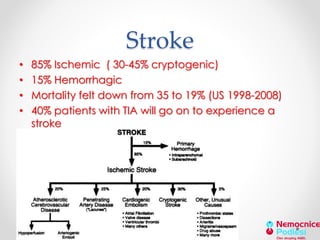
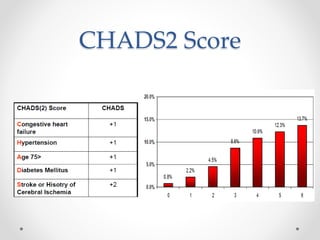
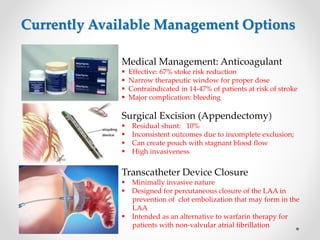
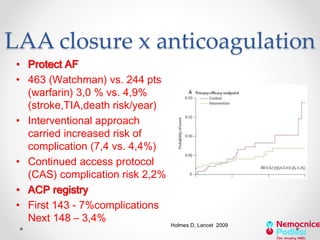
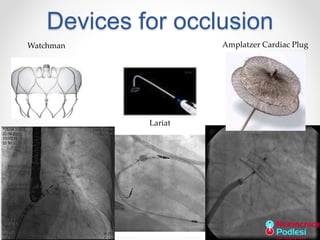
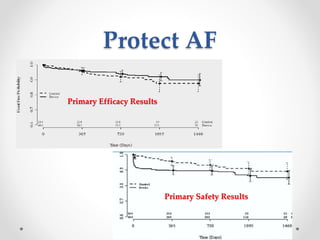
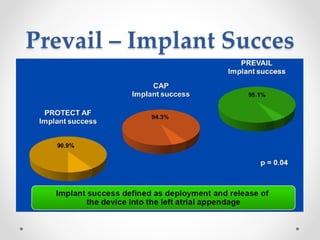
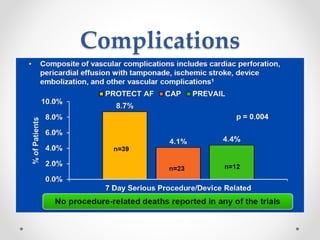
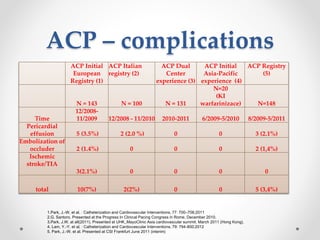
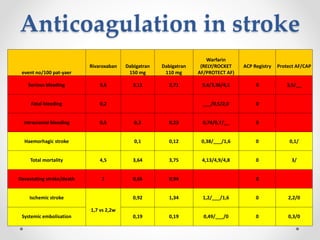
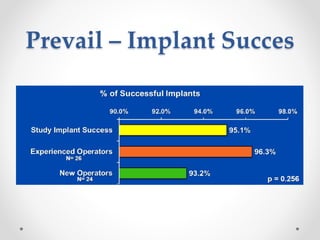
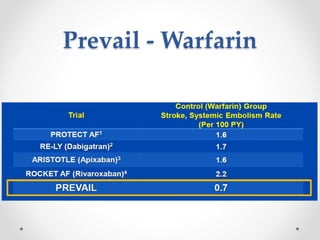
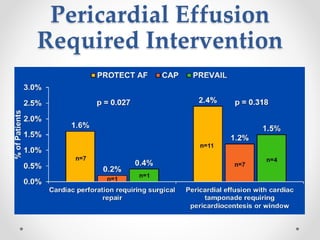
The document discusses left atrial appendage (LAA) closure as an alternative to anticoagulation for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation patients. It summarizes several studies on the Watchman device that found LAA closure to be non-inferior to warfarin for stroke risk reduction, with higher risks of complications. The ACP registry showed periprocedural complication rates with LAA closure decreased over time from 7% to 3.4% as operators gained more experience with the procedure. Overall, LAA closure is a viable alternative to anticoagulation for stroke prevention when anticoagulation is contraindicated or poses high bleeding risks, though periprocedural complications remain higher than medical management