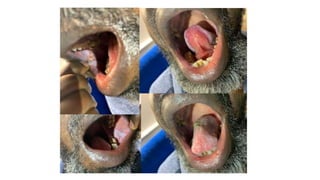
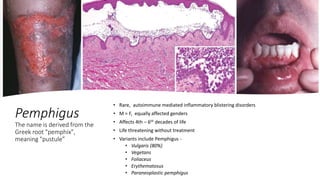
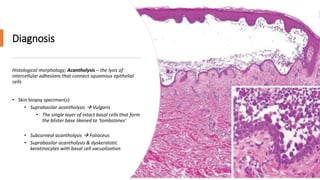
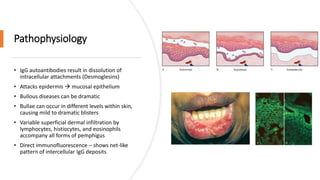
A case of chronic mouth ulcers is presented. Pemphigus is an autoimmune blistering disease that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It is caused by IgG autoantibodies that disrupt intracellular attachments between keratinocytes. Pemphigus vulgaris is the most common type and presents with oral ulcers that precede skin involvement. Diagnosis is made through skin biopsy and direct immunofluorescence. Treatment involves systemic corticosteroids and immunosuppressants to reduce pathogenic antibody levels. Prognosis has improved with corticosteroid use but mortality can still occur without treatment.