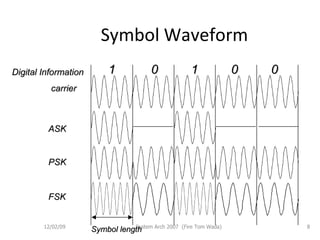
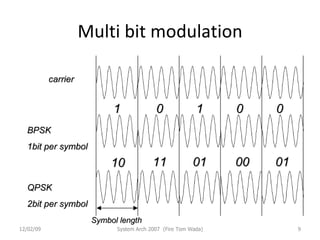
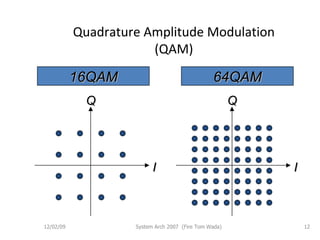
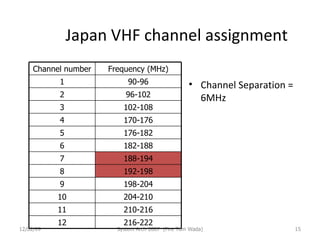
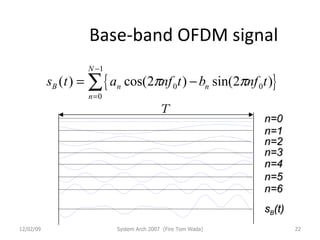
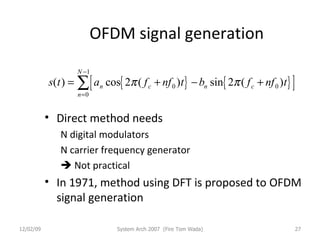
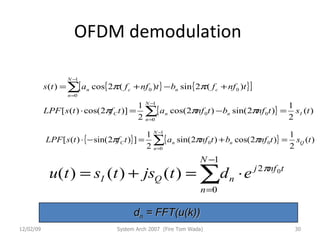
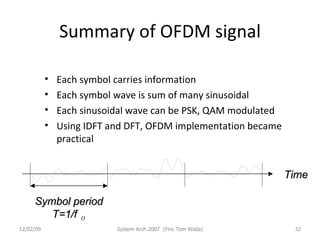
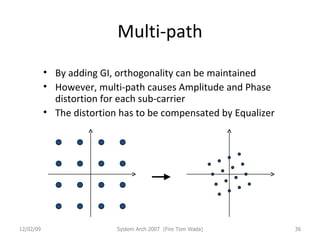
OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) is a digital modulation technique that divides the available spectrum into multiple orthogonal subcarriers. It has become popular for digital communication systems due to its ability to mitigate multi-path interference through the use of a guard interval between symbols. OFDM allows for high bandwidth efficiency by overlapping subcarriers and its implementation has been enabled by advances in DFT and LSI technology.
![Introduction to OFDM Fire Tom Wada Professor, Information Engineering, Univ. of the Ryukyus Chief Scientist at Magna Design Net, Inc [email_address] http://www.ie.u-ryukyu.ac.jp/~wada/ 06/07/09 System Arch 2007 (Fire Tom Wada)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ofdm-1229741933989253-1/85/Ofdm-1-320.jpg)