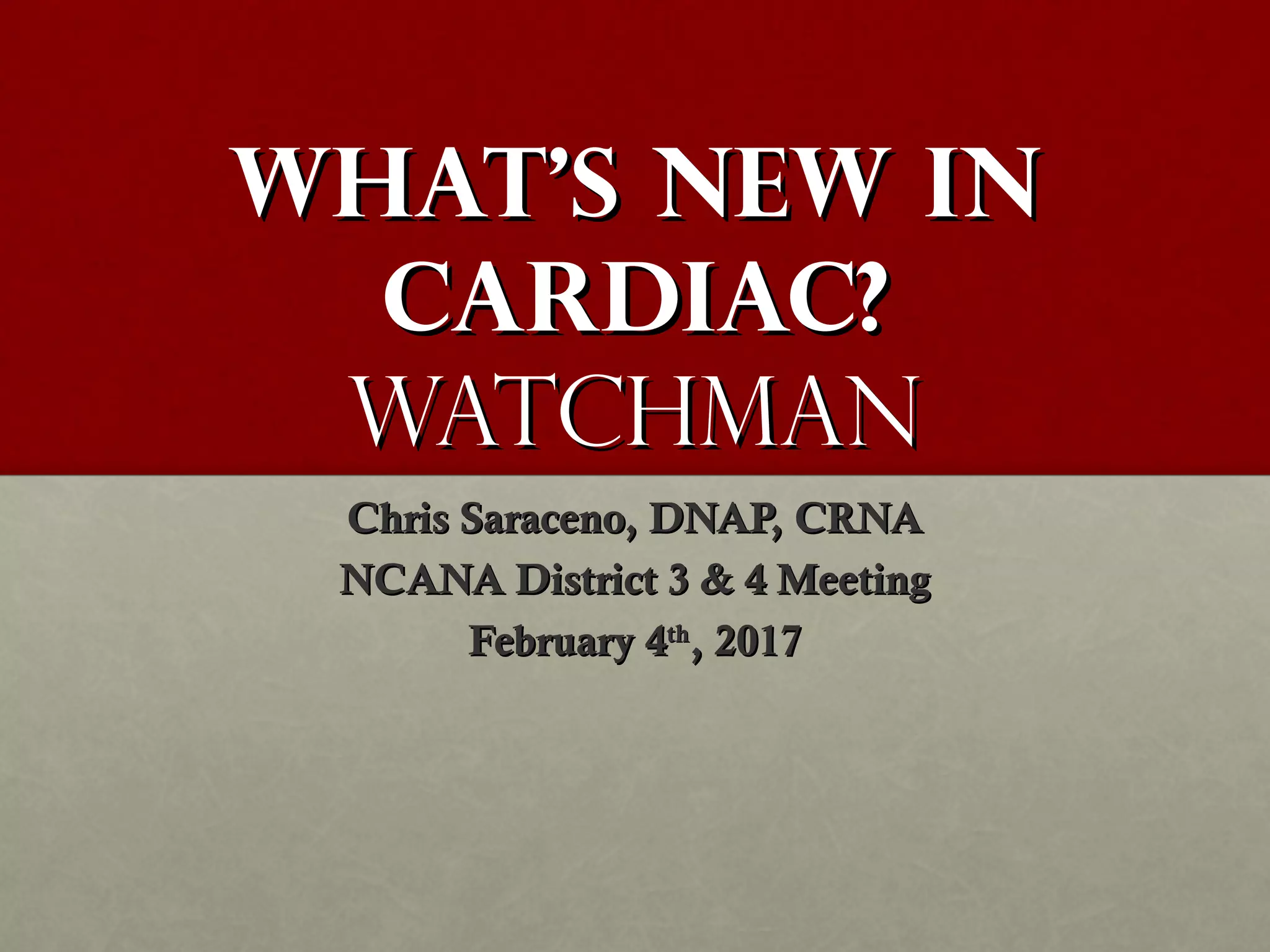
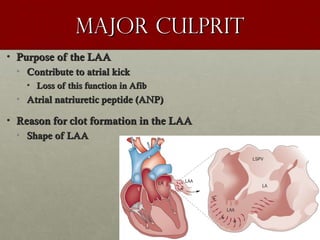
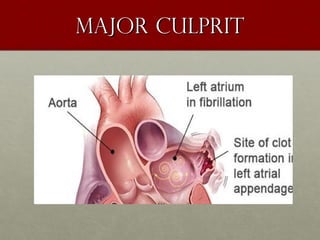
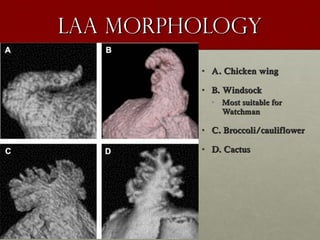
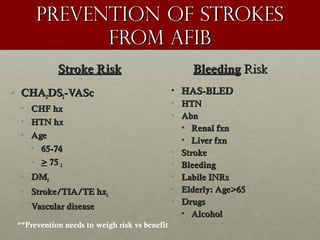
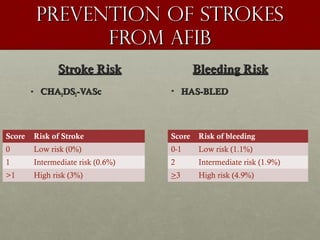
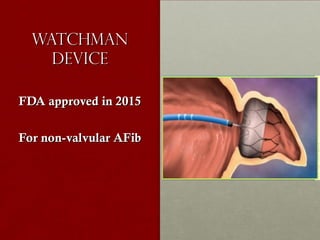
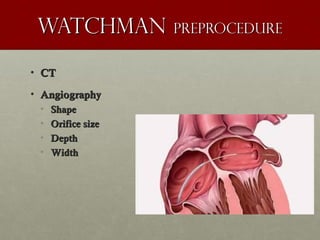
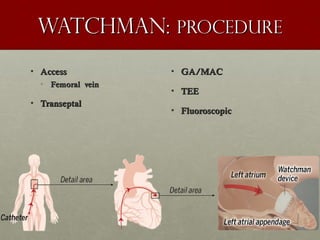
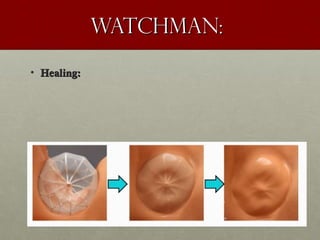
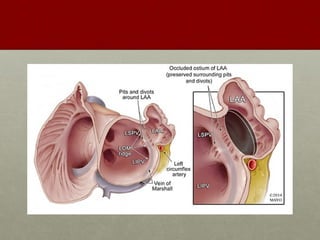
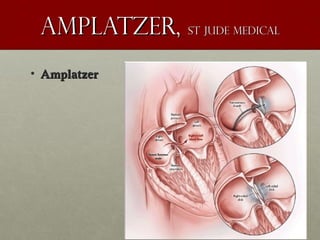
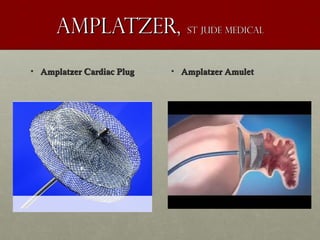
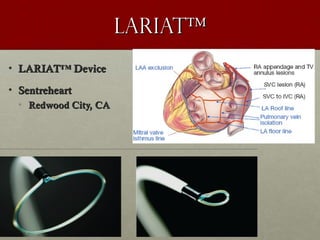
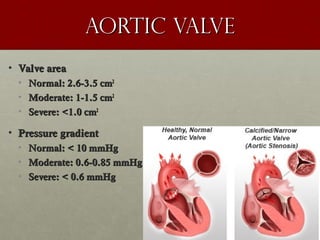
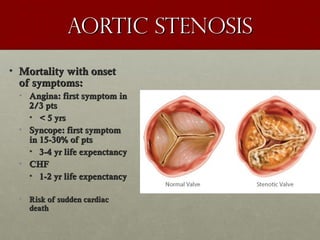
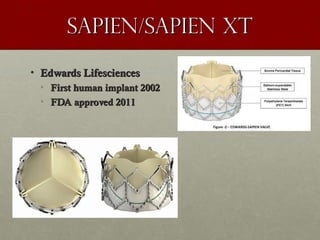
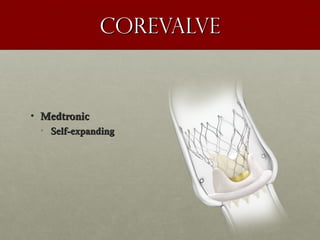
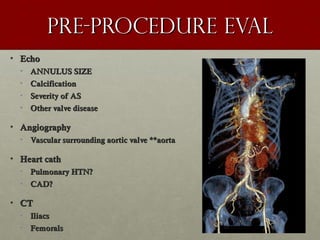
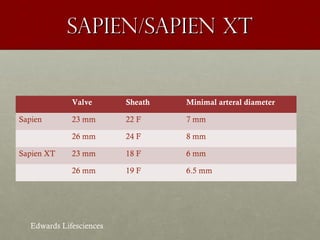
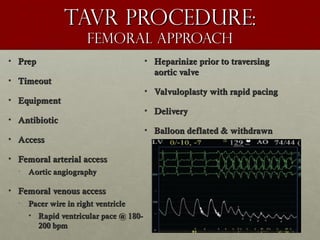
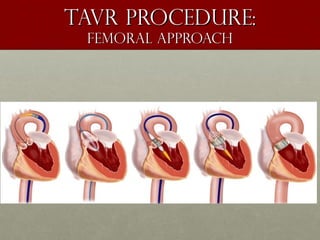
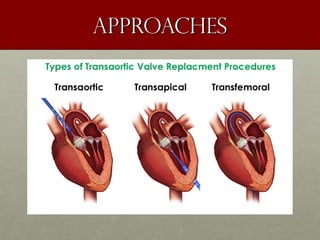
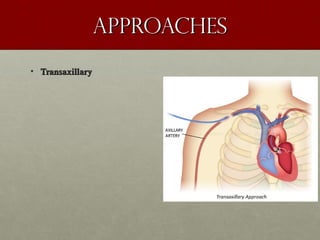
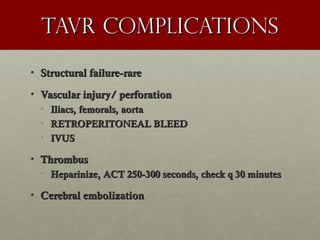
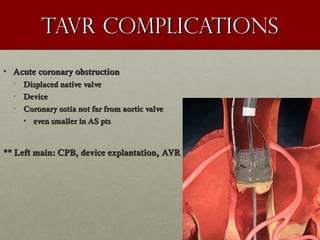
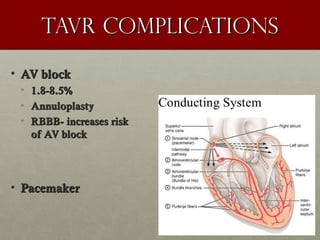
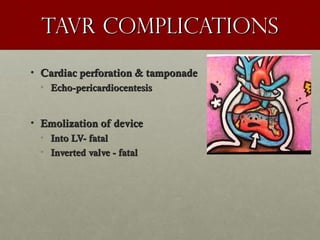
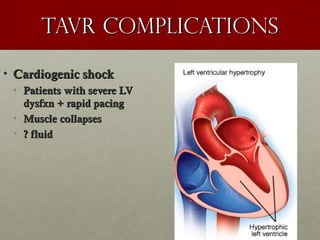
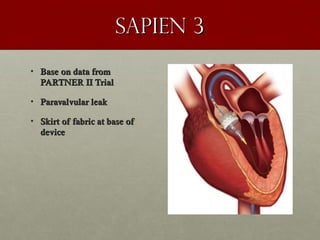
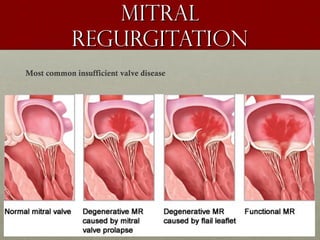
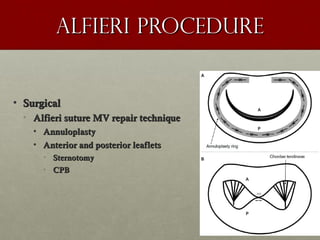
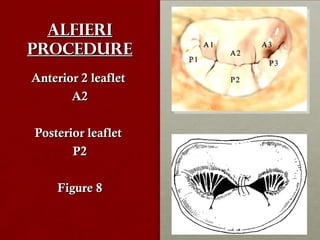
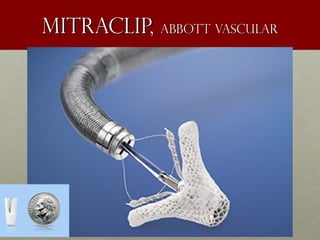
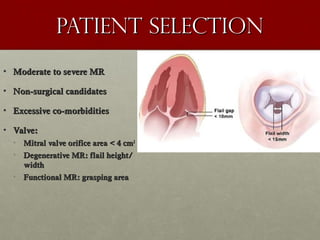
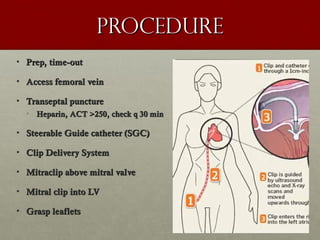
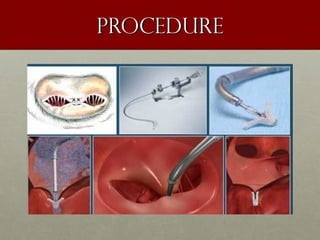
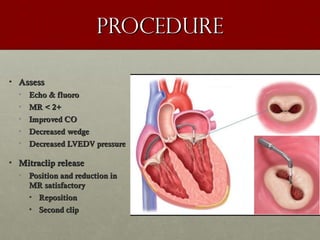
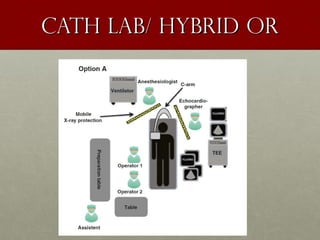
The document discusses the Watchman device, which is used to close off the left atrial appendage (LAA) as an alternative to anticoagulation for stroke prevention in patients with atrial fibrillation. It describes the procedure and risks of implanting the Watchman device, as well as alternatives like the Amplatzer cardiac plug. The document also discusses transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) procedures using the Edwards Sapien valve or Medtronic CoreValve to treat severe aortic stenosis as an alternative to open heart surgery for high-risk patients. Risks of TAVR like vascular injury, stroke, and paravalvular regurgitation are outlined.