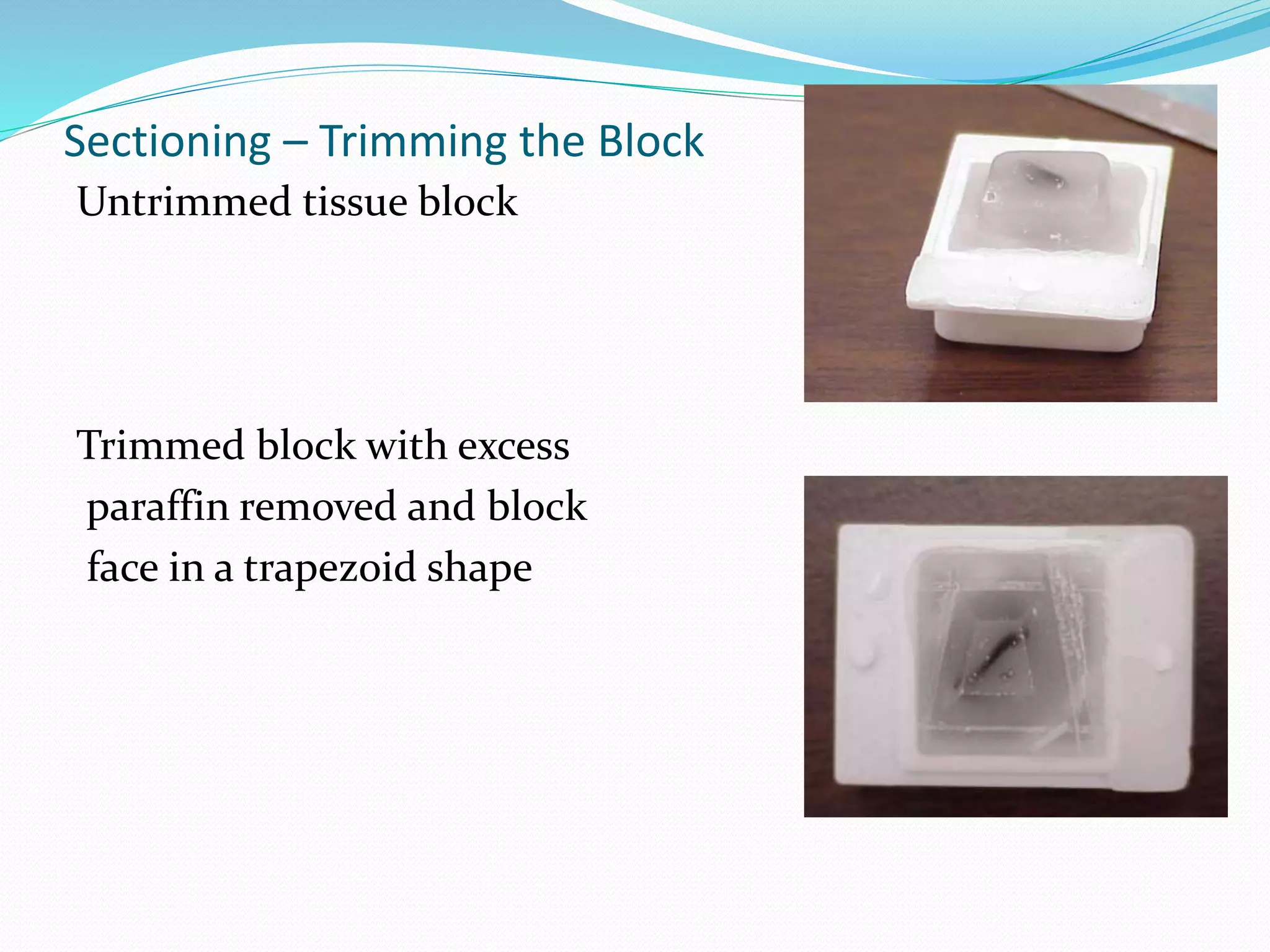
4) Infiltrating the tissue with wax to embed and block it out for sectioning.