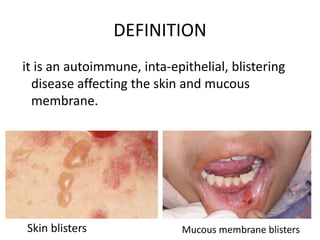
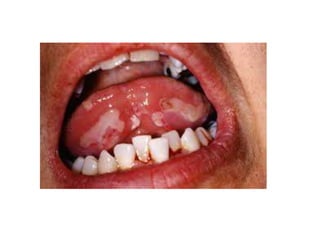
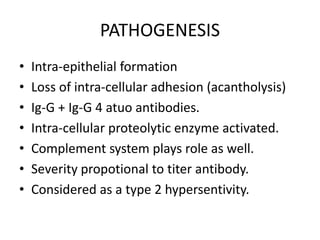
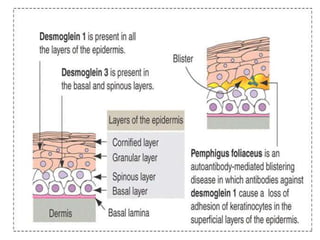
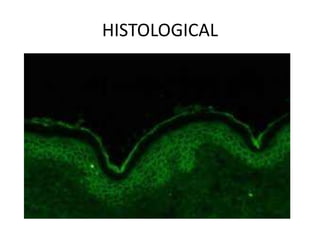
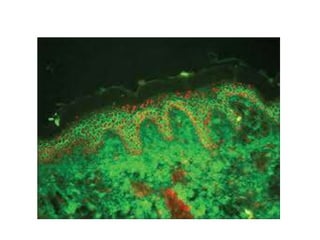
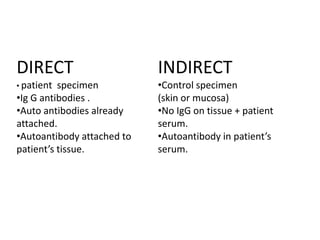
Pemphigus vulgaris is an autoimmune blistering disease primarily affecting the skin and mucous membranes, characterized by bullous eruptions and painful ulcers. The condition results from intra-epithelial acantholysis and is associated with IgG autoantibodies, leading to severe oral symptoms often before skin lesions. Management includes high-dose corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs to reduce symptoms and maintain disease-free states.