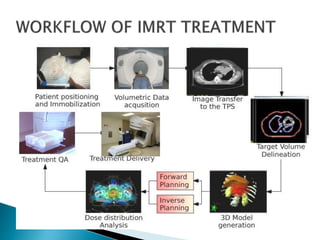
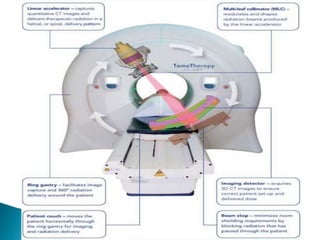
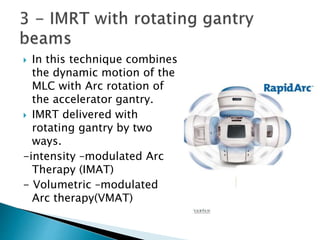
This document discusses intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT). It begins by defining IMRT as a radiation therapy technique that delivers a nonuniform radiation fluence from different beam positions to optimize the dose distribution. The principle of IMRT is to treat a patient from multiple directions with beams of varying fluence. IMRT planning uses inverse planning to optimize the dose distribution. Delivery techniques include step-and-shoot IMRT using a multileaf collimator, dynamic MLC IMRT, tomotherapy, and volumetric modulated arc therapy. The goals of IMRT include improved target dose uniformity and avoidance of critical structures.