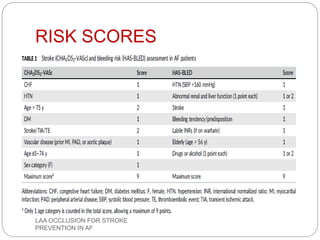
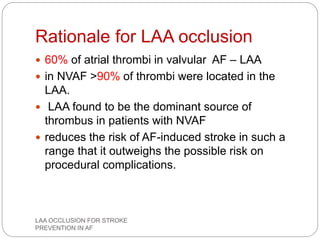
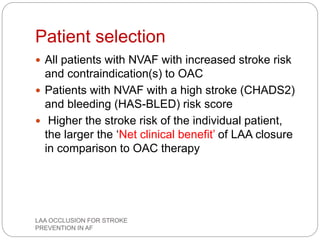
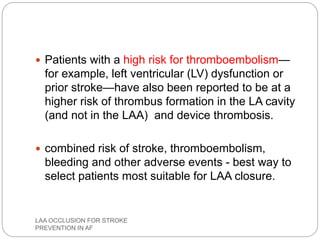
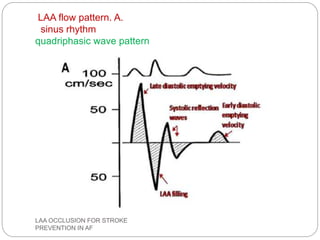
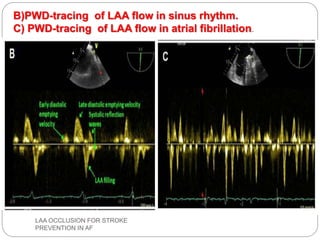
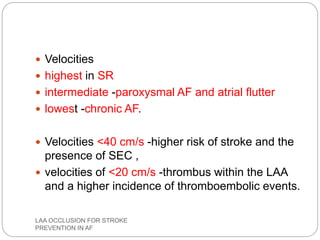
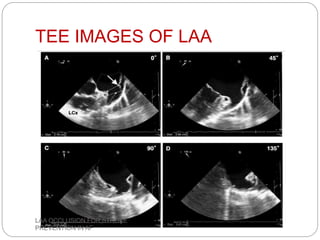
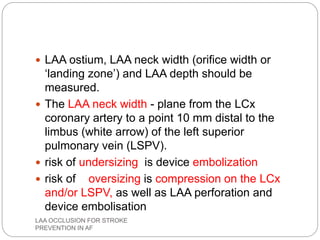
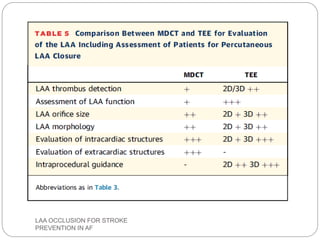
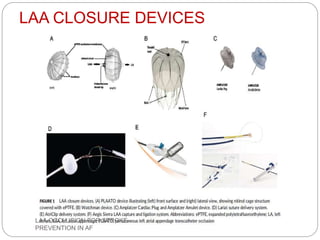
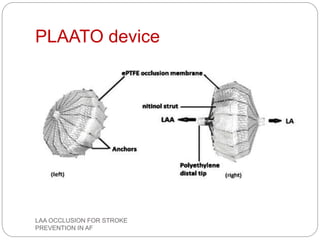
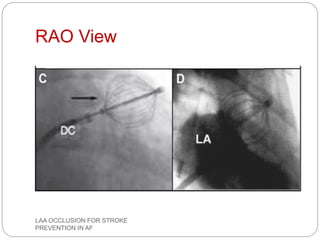
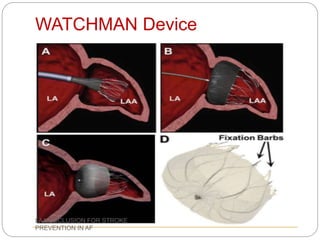
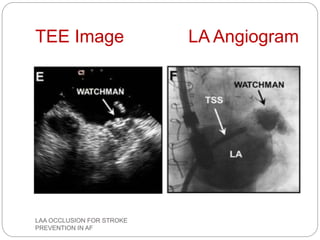
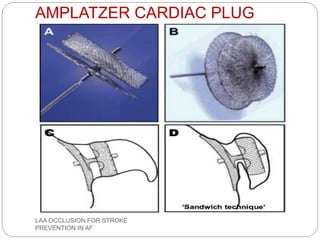
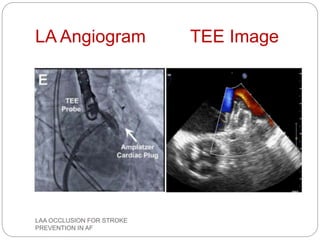
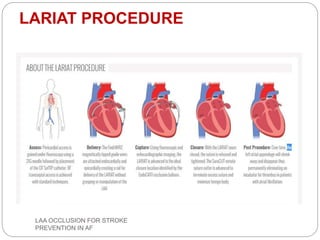
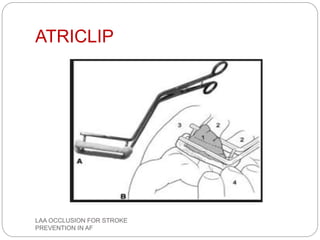
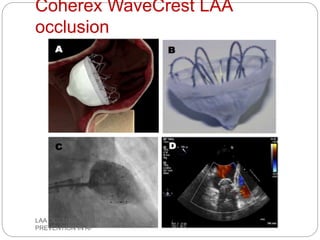
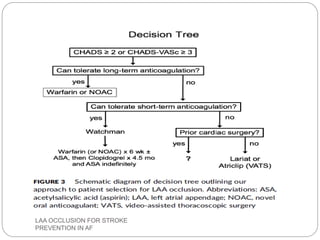
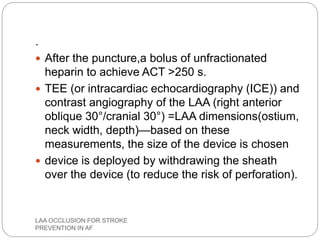
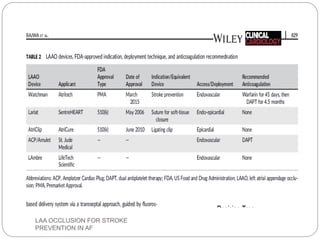
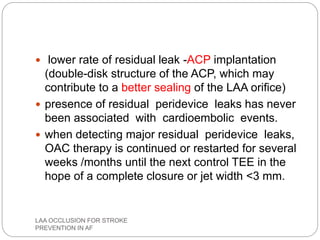
This document discusses left atrial appendage occlusion for stroke prevention in patients with atrial fibrillation. It provides background on atrial fibrillation and the increased risk of stroke. Left atrial appendage occlusion is recommended for patients with a high stroke risk who have contraindications to oral anticoagulation. The document reviews patient selection criteria and contraindications for left atrial appendage occlusion. It also examines left atrial appendage anatomy, imaging techniques for evaluation, and various closure devices including the Watchman, Amplatzer, and Lariat systems.