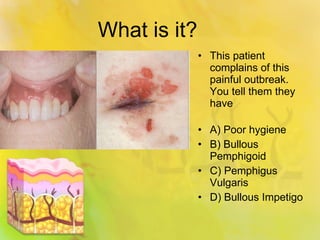
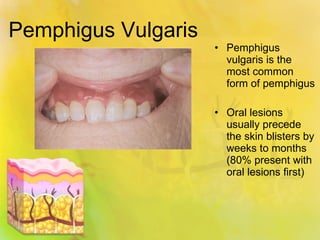
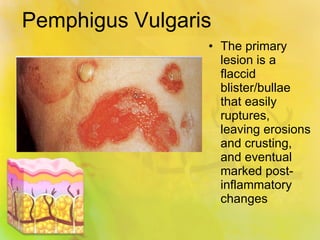
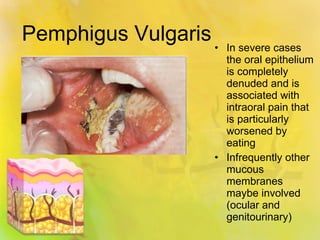
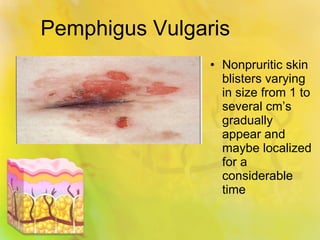
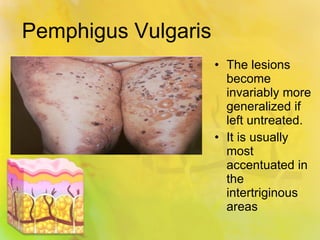
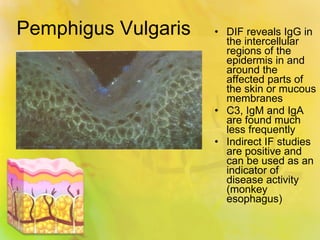
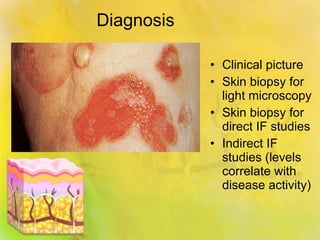
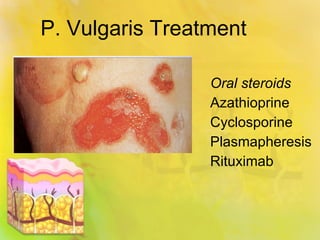
Pemphigus vulgaris is an autoimmune condition characterized by painful oral lesions and flaccid skin blisters that can lead to erosions and significant discomfort, particularly during eating. It typically presents with oral lesions before skin involvement and is diagnosed through clinical examination and skin biopsy. Treatment options include oral steroids, azathioprine, cyclosporine, plasmapheresis, and rituximab.