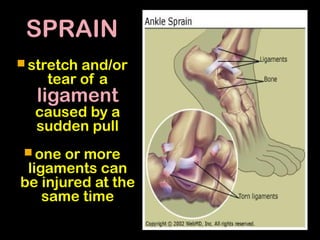
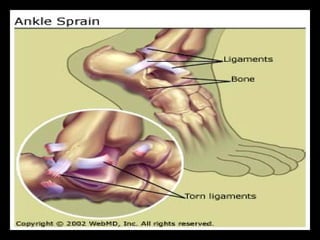
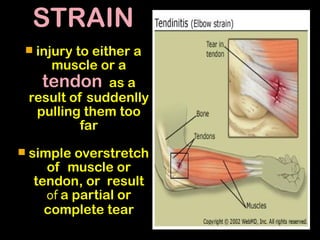
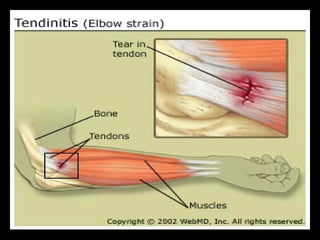
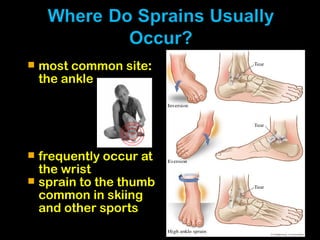
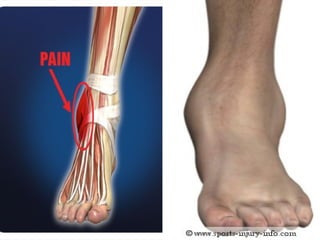
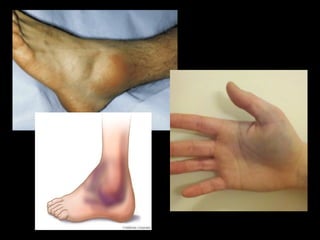
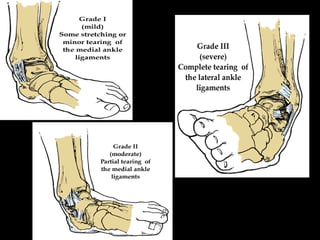
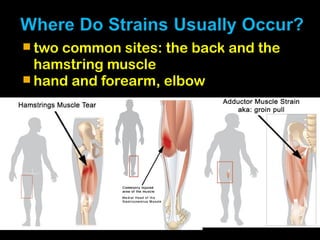
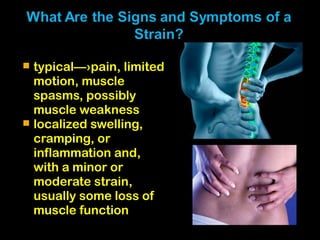
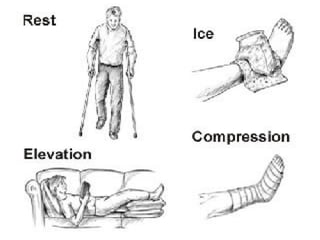
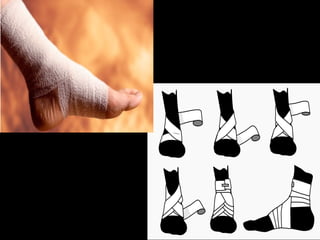
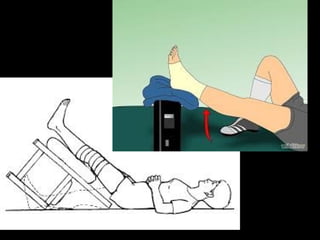
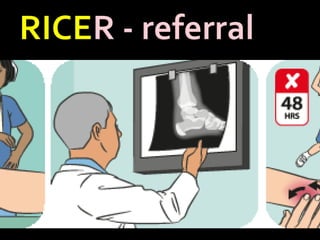
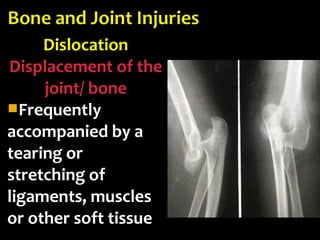
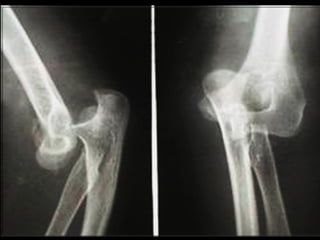
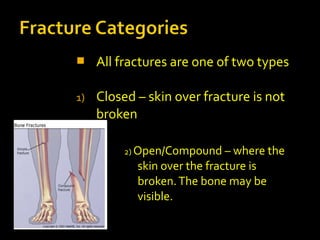
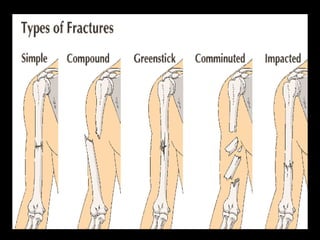
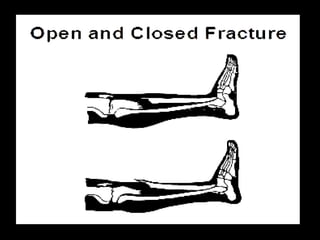
This document discusses common injuries like sprains, strains, fractures, dislocations, and provides treatment recommendations. A sprain is a ligament injury from sudden movement, while a strain is a muscle or tendon injury. RICER therapy of rest, ice, compression, elevation is recommended. For more serious injuries like fractures and dislocations, immobilization with splints is important along with seeking immediate medical care.