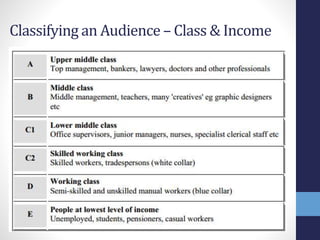
This document discusses classifying and understanding target audiences for media products. It describes how to analyze audiences based on demographics like age, income, and family life cycle stage. Understanding the target audience is important for tailoring content and maximizing its impact. Producers can appeal to audiences by considering genre conventions and iconography that certain groups expect and associate with. Researching audience interests through surveys and focus groups helps media companies determine if a new product matches what the target audience wants.